ALM-14001 HDFS Disk Usage Exceeds the Threshold
Alarm Description
The system checks the HDFS disk usage every 30 seconds and compares the actual HDFS disk usage with the threshold. The HDFS disk usage metric has a default threshold. This alarm is generated when the HDFS disk usage exceeds the threshold.
You can choose O&M > Alarm > Thresholds > HDFS and change the threshold.
When Trigger Count is 1, this alarm is cleared when the value of the disk usage of HDFS cluster indicator is less than or equal to the threshold. When Trigger Count is greater than 1, this alarm is cleared when the value of the disk usage of HDFS cluster indicator is less than or equal to 90% of the threshold.
Alarm Attributes
|
Alarm ID |
Alarm Severity |
Auto Cleared |
|---|---|---|
|
14001 |
Major |
Yes |
Alarm Parameters
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Source |
Specifies the cluster for which the alarm is generated. |
|
ServiceName |
Specifies the service for which the alarm is generated. |
|
RoleName |
Specifies the role for which the alarm is generated. |
|
HostName |
Specifies the host for which the alarm is generated. |
|
NameServiceName |
Specifies the NameService for which the alarm is generated. |
|
Trigger Condition |
Specifies the threshold for triggering the alarm. If the current indicator value exceeds this threshold, the alarm is generated. |
Impact on the System
Writing Hadoop distributed file system (HDFS) data is affected.
Possible Causes
The disk space configured for the HDFS cluster is insufficient.
Handling Procedure
Check the disk capacity and delete unnecessary files.
- On the homepage of FusionInsight Manager, choose Cluster > Services > HDFS.
- In the Chart area, click Real-time, and view the value of the monitoring item Percentage of HDFS Capacity to check whether the HDFS disk usage exceeds the threshold (80% by default). If the monitoring item is not displayed, click the drop-down list in the upper right corner of the Chart area, choose Customize > Disk, and select Percentage of HDFS Capacity.
- In the Basic Information area, click the NameNode(Active) of the failure NameService and the HDFS WebUI page is displayed.
By default, the admin user does not have the permissions to manage other components. If the page cannot be opened or the displayed content is incomplete when you access the native UI of a component due to insufficient permissions, you can manually create a user with the permissions to manage that component.
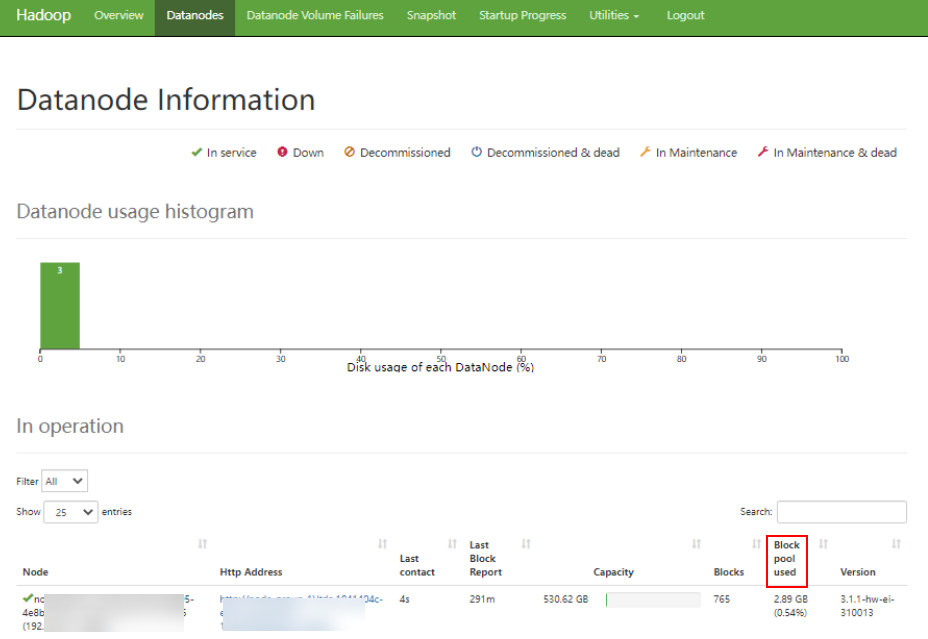
- On the HDFS web user interface (WebUI), click Datanodes tab. In the Block pool used column, view the disk usage of all DataNodes to check whether the disk usage of any DataNode exceeds the threshold.
Figure 1 Datanode Information
- Log in to the node as user root where the cluster client is installed.
- Run the following command to go to the client installation directory and complete authentication:
cd /opt/clientLoad environment variables:
source bigdata_env
If Kerberos authentication is enabled for the cluster, run the following command to complete authentication as the cluster user that has the operation permissions for HDFS.
You need to create related users on Manager in advance or contact the cluster administrator to obtain the users. For details, see Creating an MRS Cluster User.
kinit hdfsuser - Run the following command to delete unnecessary HDFS files:
- Run the following command to check files or sub-directories in the corresponding folder:
hdfs dfs -ls Folder name
- Run the following command to query the HDFS file directory size:
hdfs dfs -du HDFS file directory
For example, if you run the above command to query the size of files or sub-directories in the /tmp folder, the following command output is returned, indicating that the /tmp/hadoop-yarn directory occupies 622,222,017 bytes:
0 0 /tmp/.testHDFS 207407339 622222017 /tmp/hadoop-yarn 0 0 /tmp/hive 0 0 /tmp/hive-scratch 0 0 /tmp/logs ...
- Run the following command to delete confirmed unnecessary HDFS files:
hdfs dfs -rm -r HDFS file or directory path

Deleting files is a high-risk operation. Ensure that the files to be deleted are unnecessary files to prevent data loss.
- Run the following command to check files or sub-directories in the corresponding folder:
- Check whether the alarm is cleared.
- If yes, no further action is required.
- If no, go to Step 9.
Expand the system.
- Expand the capacity of the cluster node where HDFS is deployed. For details, see Scaling Out an MRS Cluster.
- Then, check whether the alarm is cleared.
- If yes, no further action is required.
- If no, go to Step 11.
Collect fault information.
- On the FusionInsight Manager portal, choose O&M > Log > Download.
- Select the following nodes in the required cluster from the Service:
- ZooKeeper
- HDFS
- Click
 in the upper right corner, and select a time span starting 10 minutes before and ending 10 minutes after when the alarm was generated. Then, click Download to collect the logs.
in the upper right corner, and select a time span starting 10 minutes before and ending 10 minutes after when the alarm was generated. Then, click Download to collect the logs. - Contact the O&M personnel and send the collected logs.
Alarm Clearance
After the fault is rectified, the system automatically clears this alarm.
Related Information
None
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





