Configuring a Load Balancing Policy
Generally, multiple instances are deployed for a microservice. Load balancing controls the policy for a microservice consumer to access multiple instances of a microservice provider to balance traffic. It includes polling, random, response time weigh, and session stickiness.
Prerequisites
You have created a microservice by referring to Creating a Microservice. After the microservice starts, the service instance is registered with the corresponding service based on the configurations in the YAML file. If the microservice is not created in advance or has been deleted, the microservice is automatically created when the service instance is registered.
Configuring Load Balancing
- Log in to CSE.
- Choose Exclusive ServiceComb Engines.
- Click the target engine.
- Choose Microservice Governance.
- For engines with security authentication disabled, go to 6.
- For engines with security authentication enabled, if the login user is the user imported in Importing an IAM Account, go to 6. For other users, go to 5.
- In the displayed Security Authentication dialog box, enter the account name and password, and click OK.
- If you connect to the ServiceComb engine for the first time, enter the account name root and the password entered when Creating a ServiceComb Engine.
- For details about how to create an account, see Adding an Account.
- Click the target microservice. Choose Load Balancing.
- Click New. Select the microservices to be governed and select a proper load balancing policy. For details, see the following table.
Figure 1 Configuring load balancing (for microservices accessed through Spring Cloud)
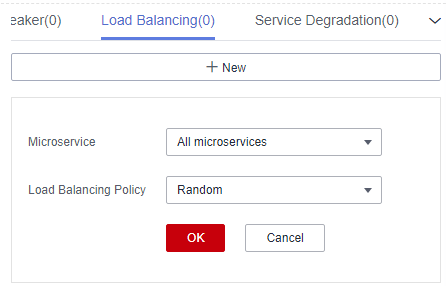 Figure 2 Configuring load balancing (for microservices accessed through Java chassis)
Figure 2 Configuring load balancing (for microservices accessed through Java chassis)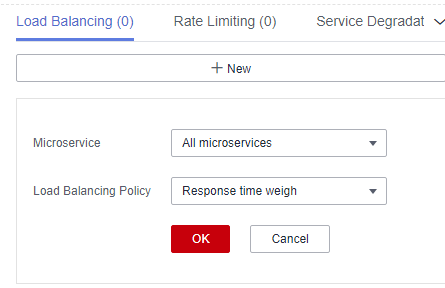
Policy
Description
Round robin
Supports routes according to the location information about service instances.
Random
Provides random routes for service instances.
Response time weigh
This configuration applies to microservices accessed through Java chassis.
Provides weight routes with the minimum active number (latency) and supports service instances with slow service processing in receiving a small number of requests to prevent the system from stopping response. This load balancing policy is suitable for applications with low and stable service requests.
Session stickiness
This configuration applies to microservices accessed through Java chassis.
Provides a mechanism on the load balancer. In the specified session stickiness duration, this mechanism allocates the access requests related to the same user to the same instance.
- Stickiness Duration: time limit for keeping a session. The value ranges from 0 to 86400, in seconds.
- Failures: number of access failures. The value ranges from 0 to 10. If the upper limit of failures or the session stickiness duration exceeds the specified values, the microservice stops accessing this instance.
- Click OK.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





