Viewing the Plan Change History
When a plan changes, the historical plan of the query statement cannot be quickly detected from the current DFX-related system catalog and system view. As a result, the slow query analysis caused by the plan change becomes complex, and the plan cannot be quickly rolled back to a better plan (fast rollback). Currently, the SPM supports plan capture. This feature is enhanced to record historical plans and provide APIs for fast plan rollback, improving the usability of the SPM.
Description
Currently, GaussDB has slow query views and basic SPM capabilities. However, when a plan change occurs, a history of an execution plan of a non-slow query cannot be recorded. In this case, this feature aims to record historical execution plans based on the SPM to improve the usability of the SPM. Currently, the SPM supports only the generic plan. Therefore, the plan type managed in this requirement is limited to the generic plan.
The following are two main situations for the current plan change:
- The optimizer generates different execution plans for the same query and finally selects the new plan.
- The optimizer switches between historical plans each time it is executed.
The two events are both referred to as change events.
This feature involves two parts: fast detection and fast recovery of plan changes. The following briefly describes these two parts:
- Fast detection
To implement full plan change history, the most direct method is to record the difference between each execution plan and the last execution plan. This method causes a large performance overhead. Therefore, this feature records change events in the following scenarios to ensure performance and resource usage:
- The optimizer generates a new plan that does not exist in the SPM baseline.
- The optimizer generates an old plan that exists in the SPM baseline but has not been executed for a period of time.
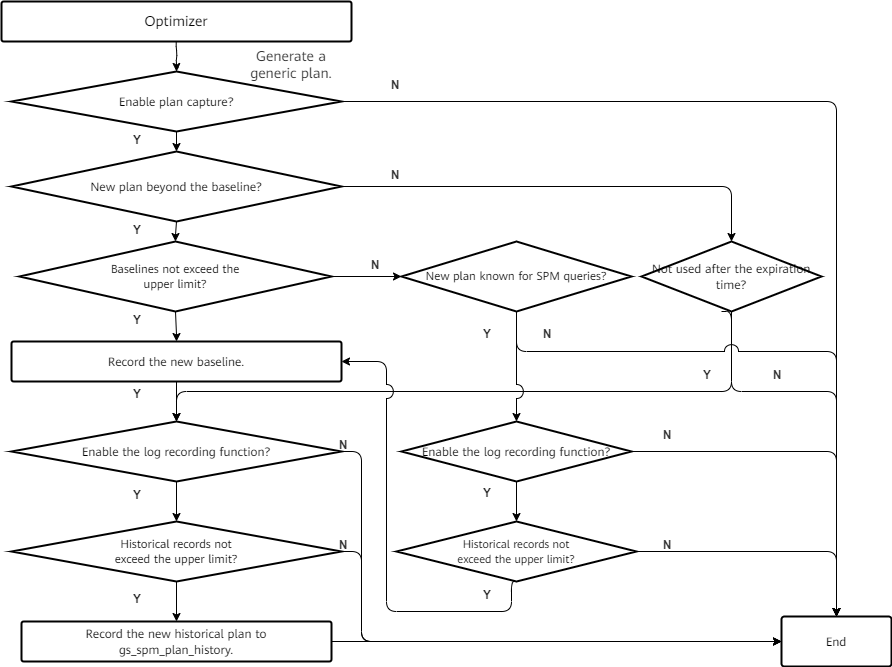
Figure 1 shows the execution process.
To use this feature, ensure that the GUC parameter spm_enable_plan_capture is set to STORE and the change history recording function spm_enable_plan_history_logging is enabled.
According to Figure 1, the change events caused by new plans are recorded except in the following cases:
- Scenario 1: If the number of captured baselines exceeds the upper limit (spm_plan_capture_max_plannum), check whether the current plan is a new plan captured by the SPM. If spm_enable_plan_history_logging is enabled and the number of historical records does not exceed the upper limit, extra baseline capture is performed and historical records are recorded.
