Creating a Component
Constraints
- A maximum of 50 application components can be created in an environment. To create more, submit a service ticket.
- CAE container-based deployment does not support images of the Arm architecture.
- If you select Images > Upload Through Page for Code Source when creating a component, only one image package can be added at a time. The file size cannot exceed 2 GB (after decompression). The image package can be in .tar or .tar.gz format. Only the image package created by the container engine client of version 1.11.2 or later can be uploaded. For details, see Creating an Image Package. To upload a file larger than 2 GB, select Upload Through Client.
- By default, no outbound IP address is bound to environments created after July 30, 2025. Before deploying a component whose source is source code repository, you need to configure an outbound IP address. Otherwise, the source code build will fail. For details, see Accessing the User VPC and Public Network in the CAE Environment.
- When you create a component and select code source, Source code repository and Software packages are not supported. You are advised to perform operations in Interconnecting CAE with GitHub Actions to Implement Automatic CI/CD Deployment.
Prerequisites
- You have created an environment. For details, see Creating an Environment.
- You have created an application. For details, see Creating an Application.
Creating a Component
- Log in to CAE.
- Choose Components.
- Select the created application and environment from the drop-down lists in the upper part of the page, and click Create Component.
- Configure the component by referring to Table 1.
Table 1 Basic component information Parameter
Item
Description
Component
-
Component name. Enter 4 to 32 characters, starting with a lowercase letter and ending with a lowercase letter or digit. Use only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-).
Version
-
Component version.
The format is A.B.C or A.B.C.D. A. B, C, and D are natural numbers, for example, 1.0.0 or 1.0.0.0.
Specifications
-
Select the instance specifications, including the CPU and memory specifications. The memory size varies according to the CPU specifications. For example, 0.5core, 1GiB; 1core, 1GiB; 1core, 2GiB; 2core, 4GiB.
NOTE:When create a large-specification instance for the first time in your environment, you need to wait longer.
Instances
-
Value range: 1 to 99. Default value: 2.
After a component is created, you can manually scale component instances. The number of instances that can be scaled ranges from 1 to 99.
Code Source
Source code repository
This function is not supported. You are advised to perform operations in Interconnecting CAE with GitHub Actions to Implement Automatic CI/CD Deployment.
- Select a code source. GitHub, GitCode, GitLab, and Bitbucket code can be identified.
- Complete the code information.
- Authorization: Select the corresponding source code authorization from the drop-down list. If you use this function for the first time, click Create Authorization and set Authorization and Mode, and click OK. Click Authorization List to view the created authorization. Select the check box on the left to Re-authorize or Delete the authorized source code.
- Username/Organization: Select a user or organization to manage code in the current project.
- Repository: Select a repository to manage code of each module in the current project.
- Branch: Select a branch to manage code.
- Language/Runtime System: Select a language of the source code from the drop-down list. For details, see Component Description.
- Custom Build: Select Default or Custom.
NOTE:
The authorization mode varies depending on the code source.
- Default command or script: preferentially executes build.sh in the root directory. If build.sh does not exist, the code will be built using the common method of the selected language. Example: mvn clean package for Java.
- Custom command: Commands are customized using the selected language. Alternatively, the default command or script is used after build.sh is modified.
- Dockerfile: Set this parameter if the component source is Source code repository. You can select Custom or Default.
NOTE:
You can select Default to change the name of the Maven artifact file specified in the default Dockerfile only when Language/Runtime System is set to Java.
- Dockerfile Address: Set this parameter if Dockerfile is set to Custom.
- Dockerfile Address is the directory where the Dockerfile is located relative to the root directory (./) of the project. The Dockerfile is used to build an image.
- The Docker program reads the Dockerfile file to generate a custom image.
- The Dockerfile address contains 1 to 255 characters, including letters, digits, periods (.), hyphens (-), underscores (_), and slashes (/).
- If the file name is Dockerfile, you can only enter a directory address and this address must end with a slash (/).
- Artifact File: Set this parameter if Dockerfile is set to Default.
Select and run the specified JAR package from multiple JAR packages generated during Maven build. The JAR package ends with .jar. Fuzzy match is supported. Examples: demo-1.0.jar and demo*.jar.
Image
- Upload the image package by Upload Through Client or Upload Through Page.
- Upload Through Client: If you select this option, log in to the VM where the container engine is located as the root user, obtain the login command, copy the command to the node, and upload the image.
- Upload Through Page: If you select this option, only one image package can be added at a time. The file size cannot exceed 2 GB (after decompression). The image package can be in .tar or .tar.gz format. Only the image package created by the container engine client of version 1.11.2 or later can be uploaded. For details, see Creating an Image Package.
To upload a file larger than 2 GB, select Upload Through Client.
- On the My Images, Open Source Images, or Shared Images page, select an image package for deployment. You can search for an image by name.
- My Images: image packages uploaded by users.
- Open Source Images: images provided by SWR.
- Shared Images: image packages shared by different accounts.
- (Optional) You can also click the link next to Code Source to go to the SWR console and perform more image management operations.
Notes:
- CAE container-based deployment does not support images of the Arm architecture.
- When you select Upload Through Page, only one image package can be added at a time. The file size cannot exceed 2 GB (after decompression). The image package can be in .tar or .tar.gz format. Only the image package created by the container engine client of version 1.11.2 or later can be uploaded. For details, see Creating an Image Package. To upload a file larger than 2 GB, select Upload Through Client.
Software package
This function is not supported. You are advised to perform operations in Interconnecting CAE with GitHub Actions to Implement Automatic CI/CD Deployment.
- Select the source of the software package. Value: CodeArts Release Repo, OBS, or GitHub Artifact.
