Configuring a Job for Synchronizing Data from DMS for Kafka to Doris
Supported Source and Destination Database Versions
|
Source Database |
Destination Database |
|---|---|
|
Kafka cluster (2.7 and 3.x) |
Doris (Doris1.2 and Doris2.0) |
Database Account Permissions
Before you use DataArts Migration for data synchronization, ensure that the source and destination database accounts meet the requirements in the following table. The required account permissions vary depending on the synchronization task type.
|
Type |
Required Permissions |
|---|---|
|
Source database connection account |
When ciphertext access is enabled for Kafka, the configured user must have the permission to publish and subscribe to topics. In other scenarios, there are no special permission requirements. For details about how to connect to a DMS Kafka instance with SASL authentication enabled, see How Do I Connect to DMS for Kafka That Uses SASL Authentication?. |
|
Destination database connection account |
The account must have the following permissions for each table in the destination database: LOAD, SELECT, CREATE, ALTER, and DROP. |

- You are advised to create independent database accounts for DataArts Migration task connections to prevent task failures caused by password modification.
- After changing the account passwords for the source or destination databases, modify the connection information in Management Center as soon as possible to prevent automatic retries after a task failure. Automatic retries will lock the database accounts.
Supported Synchronization Objects
The following table lists the objects that can be synchronized using different links in DataArts Migration.
|
Type |
Note |
|---|---|
|
Synchronization objects |
All Kafka messages can be synchronized. The CDC JSON message body can be parsed, and only messages corresponding to the specified upstream database tables can be synchronized. |
Notes
In addition to the constraints on supported data sources and versions, connection account permissions, and synchronization objects, you also need to pay attention to the notes in the following table.
|
Type |
Constraint |
|---|---|
|
Database |
|
|
Usage |
General:
Troubleshooting: If any problem occurs during task creation, startup, full synchronization, incremental synchronization, or completion, rectify the fault by referring to FAQs. |
|
Other |
|
Procedure
This section uses real-time synchronization from Kafka to Doris as an example to describe how to configure a real-time data migration job. Before that, ensure that you have read the instructions described in Check Before Use and completed all the preparations.
- Create a real-time migration job by following the instructions in Creating a Real-Time Migration Job and go to the job configuration page.
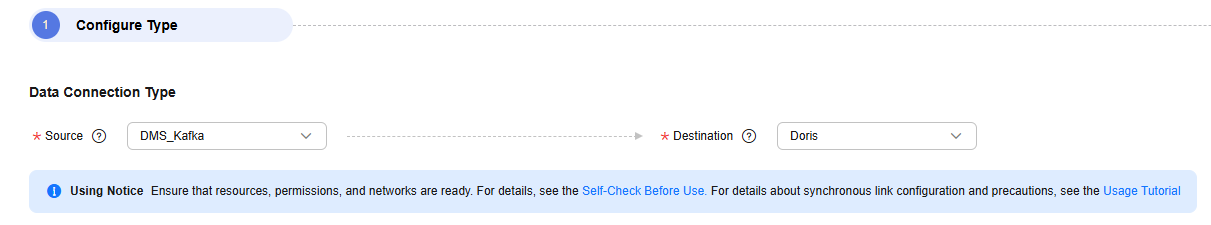
- Select the data connection type. Select Kafka for Source and Doris for Destination.
Figure 1 Selecting the data connection type
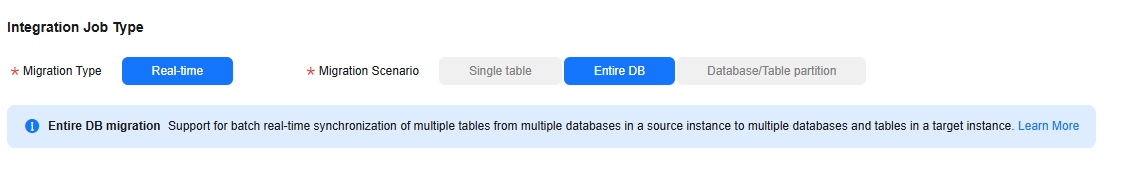
- Select a job type. The default migration type is Real-time. The migration scenario is Single table.
