CREATE PROCEDURE
Description
Creates a stored procedure.
Precautions
- If the parameters or return values of a stored procedure have precision, the precision is not checked.
- When creating a stored procedure, you are advised to explicitly specify the schemas of all operations on table objects in the stored procedure definition. Otherwise, the stored procedure may fail to be executed.
- When a stored procedure is created, a write lock is added only to the CREATE stored procedure or package, and a read lock is added only to the functions and packages on which the functions depend during compilation and execution.
- current_schema and search_path specified by SET during stored procedure creation are invalid. search_path and current_schema before and after function execution should be the same.
- When the function is called by SELECT or CALL, an argument must be provided in the output parameter. The argument does not take effect.
- A stored procedure with the PACKAGE attribute can use overloaded functions.
- Do not create an overloaded stored procedure with different parameter names but same stored procedure name and parameter list type.
- Do not create a stored procedure that has the same name and parameter list as the function.
- Do not overload stored procedures with different default values.
- Only the in, out, and inout parameters of the stored procedure cannot be reloaded after the GUC parameter behavior_compat_options is set to 'proc_outparam_override'. They can be reloaded after the parameter is disabled.
- ORA-compatible functions are created for ORA-compatible databases and PG-compatible functions are created for PG-compatible databases. Hybrid creation is not recommended.
- If a function supports overloading, you need to add the keyword PACKAGE.
- When an overloaded stored procedure is called, the variable type must be specified.
- If an undeclared variable is used in a stored procedure, an error is reported when the stored procedure is called.
- When you create a procedure, you cannot insert aggregate functions or other functions out of the average function.
- If a function is defined as IMMUTABLE or SHIPPABLE, avoid INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, MERGE, and DDL operations in the function because the CN needs to determine the execution node for these operations. Otherwise, an error may occur.
- The stored procedure does not support operations that will return a set.
- When stored procedures without parameters are called in another stored procedure, you can omit brackets and call stored procedures using their names directly.
- When other functions with output parameters are called in a stored procedure and an assignment expression, set the GUC parameter behavior_compat_options to 'proc_outparam_override', define variables of the same type as the output parameters in advance, and use the variables as output parameters to call other functions with output parameters for the output parameters to take effect. Otherwise, the output parameters of the called functions will be ignored.
- The stored procedure supports viewing, exporting, and importing parameter comments.
- The stored procedure supports viewing, exporting, and importing parameter comments between IS/AS and plsql_body.
- Users with the CREATE ANY FUNCTION permission can create or replace stored procedures in the user schemas.
- out/inout must be set to a variable but not a constant.
