Process Monitoring
Process monitoring monitors active processes on a server. After the Cloud Eye Agent is installed, it collects information such as CPU usage, memory usage, and the number of opened files of these processes. You can also configure custom process monitoring to monitor processes with specified keywords, and set alarm rules for these processes to track changes to the number of processes, helping ensure the processes run smoothly.
The Agent collects process CPU usages every minute and displays the top 5 processes, ranked by the CPU usage over the last 24 hours.
Prerequisites
Ensure that the Cloud Eye Agent has been installed on a server. For details, see Installing the Agent.
Constraints
There's no limit on the number of processes to be added, but the Agent collects only the first 16 processes.
Adding Processes for Monitoring
Process monitoring is used to monitor active processes on a host. By default, the Agent collects information such as CPU usage, memory usage, and the number of opened files of these processes. Customized process monitoring can collect the number of key processes and obtain the status of key processes at any time.
Suppose that the following processes are running on a server:
/usr/bin/java /usr/bin/ntpd /telescope /usr/bin/python
Three keywords are configured, and the collection results are as follows:
- Key word: Java, number of processes: 1
- Key word: telescope, number of processes: 1
- Key word: usr, number of processes: 3
You do not need to configure the Processes column. After you set the process keyword, the system will update the number of matched processes.
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Perform the following operations based on your resources.
- To check the process monitoring of an ECS, choose Server Monitoring > Elastic Cloud Server.
- To check the process monitoring of a BMS, choose Server Monitoring > Bare Metal Server.
- On the Server Monitoring page, locate the ECS and click View Metric to go to the OS Monitoring page.
- Click the Process Monitoring tab.
- On the Process Monitoring page, click Add Process under Custom Process Monitoring.
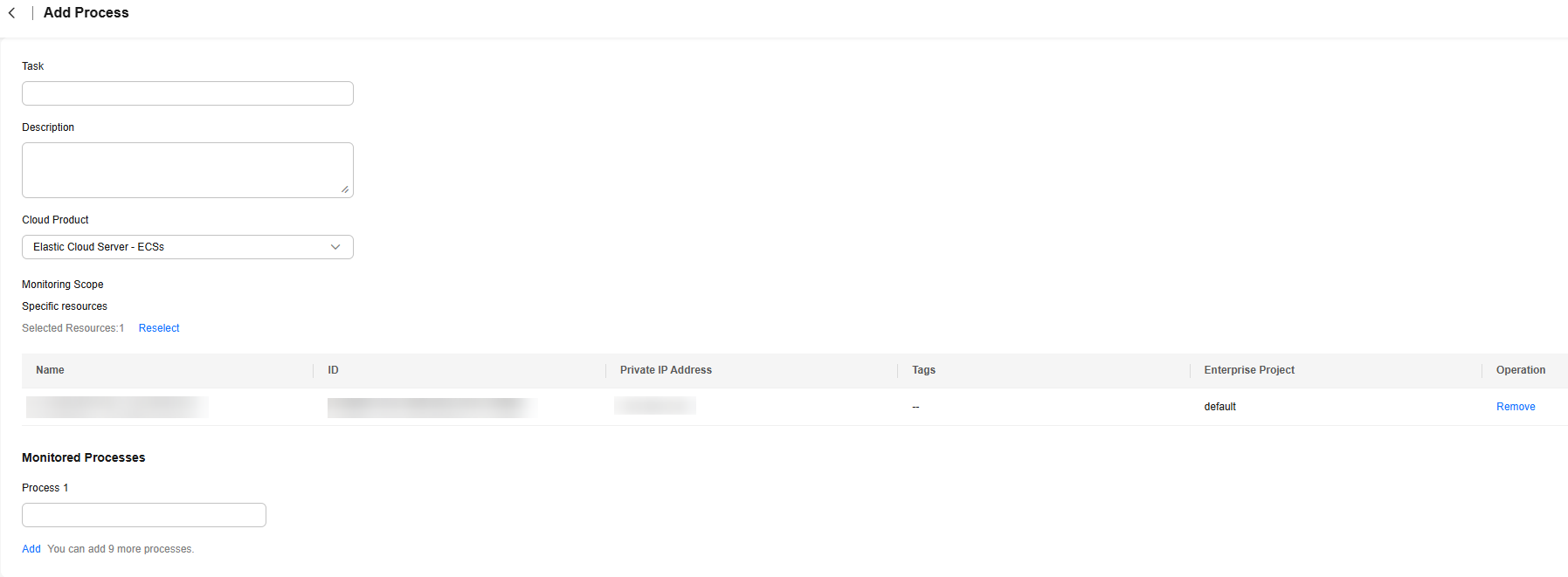
- On the Add Process page, the cloud product and monitoring scope use the default settings of the current resource and can be changed. Configure the task name and process name for process monitoring, as shown in Figure 1.