Figure 2 Setting the migration job type
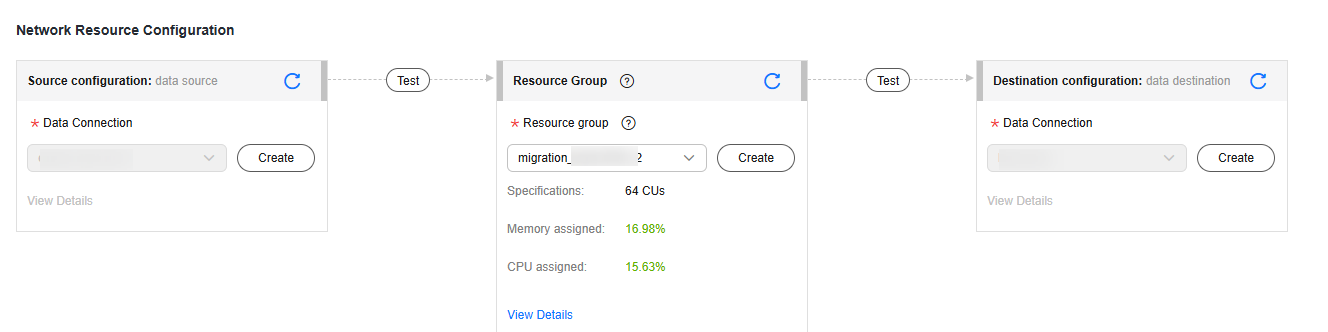
- Configure network resources. Select the created Kafka and Doris data connections and the migration resource group for which the network connection has been configured.
Figure 3 Selecting data connections and a migration resource group

If no data connection is available, click Create to go to the Manage Data Connections page of the Management Center console and click Create Data Connection to create a connection. For details, see Configuring DataArts Studio Data Connection Parameters.
If no migration resource group is available, click Create to create one. For details, see Buying a DataArts Migration Resource Group Incremental Package.
- Check the network connectivity. After the data connections and migration resource group are configured, perform the following operations to check the connectivity between the data sources and the migration resource group.
- Click Source Configuration. The system will test the connectivity of the entire migration job.
- Click Test in the source and destination and migration resource group.

If the network connectivity is abnormal, see How Do I Troubleshoot a Network Disconnection Between the Data Source and Resource Group?
- Configure source parameters.
Select the Kafka topics to be synchronized.Figure 4 Entering a Kafka topic
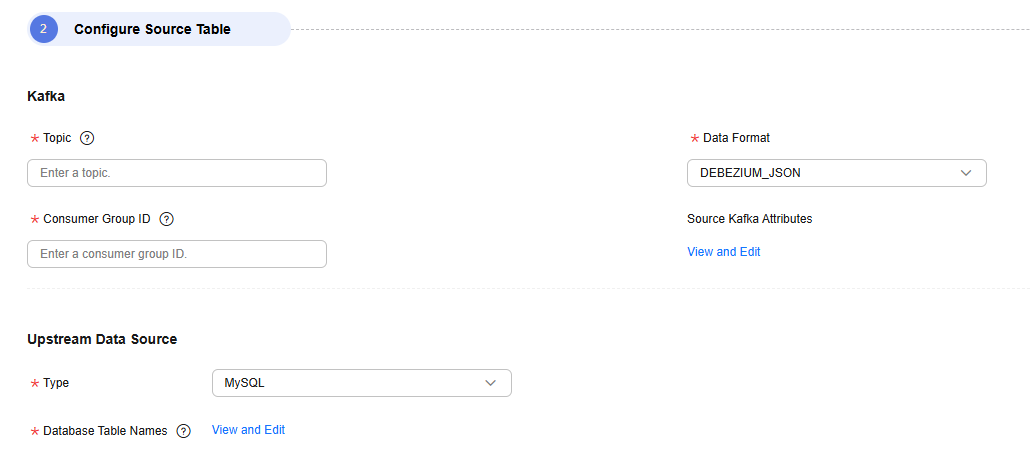
- Topic
Enter a Kafka topic to be migrated.
