Cloud Maturity Model
The purpose of assessing cloud maturity is to help your organization fully understand your capabilities during cloud transformation, identify gaps, and develop targeted improvement plans. This helps ensure that your organization's cloud transformation objectives are realistic and feasible, avoiding overly high or low expectations.
Huawei Cloud has designed the cloud maturity model based on the Cloud Maturity Model from the Open Alliance for Cloud Transformation (OACA), the Cloud Native Maturity Model from the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF), the Information Technology Service Standards (ITSS) of the China National Technical Committee 28 on Information Technology, and the Data Management Capability Maturity Model (DCMM), along with the best practices from a large number of government and enterprise customers of Huawei Cloud. This model is based on the following five principles:
- Business-driven: The assessment model must be centered on driving business growth. The cloud transformation objectives must align with your company's business strategies and objectives. Cloud transformation needs to go beyond technical benefits to bring about business benefits.
- All-element: The assessment model must go beyond technical capabilities to cover all elements, including people, technology, and processes.
- Full-stack: The assessment model must cover the full technology stack, including the Well-Architected Framework, cloud infrastructure, application modernization, big data and AI, O&M, and security protection.
- E2E: The assessment model must cover the whole journey of cloud transformation, including strategy formulation, top-level planning, solution design, adoption and implementation, and O&M.
- Integrated: The assessment model must consider integrated management capabilities between on-premises and cloud, between clouds, between regions in a cloud, and between accounts in a cloud.
Based on these principles, Huawei Cloud has designed the following 10 assessment dimensions:
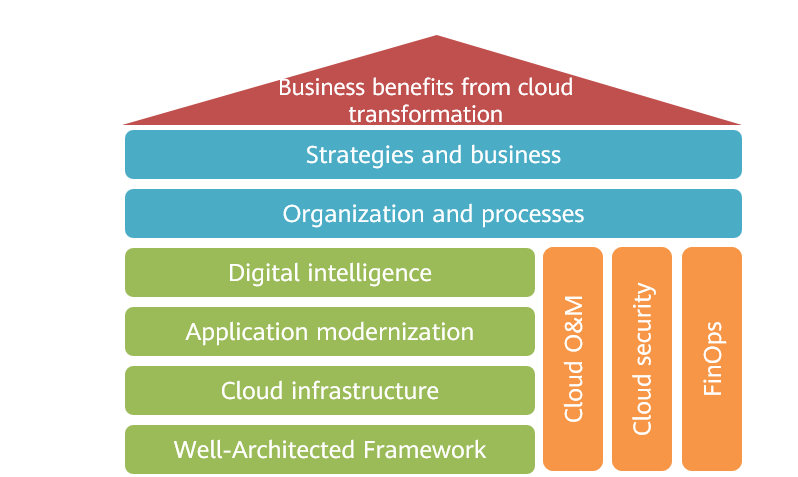
- Business benefits from cloud transformation
This dimension assesses the business and financial benefits that an organization can achieve through cloud transformation, including improved business agility, improved business continuity, reduced TCO, accelerated business innovation, and improved sustainability. This dimension is placed first because business benefits are the most important dimension. If business benefits are not achieved, it is futile to do well in other dimensions.
- Strategies and business
This dimension assesses the strategic planning capability of an organization during cloud transformation, including whether the cloud strategy is consistent with the overall business strategy and objectives, whether the key business drivers are identified, and whether clear cloud strategies, cloud transformation objectives, and migration policies are formulated. In addition, this dimension assesses the foresight, comprehensiveness, and feasibility of strategy formulation, as well as the grasp of industry trends and cloud technology trends.
- Organization and processes
This dimension assesses the adaptability and transformation capability of an organization in terms of organizational structure, personnel skills, and work processes during cloud transformation. It measures whether the organization has an organizational structure and talent team that can support cloud transformation and whether work processes suitable for the cloud environment have been established.
- Digital intelligence
This dimension assesses the organization's capabilities in big data and AI, and whether it can use cloud platform data intelligence services to achieve data-driven business innovation and intelligent transformation. It also measures the organization's data lifecycle management, data governance capabilities, and practice level in AI (such as AI development and large models).
- Application modernization
This dimension assesses whether the organization's application systems use modern design and development models, such as microservice architecture, event-driven architecture, containerization, serverless architecture, and DevSecOps practices, as well as whether it has the capability to develop and deploy cloud native applications.
- Cloud infrastructure
This dimension assesses the organization's design, deployment, and management capabilities of cloud infrastructure, including landing zone design and implementation, integrated management of networks and IAM, infrastructure automation deployment based on IaC, data backup, and auto scaling policies.
- Well-Architected Framework
This dimension assesses whether the organization follows the design principles and best practices of the Well-Architected Framework, which covers five aspects: resilience, security, performance, cost optimization, and operational excellence.