- Scenario 2: If the number of currently recorded change events exceeds the upper limit (spm_plan_capture_max_plannum), historical records are not generated.
To ensure that more historical records can be recorded during long-term running, the SPM sets a scheduled task to clear historical records every 24 hours after the database is started. The SPM checks the percentage of the current historical records to the maximum number. If the percentage exceeds the threshold, the SPM deletes historical records, the oldest historical records are deleted to ensure that the number of records is less than the percentage specified by spm_plan_history_reserved_percentage.
- Fast recovery
When a plan change occurs, you can set the baseline status of a plan at a historical time point to ACC or FIXED, and then select the function spm_enable_plan_selection to roll back the plan to the historical plan. In this way, the plan can be fixed quickly.
Examples
The following describes two scenarios: fast detection and fast rollback.
- Fast detection of the change history
-- 0. Modify database parameters. gaussdb=#SET plan_cache_mode = 'force_generic_plan'; gaussdb=#SET explain_perf_mode = pretty; gaussdb=#DEALLOCATE ALL; -- 1. Create a table. gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE test_spm_perception_t1(a int,b int, c int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO test_spm_perception_t1 SELECT a, (random()*200)::int, (random()*10000)::int FROM (SELECT generate_series(1,10000) a) test_spm_perception_t1; gaussdb=#ANALYZE test_spm_perception_t1; -- 2. Capture seq scan and plan change. gaussdb=#SET spm_enable_plan_capture = STORE; gaussdb=#SET spm_enable_plan_history_logging = ON; gaussdb=#PREPARE p_seq AS SELECT * FROM test_spm_perceptiON_t1 WHERE a = $1; gaussdb=#EXPLAIN(costs OFF) EXECUTE p_seq(1); -- 3. View the baseline and change history. gaussdb=#\x gaussdb=#SELECT sql_namespace, sql_hash, plan_hash, outline, source, status, user, creation_time, last_used_time, modification_time FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring); -[ RECORD 1 ]-----+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- sql_namespace | 16782 sql_hash | 812490094 plan_hash | 1950233227 outline | begin_outline_data | TableScan(@"sel$1" test_spm_gplan_change_perception.test_spm_perception_t1@"sel$1") | version("1.0.0") | end_outline_data source | STORE status | 0 current_user | Mike creation_time | Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST last_used_time | Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST modification_time | Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_plan_history WHERE sql_hash IN (SELECT sql_hash FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring)); -[ RECORD 1 ]------+------------------------------------ sql_hash | 812490094 plan_hash | 1950233227 plan_hash_previous | 0 userid | 10 creation_time | Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM gs_spm_plan_history_detail WHERE sql_hash IN (SELECT sql_hash FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring)); -[ RECORD 1 ]----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- sql_hash | 812490094 plan_hash | 1950233227 plan_hash_previous | 0 unique_sql_id | 2670486394 outline | begin_outline_data | TableScan(@"sel$1" test_spm_gplan_change_perception.test_spm_perception_t1@"sel$1") | version("1.0.0") | end_outline_data status | UNACC gplan | t cost | 180 sql_text | select * from test_spm_perception_t1 where a = $1 param_num | 1 source | STORE userid | 10 baseline_creation_time | Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST history_creation_time | Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST modification_time | Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST gaussdb=#SELECT dbe_sql_util.gs_spm_get_plan_history(sql_hash, creation_time + 1) FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_plan_history WHERE sql_hash IN (SELECT sql_hash FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring)); -[ RECORD 1 ]-----------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- gs_spm_get_plan_history | (812490094,1950233227," begin_outline_data | TableScan(@""sel$1"" test_spm_gplan_change_perception.test_spm_perception_t1@""sel$1"") | version(""1.0.0"") | end_outline_data",UNACC,t,180,"select * from test_spm_perception_t1 where a = $1",1,STORE,10,"Mon Jan 13 06:04:22.614726 2025 PST",f) -- 4. Clean up the environment. gaussdb=#DROP TABLE test_spm_perception_t1; gaussdb=#RESET plan_cache_mode; gaussdb=#RESET explain_perf_mode; gaussdb=#RESET spm_enable_plan_capture; gaussdb=#RESET spm_enable_plan_history_logging;
- Quickly roll back a historical plan.