- Data Format
Format of the message content in the source Kafka topic. DataArts Migration can process the following message:
DEBEZIUM_JSON: CDC JSON messages in Debezium format can be parsed and synchronized to the destination table.
- Consumer Group ID
A consumer subscribes to a topic. A consumer group consists of one or more consumers. DataArts Migration allows you to specify the Kafka consumer group to which a consumption action belongs.
- Source Kafka Attributes
You can add Kafka configuration items with the properties. prefix. The job automatically removes the prefix and transfers configuration items to the underlying Kafka client. For details about the parameters, see the configuration descriptions in Kafka documentation.
- Upstream Data Source Type
This parameter is mandatory only when Data Format is set to DEBEZIUM_JSON. Currently, only MySQL is supported, indicating that CDC JSON data is generated by MySQL.
- Database Table Names
This parameter is mandatory only when Data Format is set to DEBEZIUM_JSON. It indicates the database tables that Kafka messages come from. The task parses CDC JSON data and synchronizes only the data for which database tables have been configured.
- Topic
- Configure destination parameters.
The source Kafka data in CDC_JSON format may come from multiple upstream database tables. DataArts Migration can match upstream database tables with destination database tables.
- Set Database and Table Matching Policy.
- Database Matching Policy
- Same name as the source database: Data will be synchronized to the Doris database with the same name as the source database.
- Custom: Data will be synchronized to the Doris database you specify.
- Table Matching Policy
- Same name as the source table: Data will be synchronized to the Doris table with the same name as the source table.
- Custom: Data will be synchronized to the Doris table you specify.
Figure 5 Database and table matching policy in the sharding scenario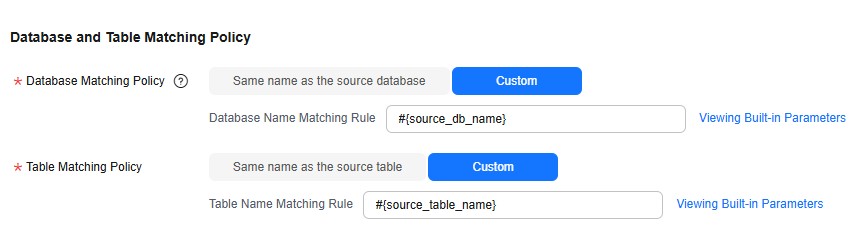

When you customize a matching policy, you can use built-in variables #{source_db_name} and #{source_table_name} to identify the source database name and table name. The table matching policy must contain #{source_table_name}.
- Database Matching Policy
- Set Doris parameters.
You can configure the advanced parameters in the following table to enable some advanced functions.
Table 5 Doris advanced parameters Parameter
Type
Default Value
Unit
Description
doris.request.connect.timeout.ms
int
30000
ms
Doris connection timeout interval
doris.request.read.timeout.ms
int
30000
ms
Doris read timeout interval
doris.request.retries
int
3
-
Number of retries upon a Doris request failure
sink.max-retries
int
3
-
Maximum number of retries upon a data writing failure
sink.batch.interval
string
1s
h/min/s
Interval at which an asynchronous thread writes data
sink.enable-delete
boolean
true
-
Whether to enable the deletion function. If this function is disabled, data deleted from the source will not be deleted from the destination.
sink.batch.size
int
20000
-
Maximum number of rows that can be written (inserted, updated, or deleted) at a time
sink.batch.bytes
long
10485760
bytes
Maximum number of bytes that can be written (inserted, updated, or deleted) at a time
logical.delete.enabled
boolean
false
-
Whether to enable logical deletion. If this function is enabled, the destination must contain the deletion flag column. When data is deleted from the source database, the corresponding data in the destination database will not be deleted. Instead, the deletion flag column is set to true, indicating that the data is not contained at the source.