- The default permission on a stored procedure is SECURITY INVOKER. To change the default permission to SECURITY DEFINER, set the GUC parameter behavior_compat_options to 'plsql_security_definer'.
- If a stored procedure with the definer specified is created in a schema of another user, the stored procedure will be executed by another user, which may cause unauthorized operations. Therefore, exercise caution when performing this operation.
- If the out parameter is used as the output parameter in an expression, the expression does not take effect in the following scenarios: The execute immediate sqlv using func syntax is used to execute a function. The select func into syntax is used to execute a function. DML statements such as INSERT and UPDATE are used to execute a function. When a function with the out output parameter is used as an input parameter, that is, fun (func (out b), a), the out b parameter does not take effect.
- When the complex function is called in a stored procedure, for example, func(x).a, a composite type is returned. Cross-schema call is supported, but the database.schema.package.func(x).b call is not supported.
- When a stored procedure with the out parameter is called, you can set the GUC parameter behavior_compat_options to 'proc_outparam_transfer_length' to pass the parameter length. The specifications and constraints are as follows:
- The following types are supported: CHAR(n), CHARACTER(n), NCHAR(n), VARCHAR(n), VARYING(n), VARCHAR2(n), and NVARCHAR2(n).
- If the out parameter does not take effect (for example, perform), the length does not need to be transferred.
- The following types do not support precision transfer: NUMERIC, DECIMAL, NUMBER, FLOAT, DEC, INTEGER, TIME, TIMESTAMP, INTERVAL, TIME WITH TIME ZONE, TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, TIME WITHOUT TIME ZONE, and TIMESTAMP WITHOUT TIME ZONE.
- Regardless of whether the GUC parameter behavior_compat_options is set to 'proc_outparam_override', the parameter length can be passed.
- To pass the length of elements of the collection type and the length of elements of the array type nested by the collection type, you need to set the GUC parameter behavior_compat_options to tableof_elem_constraints.
- Functions contain syntax and functions that use GUC parameters to control features. If GUC parameters are modified in a session, the function may retain the behavior before the modification. Therefore, exercise caution when modifying GUC parameters.
- Only the initial user can perform the REPLACE operation on the stored procedures of the initial user.
Syntax
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 |
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] PROCEDURE procedure_name [ ( {[ argname ] [ argmode ] argtype [ { DEFAULT | := | = } expression ]}[,...]) ] [ { IMMUTABLE | STABLE | VOLATILE } | { SHIPPABLE | NOT SHIPPABLE } | {PACKAGE} | [ NOT ] LEAKPROOF | { CALLED ON NULL INPUT | RETURNS NULL ON NULL INPUT | STRICT } | {[ EXTERNAL ] SECURITY INVOKER | [ EXTERNAL ] SECURITY DEFINER | AUTHID DEFINER | AUTHID CURRENT_USER} | COST execution_cost | SET configuration_parameter { [ TO | = ] value | FROM CURRENT } ][ ... ] { IS | AS } plsql_body / |
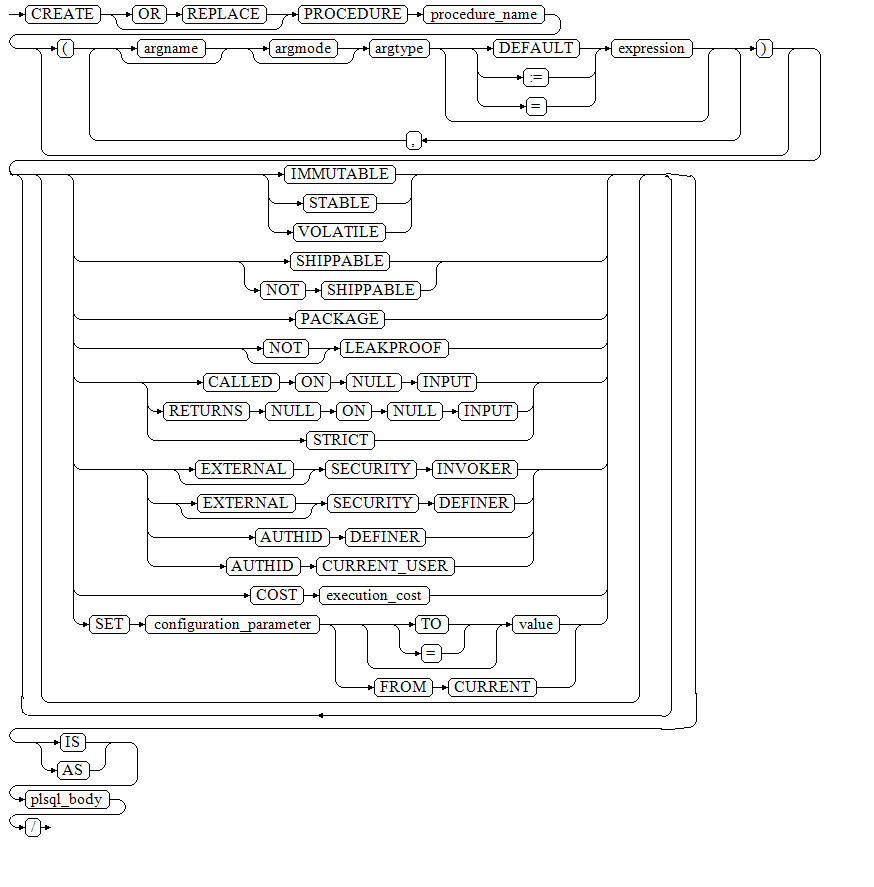
Parameters
- OR REPLACE
Replaces the original definition when two stored procedures are with the same name.
- procedure_name
Specifies the name of the stored procedure that is created (optionally with schema names).
Value range: a string that complies with the Identifier Naming Conventions.

