Identity and Permissions Design
Thanks to Huawei Cloud's extensive delivery experience, we provide the following best practices in user and permissions management.
Unified Identity and Permissions Management
The identity management system of your company is already optimal in controlling the permissions of employees as they are recruited and revoking permissions from employees who have transferred to different departments or have resigned. You are advised to use your own identity management system to implement federated identity authentication with Huawei Cloud IAM Identity Center, and synchronize users from your identity management system to IAM Identity Center based on the System for Cross-domain Identity Management (SCIM). In IAM Identity Center, you can centrally configure permissions for these users to access resources in multiple accounts. Then, the users can log in to the Huawei Cloud console using Single Sign-on (SSO), view the accounts they can access, and click Access Console to access the cloud resources in these accounts.
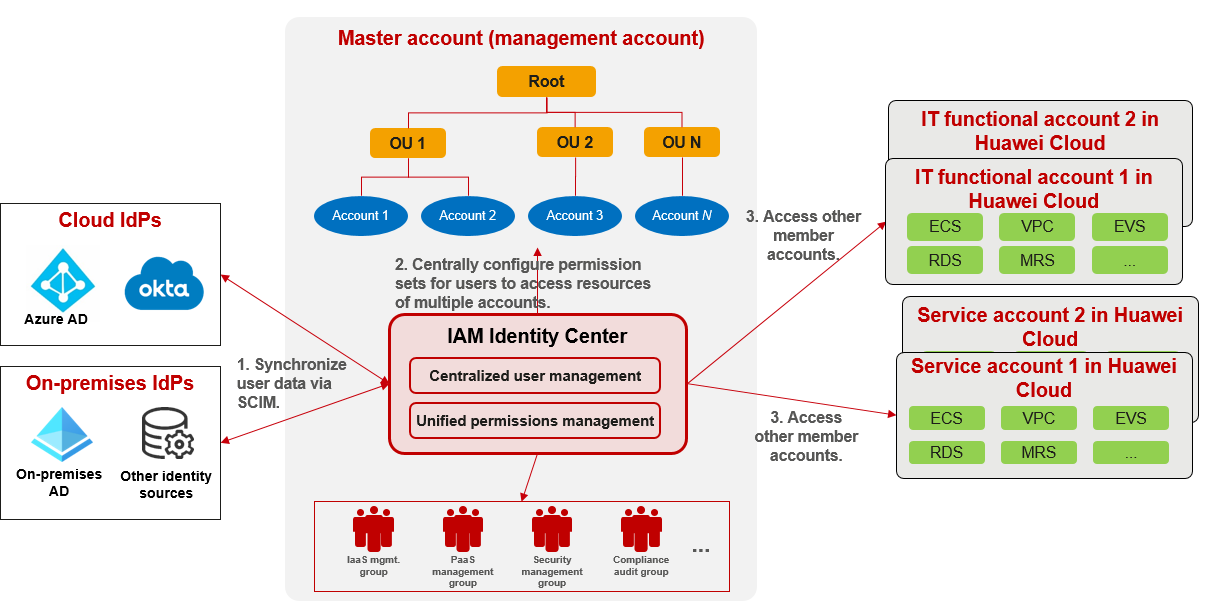
User Group and Permissions Plan
You can plan IAM Identity Center user groups based on the role division of cloud center of excellence (CCoE) and add employees to the user groups that match their responsibilities. The following table lists the recommended user groups, along with their responsibilities, accounts, and permissions granted based on the principle of least privilege (PoLP). You can refer to this table to plan user groups and permissions that meet enterprise requirements.
|
User Group |
Group Responsibility |
Recommended Permissions for Multiple Accounts |
|---|---|---|
|
Financial management group |
Manage financial elements such as bills, costs, discounts, and invoices of member accounts in a unified manner. |
BSS Administrator and BSS Finance permissions for the management account |
|
IT governance group |
Create and manage OUs, member accounts, and SCPs. |
Organizations FullAccess permission for the management account |
|
Identity and permissions management group |
Centrally create and manage users and user groups, and configure permissions, agencies, and SSO. |
|
|
Security management group |
Centrally manage and control security policies, rules, and resources for the entire company, and set security configuration baselines for other accounts of the company. |
Management permissions of security resources for all accounts, such as SecMaster, Host Security Service (HSS), Data Security Center (DSC), and Database Security Service (DBSS) |
|
Compliance audit group |
Centrally view audit logs and security-related logs (such as VPC flow logs and OBS access logs) of all accounts. |
|
|
Network management group |
Centrally deploy and manage enterprise network connection resources, such as Enterprise Router, Virtual Private Network (VPN), Direct Connect (DC), and NAT Gateway. Centrally create and manage VPCs, subnets, and network access control lists (ACLs) for each account. Centrally deploy and manage network boundary protection resources, such as Web Application Firewall (WAF) and Cloud Firewall (CFW). |
|
|
IaaS management group |
Centrally manage IaaS resources of all accounts as the cloud infrastructure administrator. |
|
|
PaaS management group |
Centrally manage middleware resources of all accounts as the middleware administrator. |
|
|
Automated O&M group |
Centrally monitor and maintain resources of all accounts. |
|
|
Data management group |
Centrally deploy and manage data platforms and collect service data from other member accounts to store, process, and analyze them on the data platforms. |
Tenant Administrator permission for the data platform account |
|
Public service management group |
Centrally deploy and manage the enterprise public resources, services, and application systems, and share them with other member accounts of the company. |
Tenant Administrator permission for the public service account |
|
Application development group |
Develop applications and manage the development environment. |
|
|
Application test group |
Test applications and manage the test environment. |
|
Permissions Configuration
The root user or Admin user of the master account is the administrator with the highest permissions. It is recommended that the CIO or IT director of the company keep the password of the root user or Admin user. The Admin user should not perform routine management and O&M operations, including creating users and configuring permissions. You are advised to use the master account's Admin user to create an identity permissions management group and its users in IAM Identity Center, and grant the required permissions to the group. Then, the users in this group can create other users and user groups and grant permissions to them. The following figure shows the recommended user group and permission configuration.