logical.delete.column
string
logical_is_deleted
-
Name of the logical deletion column. The default value is logical_is_deleted. You can customize the value.
sink.keyby.mode
string
pk
-
Partitioning mode when concurrent writes are performed on Doris. Default value: pk (primary key). If the source is Kafka, and it does not have a primary key, select table to partition data by table name.
doris.sink.flush.tasks
int
1
-
Number of concurrent flushes of a single TaskManager
sink.properties.format
string
json
-
Data format used by Stream Load. The value can be json or csv.
sink.properties.Content-Encoding
string
-
-
Compression format of the HTTP header message body. Currently, only CSV files can be compressed, and the .gzip format is supported.
sink.properties.compress_type
string
-
-
File compression format. Currently, only CSV files can be compressed. The .gz, .lzo, .bz2, .lz4, .lzop, and .deflate compression formats are supported.
- Set Database and Table Matching Policy.
- Refresh the mapping between the source and destination tables.
Figure 6 Mapping between source and destination tables
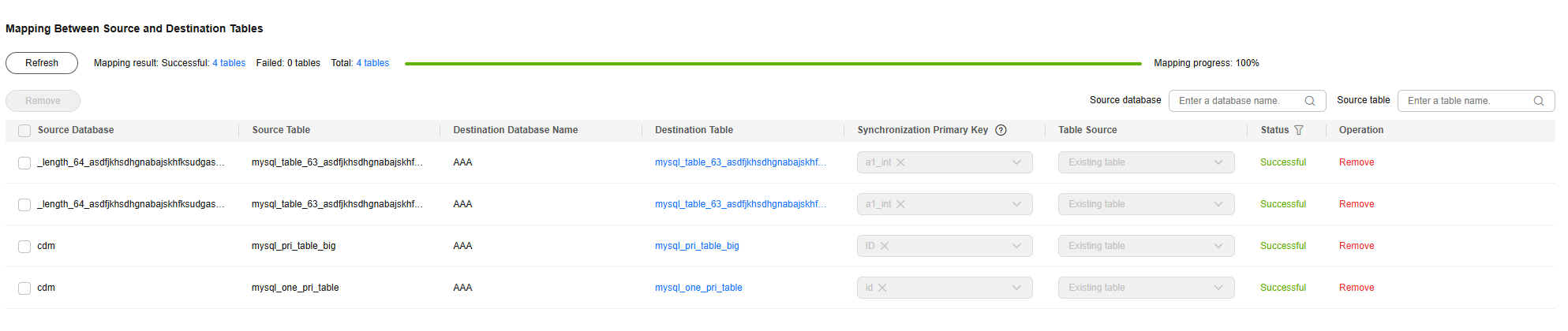
- Synchronization Primary Key
Primary key of the destination Doris table
- Table Source
This link does not support automatic table creation. You must manually create Doris tables.
- Synchronization Primary Key
- Configure DDL message processing rules.
Real-time migration jobs can synchronize data manipulation language (DML) operations, such as adding, deleting, and modifying data, as well as some table structure changes using the data definition language (DDL). You can set the processing policy for a DDL operation to Normal processing, Ignore, or Error. For details about the constraints on DDL synchronization to Hudi, see Constraints on the Hudi Destination.
- Normal processing: When a DDL operation on the source database or table is detected, the operation is automatically synchronized to the destination.
- Ignore: When a DDL operation on the source database or table is detected, the operation is ignored and not synchronized to the destination.
- Error: When a DDL operation on the source database or table is detected, the migration job throws an exception.
Figure 7 DDL configuration

- Configure task parameters.
Table 6 Task parameters Parameter
Description
Default Value
Execution Memory
Memory allocated for job execution, which automatically changes with the number of CPU cores
8GB
CPU Cores
Value range: 2 to 32
For each CPU core added, 4 GB execution memory and one concurrency are automatically added.
2
Maximum Concurrent Requests
Maximum number of jobs that can be concurrently executed. This parameter does not need to be configured and automatically changes with the number of CPU cores.
1
Auto Retry
Whether to enable automatic retry upon a job failure
No
Maximum Retries
This parameter is displayed when Auto Retry is set to Yes.
1
Retry Interval (Seconds)
This parameter is displayed when Auto Retry is set to Yes.
120s
Write Dirty Data
Whether to record dirty data. By default, dirty data is not recorded. If there is a large amount of dirty data, the synchronization speed of the task is affected.
- No: Dirty data is not recorded. This is the default value.
Dirty data is not allowed. If dirty data is generated during the synchronization, the task fails and exits.
- Yes: Dirty data is allowed, that is, dirty data does not affect task execution.
When dirty data is allowed and its threshold is set:
- If the generated dirty data is within the threshold, the synchronization task ignores the dirty data (that is, the dirty data is not written to the destination) and is executed normally.
- If the generated dirty data exceeds the threshold, the synchronization task fails and exits.
NOTE:
Criteria for determining dirty data: Dirty data is meaningless to services, is in an invalid format, or is generated when the synchronization task encounters an error. If an exception occurs when a piece of data is written to the destination, this piece of data is dirty data. Therefore, data that fails to be written is classified as dirty data.
For example, if data of the VARCHAR type at the source is written to a destination column of the INT type, dirty data cannot be written to the migration destination due to improper conversion. When configuring a synchronization task, you can configure whether to write dirty data during the synchronization and configure the number of dirty data records (maximum number of error records allowed in a single partition) to ensure task running. That is, when the number of dirty data records exceeds the threshold, the task fails and exits.
No
Dirty Data Policy
This parameter is displayed when Write Dirty Data is set to Yes. The following policies are supported:
- Do not archive: Dirty data is only recorded in job logs, but not stored.
- Archive to OBS: Dirty data is stored in OBS and printed in job logs.
Do not archive
Write Dirty Data Link
This parameter is displayed when Dirty Data Policy is set to Archive to OBS.
Only links to OBS support dirty data writes.
N/A
Dirty Data Directory
OBS directory to which dirty data will be written
N/A
Dirty Data Threshold
This parameter is only displayed when Write Dirty Data is set to Yes.
You can set the dirty data threshold as required.
NOTE:- The dirty data threshold takes effect for each concurrency. For example, if the threshold is 100 and the concurrency is 3, the maximum number of dirty data records allowed by the job is 300.
- Value -1 indicates that the number of dirty data records is not limited.
100
Custom attributes
You can add custom attributes to modify some job parameters and enable some advanced functions. For details, see Job Performance Optimization.
N/A
- No: Dirty data is not recorded. This is the default value.
- Submit and run the job.
After configuring the job, click Submit in the upper left corner to submit the job.
Figure 8 Submitting the job
After submitting the job, click Start on the job development page. In the displayed dialog box, set required parameters and click OK.
Figure 9 Starting the job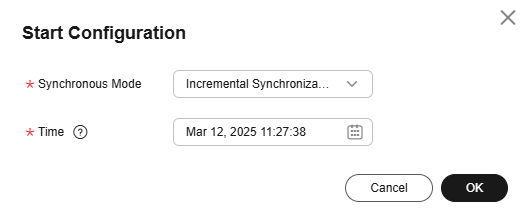
Table 7 Parameters for starting the job Parameter
Description
Offset
- Earliest: Data consumption starts from the earliest offset of the Kafka topic.
- Latest: Data consumption starts from the latest offset of the Kafka topic.
- Start Time: Data consumption starts from the offset of the Kafka topic obtained based on the time.
Minimum Timestamp
This parameter is required if Offset Parameter is set to Start Time. It specifies the start time of synchronization.
NOTE:If you set a time earlier than the earliest offset of Kafka messages, data consumption starts from the earliest offset by default.
- Monitor the job.
On the job development page, click Monitor to go to the Job Monitoring page. You can view the status and log of the job, and configure alarm rules for the job. For details, see Real-Time Migration Job O&M.
Figure 10 Monitoring the job
Performance Optimization
If the synchronization speed is too slow, rectify the fault by referring to Job Performance Optimization.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