Table 1 Parameters for adding specific processes for monitoring Parameter
Description
Example Value
Task
Name of a process monitoring task. The value can only contain letters, digits, slashes (/), parentheses, number signs (#), underscores (_), asterisks (*) at the beginning, and hyphens (-). The value cannot start with hyphen (-). The task name can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
Once a process monitoring task is created, its name cannot be changed.
Process_Monitoring
Description
Description of the process monitoring task. This is an optional parameter.
-
Cloud Product
Cloud product that requires process monitoring. You can select Elastic Cloud Server or Bare Metal Server.
Once you create a process monitoring task, the cloud product cannot be modified.
Elastic Cloud Server
Monitoring Scope
Resources that require process monitoring.
-
Monitored Processes
Name of the monitored process. The value can only contain letters, digits, slashes (/), parentheses, number signs (#), underscores (_), asterisks (*) at the beginning, and hyphens (-). The value cannot start with hyphen (-). It can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
java
- Click OK.
After the configuration is complete, you can view the number of custom processes you added in the Custom Process Monitoring area.
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Choose Server Monitoring > Process Monitoring.
- On the Process Monitoring page, click Add Process. The Add Process page is displayed.
- Configure a task name, select a cloud product, select specified resources, and configure the process name. For details about the parameters, see Table 2.
Figure 2 Adding a process

Table 2 Parameters for batch adding processes for monitoring Parameter
Description
Example Value
Task
Name of a process monitoring task. The value can only contain letters, digits, slashes (/), parentheses, number signs (#), underscores (_), asterisks (*) at the beginning, and hyphens (-). The value cannot start with hyphen (-). The task name can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
Process_Monitoring
Description
Description of the process monitoring task. This is an optional parameter.
-
Cloud Product
Cloud product that requires process monitoring. You can select Elastic Cloud Server or Bare Metal Server.
Elastic Cloud Server
Monitoring Scope
Resources that require process monitoring.
-
Monitored Processes
Name of the monitored processes. The value can only contain letters, digits, slashes (/), parentheses, number signs (#), underscores (_), asterisks (*) at the beginning, and hyphens (-). The value cannot start with hyphen (-). It can contain a maximum of 255 characters.
java
- Click OK.
Modifying a Process Monitoring Task
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Choose Server Monitoring > Process Monitoring.
- Locate the target process monitoring task and click Modify in the Operation column. The Modify Process Monitoring page is displayed.
- Modify the description, specified resources, and name of the monitored process. For details about the parameters, see Table 2.
Figure 3 Modifying a process monitoring task

- Click OK.
Deleting a Process Monitoring Task
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Choose Server Monitoring > Process Monitoring.
- Locate the target process monitoring task and click Delete in the Operation column.
- In the Delete Monitored Process dialog box, enter DELETE and click OK.
Figure 4 Deleting a process monitoring task

Viewing Process Monitoring Metrics
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Choose Server Monitoring > Process Monitoring.
- Click
 in the Monitoring column of a process monitoring task to go to the View Metric page.
in the Monitoring column of a process monitoring task to go to the View Metric page. - Set Instance, Process Name, and Process ID to view the CPU usage, memory usage, and number of opened files of a specified process in line graphs. For details about related metrics, see Table 3.
- On the View Metric page, select a monitoring period (Last 15 min, Last 30 min, Last 1h, Last 2h, Last 3h, Last 12h, Last 1d, Last 7d, or Last 30d), or select Select Range to customize one to view historical monitoring data from the last 155 days.