- Cloud O&M
This dimension assesses the organization's O&M capabilities in the cloud environment, including observability, CMDB, automated O&M, chaos engineering, ITSM, and AIOps. It also assesses whether the organization has established the most suitable cloud operations model and O&M processes for the current business situation that support agile delivery and stable operations of cloud-based business systems.
- Cloud security
This dimension assesses the organization's security measures and operations capabilities in the cloud environment, including identity security, network security, data security, host security, application security, O&M security, security management regulations, and integrated security operations.
- FinOps
This dimension assesses the organization's capabilities in managing and optimizing cloud resource costs, including cost budgeting, visualization, optimization, operations, and integrated financial management.
These assessment dimensions have taken into account the elements of people, technology, and process, spanning the entire journey and technology stack of cloud transformation, with integrated management involved. There are more than 70 assessment questions in total. Each of these questions involves five levels: initiating, emerging, performing, advancing, and leading.
Table 1 Five levels of cloud maturity Level
Score
Maturity Level
Initiating
1 point
- The understanding and application of cloud computing are in the initial stage. The application of cloud-native technologies and best practices is limited, and there are security and cost risks.
- The cloud transformation has not started yet. There is no overall planning and strategy. There is no organization or processes to support cloud transformation.
Emerging
2 points
- Cloud computing technologies are partially applied, and some preliminary results have been achieved. However, the overall system and integrity are still inadequate.
- Cloud-native technologies and best practices are gaining attention, but they are not yet seeing sufficiently widespread adoption. The automation level is low, and security and cost management need to be further strengthened.
- A transition from traditional IT to cloud-native IT is underway.
Performing
3 points
- The cloud transformation has achieved results. Technical competitiveness has been established by applying cloud computing technologies, but business advantages have not been established and business benefits are not obvious.
- Various cloud services can be used skillfully, and certain automatic management capabilities are available.
- Cloud-native technologies and best practices, such as DevOps and microservices, are systematically applied. Security and cost management have also been given appropriate attention and implemented.
- A complete process and organization are available, and the cloud transformation objectives have been established within the IT department.
Advancing
4 points
- The cloud transformation has achieved remarkable results. Business competitive advantages have been established by applying cloud computing technologies, and remarkable business benefits, such as improved business agility and continuity and increased revenue, have been achieved.
- Cloud computing has become a key factor in driving business innovation and improving competitiveness.
- Cloud-native technologies and best practices can be fully used to achieve high agility and scalability. The security and cost management systems are mature and efficient.
- Processes are effectively executed, and cloud transformation objectives are established across the organization.
Leading
5 points
- In the cloud computing field, the organization is in the leading position and can lead the innovation of technologies and business models.
- The advantages of cloud-native technologies are fully exerted to achieve highly automated and intelligent operations.
- Security and cost management reach the industry-leading level.
- Cloud transformation not only promotes the rapid development of corporate business, but also sets a benchmark for the industry.
- Close attention is paid to the changes in business requirements and cloud computing technologies to continuously iterate and optimize the solutions.
The detailed assessment and analysis from these 10 dimensions can help your organization fully assess your capabilities during the cloud transformation process. By drawing a radar chart to quickly find the gap between your organization and the industry-leading enterprises, you can efficiently formulate targeted plans for improvement.
Figure 2 Cloud maturity radar chart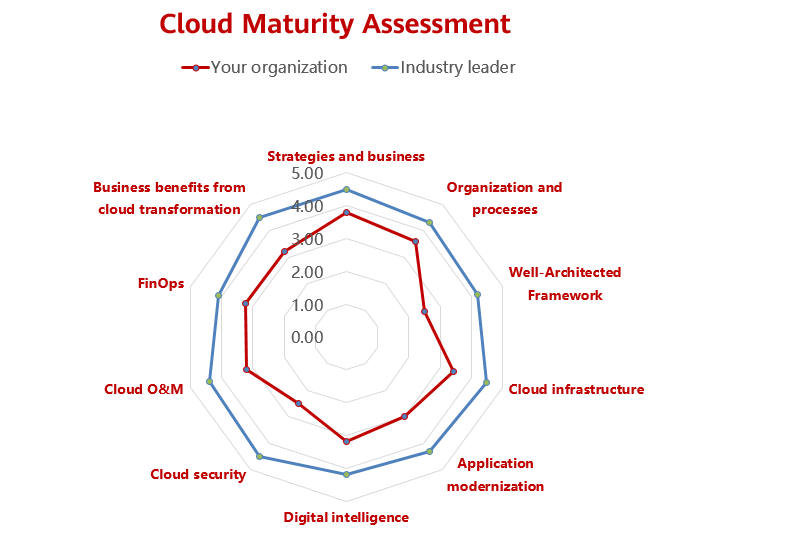
Note that the cloud maturity model is for relatively general and coarse-grained assessment. The main purpose is to help your organization quickly identify your capability gaps and determine cloud transformation objectives. It cannot replace a detailed assessment in the survey and assessment phase, which aims to help your organization design a detailed technical implementation solution.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





