Managing Views
Context
If you need to frequently query a combination of specific columns in multiple tables, you can define a view to avoid repeated query statements. A view abstracts the underlying table structure through a virtual table to simplify common query operations.
A view is a logical table. Different from a physical base table, a view does not actually reside on disks. The database stores only the query definition of the view. The actual data is always stored in the joined base table. When data in the base table changes, the view query result dynamically synchronizes the changes. The view is like a real-time data window, allowing users to access the mirrored data they are concerned about. Each time a view is accessed, the system re-executes its definition query to obtain the latest data.
Managing Views
Create a table before performing operations. For details, see Creating a Table.
- Create a view. For details, see CREATE VIEW.
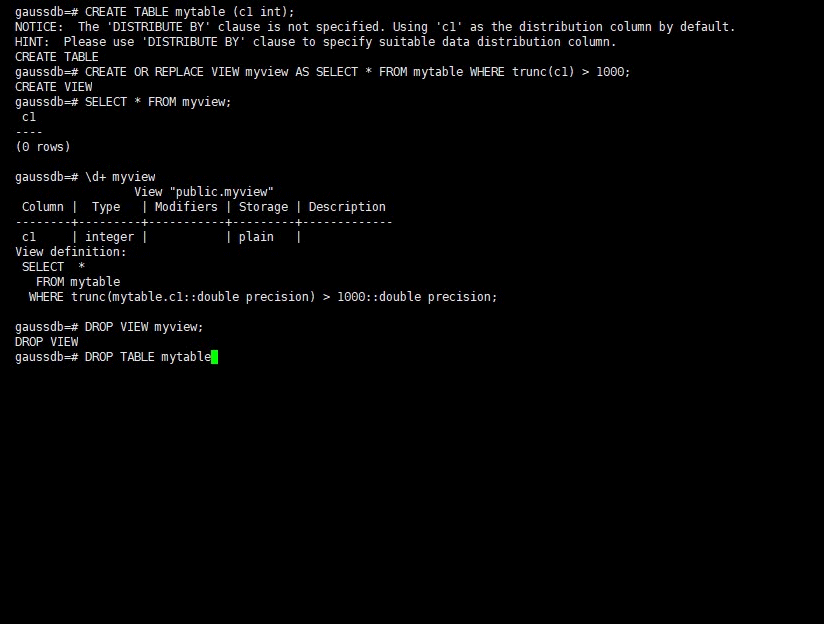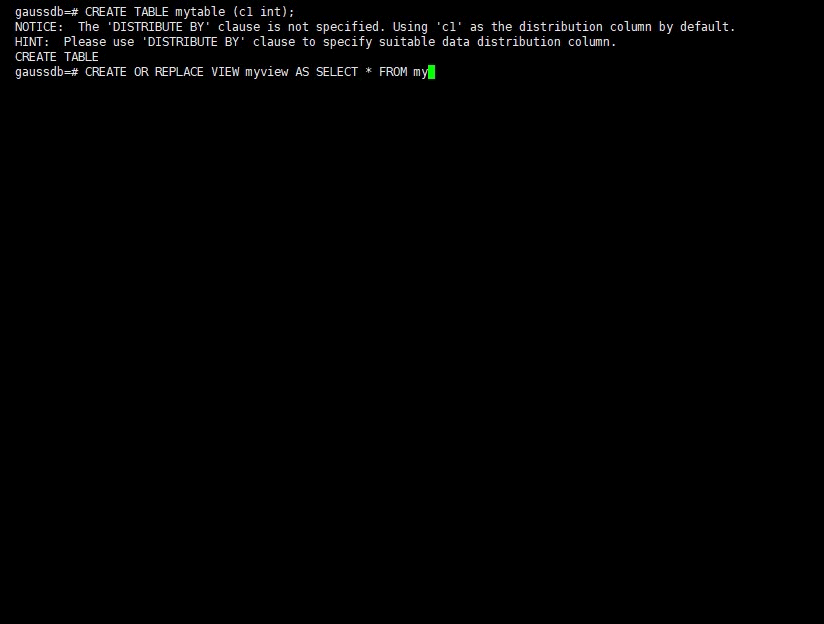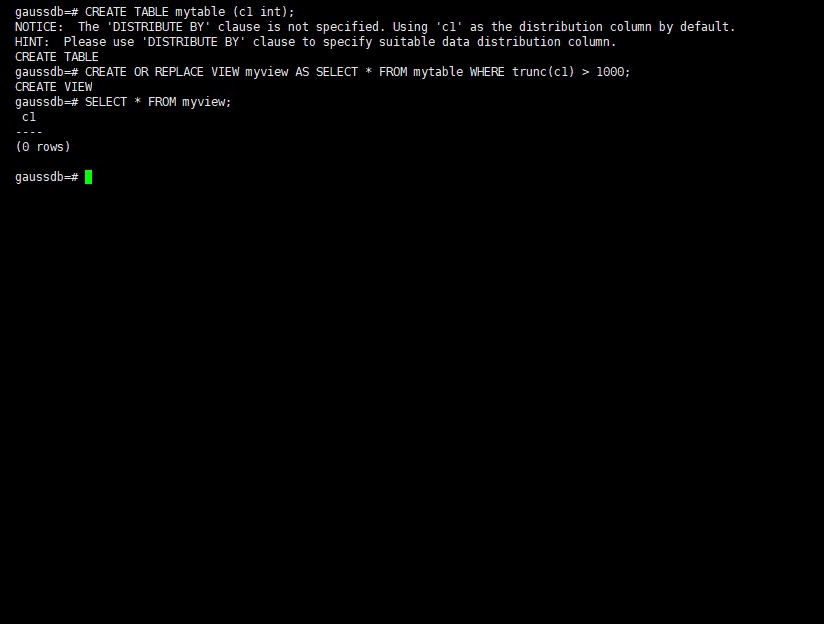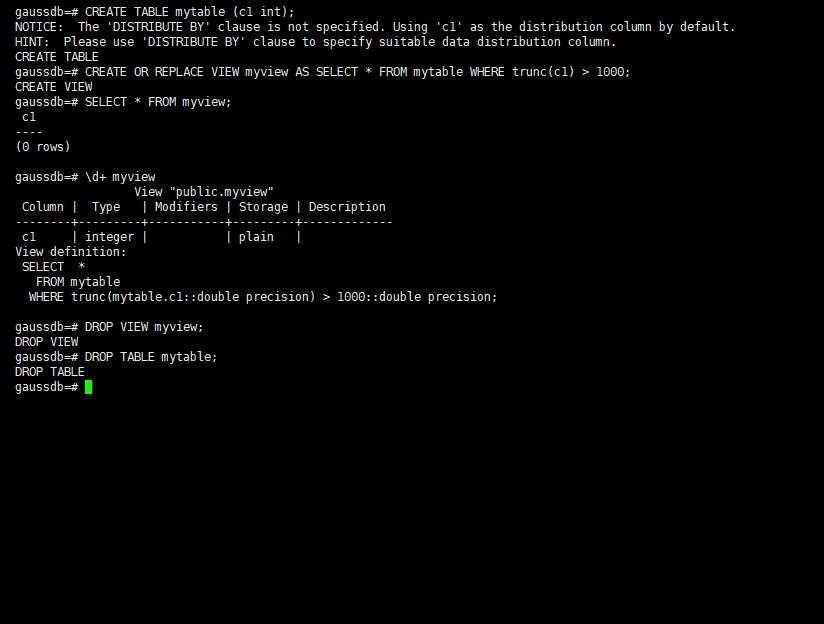
Create the myview view. In the command, tpcds.web_returns indicates the created user table that contains the wr_refunded_cash integer column.
1 2
gaussdb=#CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW myview AS SELECT * FROM tpcds.web_returns WHERE trunc(wr_refunded_cash) > 10000; CREATE VIEW

The OR REPLACE clause in CREATE VIEW is optional. If this clause is used, the database system automatically replaces the original view definition if the view already exists.
- Query a view.
- Query views of the current user.
1gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM my_views;
- Query all views.
1gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM adm_views;
- Query details about a specified view.
View details about myview.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
gaussdb=#\d+ myview View "PG_CATALOG.myview" Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Description ----------+-----------------------+-----------+----------+------------- USERNAME | CHARACTER VARYING(64) | | extended | View definition: SELECT PG_AUTHID.ROLNAME::CHARACTER VARYING(64) AS USERNAME FROM PG_AUTHID;
- Drop a view.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