Viewing Custom Process Monitoring
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Perform the following operations based on your resources.
- To check the process monitoring of an ECS, choose Server Monitoring > Elastic Cloud Server.
- To check the process monitoring of a BMS, choose Server Monitoring > Bare Metal Server.
- On the Server Monitoring page, locate the ECS and click View Metric to go to the OS Monitoring page.
- Click the Process Monitoring tab.
- Under Custom Process Monitoring, locate a custom process and click
 on the left of the process name.
on the left of the process name. - Locate the row containing the target process ID and click View Details in the Operation column. On the displayed View Metric drawer, view the CPU usage, memory usage, and number of opened files of the current process. For details about the metrics, see Table 3. In the upper left corner, select a monitoring period (Last 15 min, Last 30 min, Last 1h, Last 2h, Last 3h, Last 12h, Last 1d, Last 7d, or Last 30d), or select Select Range to customize one, to view historical monitoring data from the last 155 days.
- In the Custom Processes area, details of custom processes running on the host is displayed.
Table 3 Process Monitoring metrics Metric
Description
Value Range
Collection (Linux)
Collection (Windows)
CPU Usage
CPU consumed by a process
0 to 1 x Number of vCPUs
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Check the metric value changes in the /proc/pid/stat file.
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Call the Windows API GetProcessTimes to obtain the CPU usage of the process.
Memory Usage
Memory consumed by a process
0 to 1
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Memory Usage = RSS x PAGESIZE/MemTotal
RSS: Obtain its value by checking the second column of the /proc/pid/statm file.
PAGESIZE: Obtain its value by running the getconf PAGESIZE command.
MemTotal: Obtain its value from the /proc/meminfo file.
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Call Windows API procGlobalMemoryStatusEx to obtain the total memory size. Call GetProcessMemoryInfo to obtain the used memory size. Use the used memory size to divide the total memory size to get the memory usage.
Opened Files
The number of opened files consumed by the process
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can run the ls -l /proc/pid/fd command to view the number.
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Run Windows API NtQuerySystemInformation to obtain information about all opened handles in the system, check whether each handle is a file handle opened by the current process, and obtain the number of files opened by the current process.
In Windows, the specified_process_file metric of some processes cannot be collected due to causes like insufficient permissions.
Enabling Alarm Notifications for Custom Process Monitoring
You can configure alarm notifications. When the number of processes decreases or increases, Cloud Eye will notify you immediately.
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Perform the following operations based on your resources.
- To check the process monitoring of an ECS, choose Server Monitoring > Elastic Cloud Server.
- To check the process monitoring of a BMS, choose Server Monitoring > Bare Metal Server.
- On the Server Monitoring page, locate the ECS and click View Metric to go to the OS Monitoring page.
- Click the Process Monitoring tab.
- On the Custom Process Monitoring page, locate the target process and click Create alarm rules in the Operation column.
- On the displayed page, configure the alarm policies and notifications.
For details about alarm notification parameters, see Table 3.
- Click Create.
Querying the System Processes
After the Agent is installed, you can check system processes on Cloud Eye.
To query the number of processes, perform the following steps:
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Perform the following operations based on your resources.
- To check the process monitoring of an ECS, choose Server Monitoring > Elastic Cloud Server.
- To check the process monitoring of a BMS, choose Server Monitoring > Bare Metal Server.
- On the Server Monitoring page, locate the ECS and click View Metric to go to the OS Monitoring page.
- Click the Process Monitoring tab.
In the System Processes area, the process information is displayed. Table 4 describes the metrics of system processes.
Table 4 System process metrics Metric
Description
Value Range
Collection (Linux)
Collection (Windows)
Running Processes
Number of processes that are running
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can obtain the state of each process by checking the Status value in the /proc/pid/status file, and then collect the total number of processes in each state.
Not supported
Idle Processes
Number of processes that are idle
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can obtain the state of each process by checking the Status value in the /proc/pid/status file, and then collect the total number of processes in each state.