- If you select CodeArts Release Repo, upload the software package to the software release repository in advance. For details, see Uploading a Software Package.
- If you select OBS, upload the software package to the OBS bucket in advance. For details, see Uploading an Object.
- If you select GitHub Artifact, enter an authorization name and select an authorization mode. The authorization mode can be OAuth or private token.
NOTE:
To obtain a token, perform the following steps:
- Log in to the token creation page of GitHub.
- Click Generate new token > Generate new token (classic).
- On the setting page, create a token with correct permissions and select the following scopes: repo, read:org, admin:repo_hook, admin:org_hook and read:user.
- Click Generate token. The token is returned only once. Record and save the token.
- Language/Runtime System: Select a language of the software package from the drop-down list. For details, see Component Description.
- Build Type: Select System default or Custom Dockerfile.
- System default: Use the default Dockerfile based on the selected language or runtime system.
- Custom Dockerfile: Customize the Dockerfile based on the selected language.
- Create a component.
- Click Configure Component. For details, see Component Configurations.
- Click Create and Deploy Component. In the displayed dialog box, click Deploy Now.
- (Optional) During component deployment, you can click Terminate Task at any time to manually terminate the task. The termination result is classified into three scenarios.
- Scenario 1: After you click Terminate Task in the build phase (source code/software package components in the deployment, upgrade, or rollback phase), the build job will be canceled and not enter the deployment phase.
For example, CompA is a source code component and is originally in the Running state. When you upgrade CompA , click Terminate Task. If the component is still in the Building job phase, the upgrade job is terminated immediately and will not enter the deployment phase.
- Scenario 2: If the Deployment of a component has taken effect in Kubernetes during the deployment phase, the Deployment process will not be terminated after you click Terminate Task. The termination only exits the waiting state, but cannot prevent the Deployment from taking effect on the component pod.
For example, scale out one CompB instance to three instances. This scaling takes effect at once and new instances are about to be started in component deployment. After you click Terminate Task, the deployment task displayed on CAE exits immediately. However, the preceding scaling is still executed on the Kubernetes system. As a result, there are three instances.
- Scenario 3: If the component deployment duration is short (for example, the deployed image is started quickly or only a few configurations of the component are modified), the termination takes effect after a period of time. As a result, the component deployment task cannot be blocked.
For example, the image of CompC is started quickly, and the component deployment duration is short. Originally, CompA is in the Running state. Restart CompA. During the waiting period, click Terminate Task. The termination takes effect after a period of time. Before the termination takes effect, the component is deployed, and CompA changes to the Running state.
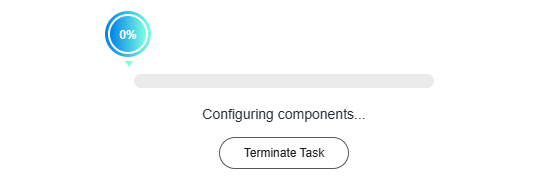
- Scenario 1: After you click Terminate Task in the build phase (source code/software package components in the deployment, upgrade, or rollback phase), the build job will be canceled and not enter the deployment phase.
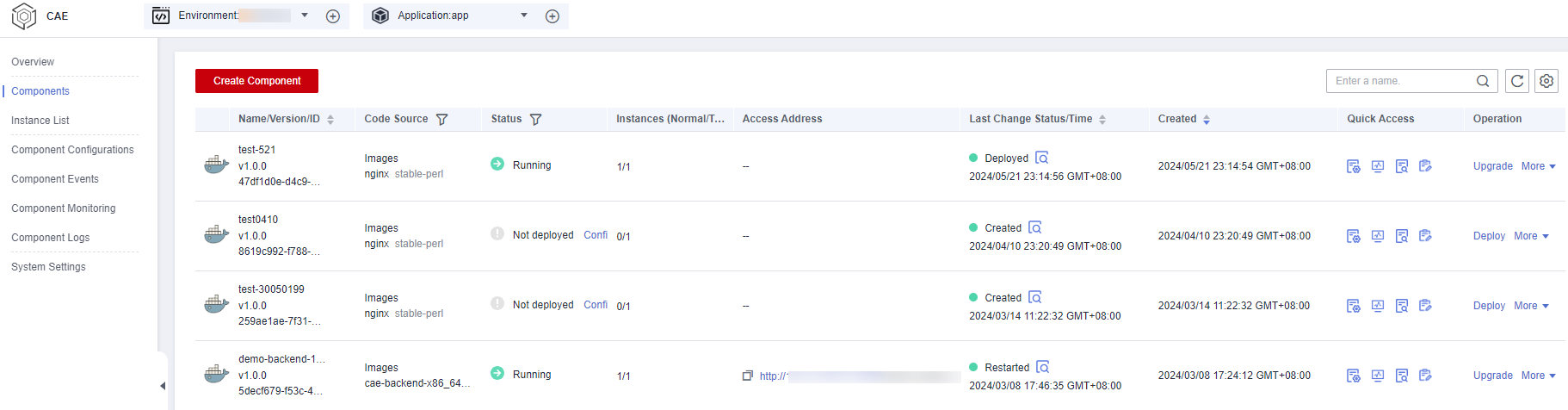
- After the component is created or deployed, you can view the environment ID, application ID, component ID, component name, code source, status, number of instances, and creation time on the Components page.
Figure 1 Component list
- If a component is in the Not deployed state, click Configure in the Status column to configure and deploy it.
- If a component is in the Running state, click
 in the Quick Access column to reconfigure it and make the configurations take effect.
in the Quick Access column to reconfigure it and make the configurations take effect.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