Permissions Use
For unified management, IT management personnel need to use the multi-account authorization method of IAM Identity Center to access and manage cloud resources of other accounts. For example, if the IaaS and PaaS administrators need to centrally manage IaaS and middleware resources of each account in a company, they can use the multi-account authorization method of IAM Identity Center to access these resources, as shown in the following figure.
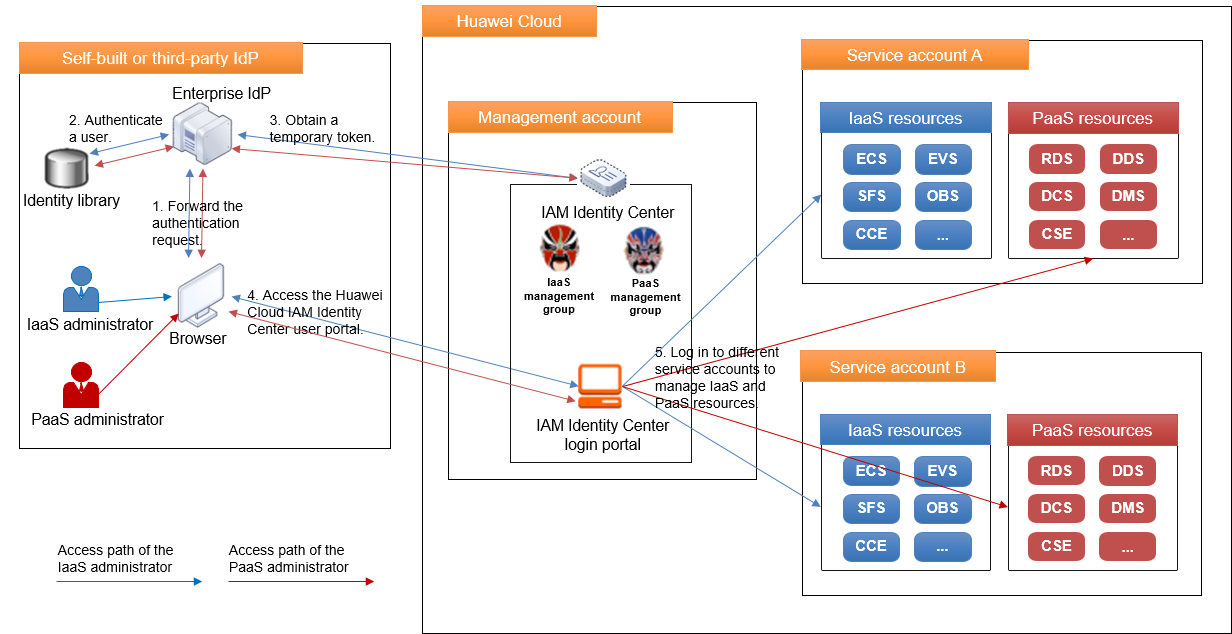
Other Best Practices for Identity and Permissions Management
- Grant groups only the permissions essentially required to perform specific tasks by following the PoLP. If the responsibilities of a group were changed, adjust the granted permissions immediately.
- To simplify authorization, grant permissions to user groups instead of users.
- Ensure that permission configuration, permission use, and permission audit are performed by different natural persons or teams who are not part of the community of shared interests.
- Perform secondary authentication for sensitive operations such as deleting and updating key resources and using a large amount of money.
- Do not share your password. Instead, create a user for each person who needs to manage or use Huawei Cloud resources, and assign permissions to that user. In this way, all operations performed on Huawei Cloud can be tracked and audited.
- The enterprise CTO or CIO keeps the password of the root user (with the same name as the account) of the master account. The owner of the business unit to which the member account belongs keeps the password of the member account's root user.
- The root user (with the same name as the account) has high permissions. Do not use the root user to access Huawei Cloud. Instead, create one or more common users and grant permissions to them by following the PoLP, and then use these users to perform routine management.
- Use service control policies (SCPs) to control the permissions of the root user of the member account.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





