Creating an IAM User and Granting DataArts Studio Permissions – Identity Policies
- Create IAM users for employees based on your enterprise's organizational structure. Each IAM user will have their own security credentials for accessing DataArts Studio resources.
- Grant users only the permissions required to perform a given task based on their job responsibilities.
- Entrust a Huawei account or cloud service to perform efficient O&M on your DataArts Studio resources.
If you do not require individual IAM users for permissions management, skip this topic.
Example Authorization Process shows the process flow of identity policy-based authorization.
Context
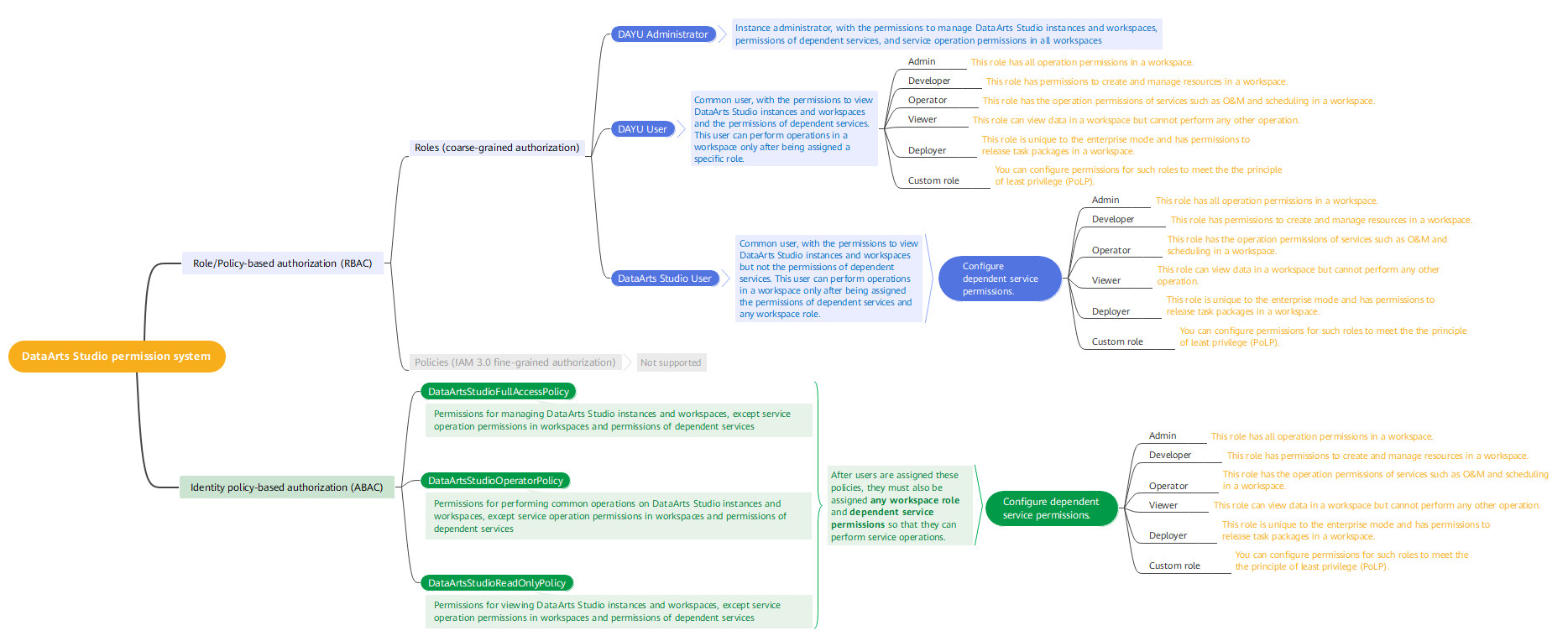
Before assigning permissions to a user group, you need to learn the DataArts Studio permission system. This section describes how to assign permissions to an IAM user through an identity policy.
Notes and Constraints
- System-defined identity policies provide users with permissions related to instances and workspaces. After permissions of dependent services are configured, service operation permissions in a specific workspace are provided by workspace roles.
-
If you assign both a role/policy-based permission (DAYU Administrator, DAYU User, or DataArts Studio User) and an identity policy-based permission (DataArtsStudioFullAccessPolicy, DataArtsStudioOperatorPolicy, DataArtsStudioReadOnlyPolicy, or custom identity policies) to an IAM user, the IAM user will have the following permissions:
- If both permissions contain the deny action, the deny policy prevails.
- The allow actions in the two permissions both take effect.
Example Authorization Process
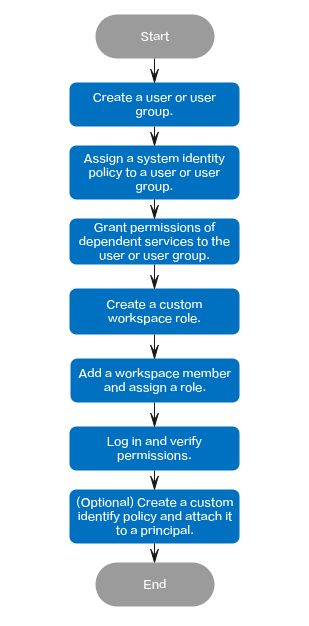
- Create a user or user group.