-- 0. Modify database parameters. gaussdb=#SET plan_cache_mode = 'force_generic_plan'; gaussdb=#SET explain_perf_mode = pretty; gaussdb=#DEALLOCATE ALL; -- 1. Create a table. gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE test_spm_rollback_t1(a int,b int, c int); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO test_spm_rollback_t1 SELECT a, (random()*200)::int, (random()*10000)::int FROM (SELECT generate_series(1,10000) a) test_spm_rollback_t1; gaussdb=#CREATE INDEX on test_spm_rollback_t1(a); gaussdb=#ANALYZE test_spm_rollback_t1; -- 2. Capture seq scan and plan change. gaussdb=#SET enable_indexscan = OFF; gaussdb=#SET enable_bitmapscan = OFF; gaussdb=#SET spm_enable_plan_capture = STORE; gaussdb=#SET spm_enable_plan_history_logging = ON; gaussdb=#PREPARE p_seq AS SELECT * FROM test_spm_rollback_t1 WHERE a = $1; gaussdb=#EXPLAIN(costs OFF) EXECUTE p_seq(1); id | operation ----+-------------------------------------- 1 | -> Seq Scan on test_spm_rollback_t1 (1 row) Predicate Information (identified by plan id) ----------------------------------------------- 1 --Seq Scan on test_spm_rollback_t1 Filter: (a = $1) (2 rows) -- 3. View the baseline and change history. gaussdb=#\x gaussdb=#SELECT sql_namespace, sql_hash, plan_hash, outline, source, status, user, creation_time, last_used_time, modification_time FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring); -[ RECORD 1 ]-----+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- sql_namespace | 16782 sql_hash | 2903888774 plan_hash | 602237302 outline | begin_outline_data | TableScan(@"sel$1" test_spm_gplan_change_rollback.test_spm_rollback_t1@"sel$1") | version("1.0.0") | end_outline_data source | STORE status | 0 current_user | Mike creation_time | Tue Jan 14 06:38:14.314703 2025 PST last_used_time | Tue Jan 14 06:38:14.314703 2025 PST modification_time | Tue Jan 14 06:38:14.314703 2025 PST gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_plan_history WHERE sql_hash in (SELECT sql_hash FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring)); -[ RECORD 1 ]------+------------------------------------ sql_hash | 2903888774 plan_hash | 602237302 plan_hash_previous | 0 userid | 10 creation_time | Tue Jan 14 06:38:14.314703 2025 PST -- 4. Set the baseline of the historical plan to ACC. gaussdb=#SELECT dbe_sql_util.gs_spm_accept_historical_plan(sql_hash, creation_time + 1, 'ACC') FROM gs_spm_plan_history WHERE sql_hash in (SELECT sql_hash FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring)); gs_spm_accept_historical_plan ------------------------------- 602237302 (1 row) gaussdb=#SELECT sql_namespace, sql_hash, plan_hash, outline, source, status, user, creation_time, last_used_time, modification_time FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_baseline WHERE sql_namespace = get_schema_oid(CURRENT_SCHEMA::cstring); -[ RECORD 1 ]-----+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- sql_namespace | 16782 sql_hash | 2903888774 plan_hash | 602237302 outline | begin_outline_data | TableScan(@"sel$1" test_spm_gplan_change_rollback.test_spm_rollback_t1@"sel$1") | version("1.0.0") | end_outline_data source | STORE status | 1 current_user | Mike creation_time | Tue Jan 14 06:38:14.314703 2025 PST last_used_time | Tue Jan 14 06:38:14.314703 2025 PST modification_time | Tue Jan 14 06:38:14.314703 2025 PST -- 5. Open the plan selection page to quickly roll back to seq scan. gaussdb=#SET spm_enable_plan_history_logging = OFF; gaussdb=#RESET enable_indexscan; gaussdb=#RESET enable_bitmapscan; gaussdb=#DEALLOCATE