How Can I Tune the Local Disk Read IOPS Performance of I9 ECSs?
Performance Tuning Scenarios
Ultra-high I/O ECSs use the QingTian architecture and are equipped with high-performance Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) local disks. Each flavor contains 1 to 12 NVMe local disks.
You are advised to tune the performance for I9 ECSs with 64 vCPUs or more. Performance tuning may have impact on access latency.
You can adjust the number of interrupt aggregations to optimize the performance of i9.16xlarge.4, i9.32xlarge.4, i9.16xlarge.8, and i9.32xlarge.8 ECSs.
Background
Interrupt coalescing optimizes frequent hardware interrupts in computer systems or network devices by aggregating multiple interrupts into a single event. This reduces the CPU overhead for handling interruptions, resulting in better system performance.
Interrupt Coalescing Count is a key parameter in NVMe devices. It refers to the specific number of I/O operations that are accumulated before the device triggers an interrupt. For example, if the Interrupt Coalescing Count is 0x0109 (265 in decimal), the device triggers an interrupt after accumulating 265 I/O operations. You can adjust this parameter to balance the interrupt frequency and delay. This is the key in performance tuning.
In practice, a too large or too small value of Interrupt Coalescing Count may affect performance. To achieve the optimal performance, you need to consider the hardware configuration (such as vCPUs and storage device load).- If the value is too small, interrupts are too frequent. This can increase the CPU overhead and reduce system performance.
- If the value is too large, the delay may increase, affecting the response of real-time tasks.
Vendors usually provide a default maximum value for reference. You can adjust the value based on site requirements.
You can use the nvme set-feature command to dynamically adjust the Interrupt Coalescing Count value based on the hardware configuration and load.
During the tuning, you are advised to use a performance monitoring tool to monitor performance metrics and gradually adjust the value and test the performance to achieve the best results.
Procedure
The following uses the i9.32xlarge.4 flavor as an example to describe how to batch tune read IOPS performance for local disks.
- Log in to the ECS console and access the ECS list page.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and project. - Select the ECS you want to log in to and click Remote Login in the Operation column.
You can log in using multiple methods. For details, see Login Overview (Windows) and Login Overview (Linux).
- Perform batch interrupt aggregation tuning on local NVMe disks.
for i in $(seq 0 7);do nvme set-feature /dev/nvme$i -f 0x08 --value 0x0109; done
Figure 1 Batch tuning of read IOPS performance for local disks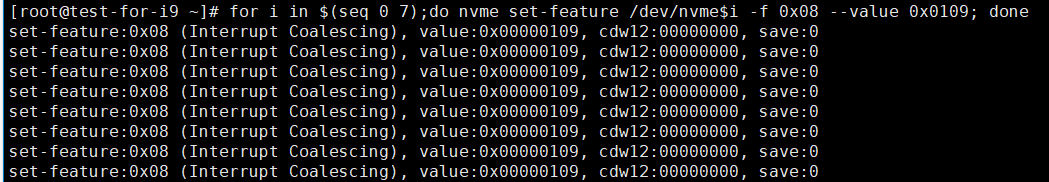
Table 1 Parameters in the command Parameter
Description
seq 0 7
Iterates through NVMe device IDs from 0 to 7, which means to tune 8 NVMe devices. If there are 12 NVMe devices, the device IDs are from 0 to 11.
Adjust the device ID range based on the site requirements. For details about the number of NVMe devices included in the flavor, see Ultra-high I/O ECSs.
/dev/nvme$i
Specifies the (i+1)th NVMe device.
-f 0x08
0x08: sets the interrupt aggregation count.
--value 0x0109
Sets the interrupt aggregation count to 0x0109. This means the device will trigger an interrupt after accumulating 265 I/O operations.
NOTE:0x0109 is the reference value recommended by the vendor. You can start from the reference value and gradually adjust it to achieve the optimal performance.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