Use a Huawei account to log in to the IAM console and create a user or user group. For details, see Creating a User or Creating a User Group.

An IAM user can pass the authentication and access DataArts Studio through an API or SDK only if Programmatic access is selected for Access Type during the creation of the IAM user.
- Assign a system identity policy to a user or user group.
Assign a system policy of DataArts Studio to the user or user group, for example, DataArtsStudioFullAccessPolicy, DataArtsStudioOperatorPolicy, or DataArtsStudioReadOnlyPolicy. Alternatively, attach a system policy to the user or user group. For details, see Attaching a System-defined Identity Policy to a User or User Group.
- Grant permissions of dependent services to the user or user group.
Table 1 lists the permissions of the services on which DataArts Studio depends. The authorization procedure is as follows:
- On the IAM console, choose Permissions > Policies/Roles and click Create Custom Policy. Select JSON for Policy View and create two policies: DataArtsStudio_PermissionsOfDependentServices_global and DataArtsStudio_PermissionsOfDependentServices_region.
- Choose Users or User Groups and click Authorize in the Operation column. Select Policies/Roles for Authorization Model and select the following system roles and custom policies:
- System role DIS Operator
- Custom policy DataArtsStudio_PermissionsOfDependentServices_global
- Custom policy DataArtsStudio_PermissionsOfDependentServices_region
- (Optional) The image read permission in SWR is required only when a custom image is selected using a DLI Spark node of a job in DataArts Factory. Log in to the SWR console as an SWR administrator. In the navigation pane, choose My Images. Click an image to go to its details page and grant the read permission of the image to the user.
- After the preceding steps, dependent service permissions have been granted.
Table 1 Minimum permissions for developers on the services on which DataArts Studio depends Permission Type
Role/Policy-based permissions–system role
Role/Policy-based permissions–custom policy
Role/Policy-based permissions–custom policy
Mandatory
Mandatory
Mandatory
Mandatory
Permission
- DIS Operator
- DIS User
- (Optional and not recommended) SWR Admin
NOTE:
The image read permission in SWR is required only when a custom image is selected for a DLI Spark node of a job in DataArts Factory.
You are advised to add the read permission of the image by referring to User Permissions. You are not advised to directly assign the SWR Admin system role to users because this may result in excessive permissions.
DataArtsStudio_PermissionsOfDependentServices_global: custom policy for a global dependent cloud service{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "obs:object:GetObject", "obs:object:PutObject", "obs:object:DeleteObject", "obs:bucket:GetBucketStorage", "obs:bucket:GetBucketLocation", "obs:bucket:ListAllMyBuckets", "obs:bucket:ListBucket", "obs:bucket:ListBucketVersions", "obs:bucket:CreateBucket", "obs:bucket:DeleteBucket", "rms:resources:list", "iam:agencies:listAgencies" ] } ]}DataArtsStudio_PermissionsOfDependentServices_region: custom policy for a regional dependent cloud service{ "Version": "1.1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "cdm:cluster:get", "cdm:cluster:list", "cdm:cluster:create", "cdm:link:operate", "cdm:job:operate", "ces:*:get", "ces:*:list", "cloudtable:*:get", "cloudtable:*:list", "css:*:get", "css:*:list", "dis:streams:list", "dis:transferTasks:list", "dli:queue:submitJob", "dli:queue:cancelJob", "dli:table:insertOverwriteTable", "dli:table:insertIntoTable", "dli:table:alterView", "dli:table:alterTableRename", "dli:table:compaction", "dli:table:truncateTable", "dli:table:alterTableDropColumns", "dli:table:alterTableSetProperties", "dli:table:alterTableChangeColumn", "dli:table:showSegments", "dli:table:alterTableRecoverPartition", "dli:table:dropTable", "dli:table:update", "dli:table:alterTableDropPartition", "dli:table:alterTableAddPartition", "dli:table:alterTableAddColumns", "dli:table:alterTableRenamePartition", "dli:table:delete", "dli:table:alterTableSetLocation", "dli:table:describeTable", "dli:table:showPartitions", "dli:table:showCreateTable", "dli:table:showTableProperties", "dli:table:select", "dli:resource:updateResource", "dli:resource:useResource", "dli:resource:getResource", "dli:resource:listAllResource", "dli:resource:deleteResource", "dli:database:explain", "dli:database:createDatabase", "dli:database:dropFunction", "dli:database:createFunction", "dli:database:displayAllDatabases", "dli:database:displayAllTables", "dli:database:displayDatabase", "dli:database:describeFunction", "dli:database:createView", "dli:database:createTable", "dli:database:showFunctions", "dli:database:dropDatabase", "dli:group:useGroup", "dli:group:updateGroup", "dli:group:listAllGroup", "dli:group:getGroup", "dli:group:deleteGroup", "dli:column:select", "dli:jobs:start", "dli:jobs:export", "dli:jobs:update", "dli:jobs:list", "dli:jobs:listAll", "dli:jobs:get", "dli:jobs:delete", "dli:jobs:create", "dli:jobs:stop", "dli:variable:update", "dli:variable:delete", "dws:cluster:list", "dws:cluster:getDetail", "dws:openAPICluster:getDetail", "ecs:servers:get", "ecs:servers:list", "ecs:servers:stop", "ecs:servers:start", "ecs:flavors:get", "ecs:cloudServerFlavors:get", "ecs:cloudServers:list", "ecs:availabilityZones:list", "ges:graph:access", "ges:metadata:create", "ges:jobs:list", "ges:graph:operate", "ges:jobs:getDetail", "ges:graph:getDetail", "ges:graph:list", "ges:metadata:list", "ges:metadata:getDetail", "ges:metadata:delete", "ges:metadata:operate", "kms:cmk:get", "kms:cmk:list", "kms:cmk:create", "kms:cmk:decrypt", "kms:cmk:encrypt", "kms:dek:create", "kms:dek:encrypt", "kms:dek:decrypt", "mrs:cluster:get", "mrs:cluster:list", "mrs:job:get", "mrs:job:list", "mrs:job:submit", "mrs:job:stop", "mrs:job:delete", "mrs:sql:execute", "mrs:sql:cancel", "rds:*:get", "rds:*:list", "smn:topic:publish", "smn:topic:list", "vpc:publicIps:list", "vpc:publicIps:get", "vpc:vpcs:get", "vpc:vpcs:list", "vpc:subnets:get", "vpc:securityGroups:get", "vpc:firewalls:list", "vpc:routeTables:list", "vpc:subNetworkInterfaces:list" ] } ]} - Create a custom workspace role for the user, add it as a workspace member, and assign a role to the member.
DataArts Studio workspace roles determine the permissions of the IAM users to whom permissions have been granted through system-defined policies. There are four preset roles: admin, developer, operator, and viewer. If the four preset roles can meet your requirements, you do not need to create a custom role. Instead, you can directly add the user to the workspace and assign a preset role to the user. Otherwise, you need to create a custom role, add the user to the workspace, and assign the custom role to the user. For details about how to create a custom role, see (Optional) Defining a Workspace Role. For details about how to add a workspace member and assign a role, see Adding Workspace Members and Assigning Roles. For details about the permissions of the roles, see Permissions.
- Log in to the console and verify permissions.
Log in to the console using the created user and verify permissions of the user.
- Choose Service List > DataArts Studio. Locate a DataArts Studio instance and click Access. Check whether the workspace list is displayed.
- Access a service module (for example, Management Center) to which your current user has been added and check whether you can perform the operations allowed for the workspace role assigned to you.
Example Custom Identity Policies in DataArts Studio
Custom identity policies can be created as a supplement to the system-defined identity policies of DataArts Studio. For the actions supported in custom identity policies, see Permissions Policies and Supported Actions.
You can create custom identity policies in either of the following ways:
- Visual editor: Select cloud services, actions, resources, and request conditions. This does not require knowledge of policy syntax.
- JSON: Create a JSON policy or edit an existing one.
For details, see Creating a Custom Identity Policy and Attaching It to a Principal.
When creating a custom identity policy, use the Resource element to specify the resources the identity policy applies to and use the Condition element (service-specific condition keys) to control when the identity policy is in effect. For the supported resource types and condition keys, see Permissions Policies and Supported Actions. The following lists examples of custom identity policies for DataArts Studio.

Due to API restrictions, you cannot specify the workspace or instance for some operations when you create a custom identity policy. As a result, the permission configuration does not meet your expectation. For example, if an operation that does not support specific resources is allowed but a specific resource is specified for the operation, all resource operations are rejected. If an operation that does not support specific resources is denied but a specific resource is specified for the operation, all resource operations are allowed.
"Resource": [
"DataArtsStudio:*:*:workspace:*",
"DataArtsStudio:*:*:instance:*"
]
The DataArts Studio operations that cannot be performed on specified resources are as follows:
- Operations that can be performed only on specified instances but not on specified workspaces:
- DataArtsStudio:workspace:create
- DataArtsStudio:workspace:list
- Operations that cannot be performed on specified instances or workspaces:
- DataArtsStudio:instance:create
- DataArtsStudio:instance:get
- DataArtsStudio:instance:list
- DataArtsStudio:instance:resize
- DataArtsStudio:instance:getAgency
- DataArtsStudio:instance:createAgency
- DataArtsStudio:instance:uploadDriver
- DataArtsStudio:instance:deleteDriver
- DataArtsStudio:instance:listDrivers
- DataArtsStudio:instance:listTags
- DataArtsStudio:workspace:listTags
- Example 1: Grant the permissions to query instances and workspaces.
{ "Version": "5.0", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "DataArtsStudio:workspace:get", "DataArtsStudio:instance:get" ] } ] } - Example 2: Create a custom identity policy containing multiple actions.
A custom policy can contain the actions of one or multiple services. The following is an example policy containing actions of multiple services:
{ "Version": "5.0", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "DataArtsStudio:workspace:get", "DataArtsStudio:instance:get" ] }, { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "iam:groups:get", "iam:users:get" ] } ] }
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