Not supported
Zombie Processes
Number of zombie processes
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can obtain the state of each process by checking the Status value in the /proc/pid/status file, and then collect the total number of processes in each state.
Not supported
Blocked Processes
Number of processes that are blocked
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can obtain the state of each process by checking the Status value in the /proc/pid/status file, and then collect the total number of processes in each state.
Not supported
Sleeping Processes
Number of processes that are sleeping
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can obtain the state of each process by checking the Status value in the /proc/pid/status file, and then collect the total number of processes in each state.
Not supported
Total Processes
Total number of processes
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can obtain the state of each process by checking the Status value in the /proc/pid/status file, and then collect the total number of processes in each state.
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Obtain the total number of processes by using the system process status support module psapi.dll.
Viewing Top Processes with the Highest CPU Usage
- The Agent collects process CPU usages every minute and displays the top 5 processes, ranked by the CPU usage over the last 24 hours.
- Run the top command to query the CPU usage and memory usage of a process.
- Run the lsof or ls /proc/pid/fd |wc -l command to query the number of files opened by the current process. In the command, replace pid with the ID of the process to be queried.
- If a process occupies multiple CPUs, the CPU usage may exceed 100% because the collection result is the total usage of multiple CPUs.
- The top 5 processes are not fixed. The process list displays the top 5 processes that have entered the statistical period of 1 minute in the last 24 hours.
- The CPU usage, memory usage, and number of opened files are collected only for the top 5 processes for which monitoring has been enabled in the last 24 hours. If such a process has been stopped, its data will not be displayed.
- The time in the list indicates the time when a process was created.
- If the system time on the client browser is different from that on the monitored ECS, the graph may not show any metric data. In this case, synchronize the local time with the ECS time.
- The Agent of the new version no longer reports data on the top 5 processes, and process monitoring will become unavailable. You are advised to use Custom Process Monitoring instead.
To query information about the top 5 processes with the highest CPU usages
- Log in to the Cloud Eye console.
- Perform the following operations based on your resources.
- To check the process monitoring of an ECS, choose Server Monitoring > Elastic Cloud Server.
- To check the process monitoring of a BMS, choose Server Monitoring > Bare Metal Server.
- On the Server Monitoring page, locate the ECS and click View Metric to go to the OS Monitoring page.
- Click the Process Monitoring tab.
- Click Configure under TOP 5 Processes with Highest CPU Usage.
- In the displayed TOP 5 Processes with Highest CPU Usage dialog box, enable monitoring for target processes and click OK.
Locate a process and click View Details in the Operation column. On the displayed View Metric drawer, view the CPU usage, memory usage, and number of opened files of the process. For details about the metrics, see Table 5. In the upper left corner, select a monitoring period (Last 15 min, Last 30 min, Last 1h, Last 2h, Last 3h, Last 12h, Last 1d, Last 7d, or Last 30d), or select Select Range to customize one, to view historical monitoring data from the last 155 days.
Table 5 Process Monitoring metrics Metric
Description
Value Range
Collection (Linux)
Collection (Windows)
CPU Usage
CPU consumed by a process
pHashId (process name and process ID) is the value of md5.
0 to 1 x Number of vCPUs
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Check the metric value changes in the /proc/pid/stat file.
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Call the Windows API GetProcessTimes to obtain the CPU usage of the process.
Memory Usage
Memory consumed by a process
pHashId (process name and process ID) is the value of md5.
0 to 1
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
Memory Usage = RSS x PAGESIZE/MemTotal
- RSS: Obtain its value by checking the second column of the /proc/pid/statm file.
- PAGESIZE: Obtain its value by running the getconf PAGESIZE command.
- MemTotal: Obtain its value from the /proc/meminfo file.
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
- Call Windows API procGlobalMemoryStatusEx to obtain the total memory size.
- Call GetProcessMemoryInfo to obtain the used memory size.
- Use the used memory size to divide the total memory size to get the memory usage.
Opened Files
The number of opened files consumed by the process
pHashId (process name and process ID) is the value of md5.
≥ 0
Monitored object: ECSs or BMSs
You can run the ls -l /proc/pid/fd command to view the number.
Not supported
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot