Introduction to Hudi
Apache Hudi indicates Hadoop Upserts Deletes and Incrementals. It is used to manage large analysis data sets stored on the DFS in Hadoop.
Hudi is not just a data format. It is also a set of data access methods (similar to the access layer of GaussDB(DWS) storage). In Apache Hudi 0.9, big data components such as Spark and Flink have their own clients. The following figure shows the logical storage of Hudi.
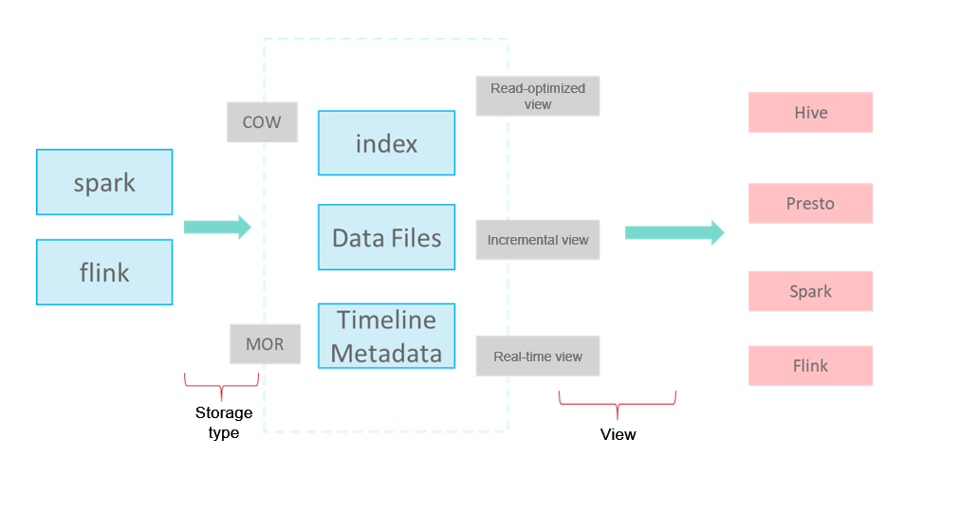
- Write Mode
COW: copy-on-write, applicable to scenarios with few updates.
MOR: replication on read. For UPDATE & DELETE, delta log files are written incrementally. During analysis, base and delta log files are compacted asynchronously.
- Storage Format
index: index of the primary key. The default value is bloomfilter at the file group level.
data files: base file + delta log file (for updating and deleting base files)
timeline metadata: manages version logs.
- Views
Read-optimized view: reads the base file generated after compaction. The reading of data that is not compacted has some latency (efficient read).
Real-time view: reads the latest data. The base file and delta file are combined during the read (frequent updates).
Incremental view: reads the incremental data written to Hudi, similar to CDC (stream and batch integration).
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