You are advised not to create a function with the same name as a system function. Otherwise, you need to specify the schema of the function when calling the function.
- argmode
Specifies the mode of an argument.

VARIADIC specifies parameters of the array type.
Value range: IN, OUT, INOUT, and VARIADIC. The default value is IN. Only the parameter of the OUT mode can be followed by VARIADIC. The parameters of OUT and INOUT cannot be used in procedure definition of RETURNS TABLE.
- argname
Specifies the argument name.
Value range: a string that complies with the Identifier Naming Conventions.
- argtype
Specifies the type of an argument. You can use %ROWTYPE to indirectly reference the type of a table, or %TYPE to indirectly reference the type of a column in a table or composite type.
Value range: a valid data type

No specific order is applied to argname and argname. The following order is advised: argname, argmode, and argtype.
- expression
Specifies the default expression of a parameter.

- If a_format_version is set to 10c and a_format_dev_version is set to s2, the default expression is not supported when the parameter is in INOUT mode.
- It is recommended that you define all default parameters after all non-default parameters.
- If a function with default parameters is called, input parameters are added to the function from left to right. If inputs of non-default parameters are missing, an error is reported.
- If proc_uncheck_default_param is enabled and a function with default parameters is called, input parameters are added to the function from left to right. These inputs can be set to default values. If an input of a non-default parameter is missing, the previous default value is used to fill this parameter.
- When a_format_version is set to 10c, a_format_dev_version is set to s1, proc_outparam_override is disabled, and the function parameters include the output parameter out and default, the default value cannot be used.
- IMMUTABLE, STABLE,...
Specifies a constraint. The function of each parameter is similar to that of CREATE FUNCTION. For details, see CREATE FUNCTION.
- plsql_body
Specifies the PL/SQL stored procedure body.
When a stored procedure is created, the PLSQL_BODY can end with "END;" or "END procedure_name;".

Constraints for storage procedures ending with "END procedure_name;":
- It is supported only in ORA-compatible mode (database level).
- Only the ORA-style creation syntax is supported.
- Only the scenario where the stored procedure name is set after END is supported.
- In the DBE_PLDEVELOPER.gs_source, my_source, db_source and adm_source views, the definition of the stored procedure stays consistent (if the created procedure is "END+name", it is displayed as "END+name"). In the pg_proc and \sf views, the outermost END is not followed by a name in any case. The innermost END is displayed as defined during creation (if the created procedure is "END+name", it is displayed as "END+name").
- The stored procedure cannot retain the name following the outermost END in the SQL file generated by gs_dump.
- If a stored procedure is named IF/LOOP or a subprogram is nested, the stored procedure cannot be ended with END IF/LOOP.

When you perform password-related operations, such as user creation, password change, and encryption/decryption, in a stored procedure, the password will be recorded in the system catalogs and logs in plaintext. To prevent sensitive information leakage, you are advised not to perform password-related operations in a stored procedure.
Examples
- Create a stored procedure.
-- Create a stored procedure and return the sum of the input parameters. gaussdb=#CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_add(i int, j int) AS BEGIN dbe_output.print_line('result is: '|| i+j); END; / -- Use CALL to call a stored procedure. gaussdb=#CALL proc_add(16,17); -- Use a program block to call a stored procedure. gaussdb=#BEGIN proc_add(16,17); END; / -- Drop. gaussdb=#DROP PROCEDURE proc_add;
- Create a stored procedure ending with END in an ORA-compatible database.
Create a stored procedure. -- Create a stored procedure and print the sum of the input parameters. gaussdb=#CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE proc_add(i int, j int) AS BEGIN dbe_output.print_line('result is: '|| i+j); END proc_add; / -- Use CALL to call a stored procedure. gaussdb=#CALL proc_add(16,17); -- Use a program block to call a stored procedure. gaussdb=#BEGIN proc_add(16,17); END; / -- Drop. gaussdb=#DROP PROCEDURE proc_add;
- Create a stored procedure whose parameter model is VARIADIC.
-- Create the stored procedure pro_variadic. gaussdb=#CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE pro_variadic (var1 VARCHAR2(10) DEFAULT 'hello!',var4 VARIADIC int4[]) AS BEGIN dbe_output.print_line(var1); for i in 1..array_length(var4,1) loop dbe_output.print_line(var4[i]); end loop; END; / -- Execute the stored procedure. gaussdb=#SELECT pro_variadic(var1=>'hello', VARIADIC var4=> array[3,5,11,2]); -- Drop. gaussdb=#DROP PROCEDURE pro_variadic;
- Parameter models: IN and OUT
- IN (default) indicates that the parameter is an input parameter.
- OUT indicates that the parameter is an output parameter.
- IN OUT indicates that the parameter is an input and output parameter
-- Create the stored procedure proc_add1. num1 and num2 are input parameters, and num3 is an output parameter. gaussdb=#CREATE PROCEDURE proc_add1 (num1 in int, num2 in int, num3 out int) AS BEGIN num3 := num1 + num2; END; / -- Use a program block to call the stored procedure and use variable c to receive the parameters sent by the stored procedure. gaussdb=#DECLARE a int := 20; b int := 32; c int := 0; BEGIN proc_add1(a,b,c); dbe_output.put_line(c); END; / -- Drop. gaussdb=#DROP PROCEDURE proc_add1;
Helpful Links
Suggestions
- analyse | analyze
- Do not run ANALYZE in a transaction or anonymous block.
- Do not run ANALYZE in a function or stored procedure.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