ALL; gaussdb=#PREPARE p_seq AS SELECT * FROM test_spm_rollback_t1 WHERE a = $1; gaussdb=#EXPLAIN (costs OFF) EXECUTE p_seq(1); id | operation ----+------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | -> Index Scan using test_spm_rollback_t1_a_idx on test_spm_rollback_t1 (1 row) Predicate Information (identified by plan id) --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 --Index Scan using test_spm_rollback_t1_a_idx on test_spm_rollback_t1 Index Cond: (a = $1) (2 rows) gaussdb=#SET spm_enable_plan_selection = ON; gaussdb=#EXPLAIN (costs OFF) EXECUTE p_seq(1); id | operation ----+-------------------------------------- 1 | -> Seq Scan on test_spm_rollback_t1 (1 row) ====== Query Others ===== -------------------------------------------------------------- use_baseline: Yes, sql_hash: 2903888774, plan_hash: 602237302 (1 row) -- 6. Clean up the environment. gaussdb=#DROP TABLE test_spm_rollback_t1; gaussdb=#RESET plan_cache_mode; gaussdb=#RESET explain_perf_mode; gaussdb=#RESET enable_indexscan; gaussdb=#RESET enable_bitmapscan; gaussdb=#RESET spm_enable_plan_capture; gaussdb=#RESET spm_enable_plan_history_logging;
Best Practices
You are advised to set spm_enable_plan_capture to STORE during off-peak hours to capture plans. After batch service execution is complete, set spm_enable_plan_history_logging to STORE to record historical changes.
When a plan change occurs, perform the following steps:
- Obtain unique_sql_id, for example, by using statement_history.
gaussdb=#SELECT unique_query_id FROM DBE_PERF.statement_history; - Obtain sql_hash from PG_CATALOG.GS_SPM_ID_HASH_JOIN based on unique_sql_id.
gaussdb=#SELECT sql_hash FROM PG_CATALOG.gs_spm_id_hash_join WHERE unique_sql_id = $unique_query_id; - Based on sql_hash and the time when the time change occurs, use the system function (DBE_SQL_UTIL.GS_SPM_GET_PLAN_HISTORY), view (PG_CATALOG.GS_SPM_PLAN_HISTORY_DETAIL) or system catalog (PG_CATALOG.GS_SPM_PLAN_HISTORY) to query the time change history.
gaussdb=#SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.gs_spm_plan_history WHERE sql_hash = $sql_hash; - After the plan that changes is locked, find plan_hash and use the system function (DBE_SQL_UTIL.GS_SPM_ACCEPT_HISTORICAL_PLAN) to receive the historical plan of the specified time, or directly use the system function (DBE_SQL_UTIL.GS_SPM_SET_PLAN_STATUS) to set the corresponding baseline status. The baseline status can be set to ACC or FIXED.
gaussdb=#SELECT dbe_sql_util.gs_spm_accept_historical_plan($sql_hash, $given_time, 'ACC'); - Enable spm_enable_plan_selection to quickly roll back the plan.
gaussdb=#SET spm_enable_plan_selection = ON;

- This feature supports only generic plans.
- The GUC parameters related to this feature include spm_enable_plan_history_logging, spm_enable_plan_history_logging_expired_time, and spm_plan_history_reserved_percentage.
- The GUC parameter spm_plan_history_reserved_percentage is added to specify the percentage of the number of records that can be written in gs_spm_plan_history.
- For quick detection and quick rollback, spm_enable_plan_capture is set to STORE and spm_enable_plan_history_logging is set to on.
- This feature aims to solve the plan change caused by the generation of a new plan. If the plan change is caused by the intelligent optimizer selecting the optimal plan from multiple existing plans, but it does not exceed the expiration time, the plan change is not caused by the generation of a new plan and is not supported by this feature.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot