Best Practices for Disaster Recovery
How Disaster Recovery Works
Disaster recovery (DR) works as follows:
- Log transmission: Logs are replicated from the primary instance to the standby instance (also referred to as the DR instance) using a streaming full/incremental build mechanism.
Figure 1 DR workflow diagram
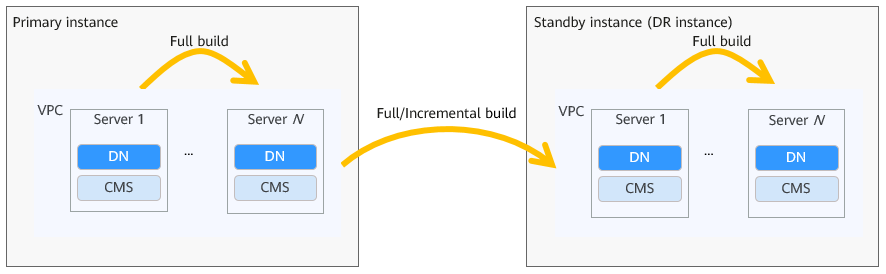
- Initial full data synchronization: The DR instance is initialized by restoring a full backup taken from the primary instance.
- Incremental log synchronization: Based on the log sequence number (LSN) provided by the full backup, the primary instance starts an archive thread that writes incremental logs to the data disk of the main standby node in the DR instance. The main standby node continuously reads logs from the disk and replays them in real time.
- Data consistency: The primary instance periodically creates consistency points (barriers). All nodes in the DR instance use these barriers to control log replay progress, ensuring recovery from one consistency point to the next.
Constraints
- DR is only supported for distributed instances in combined deployment, and the number of nodes in the primary instance must match that in the DR instance.
- When creating a DR relationship, the storage capacity of the DR instance must be greater than or equal to that of the primary instance. If the data in the primary instance exceeds the capacity of the DR instance, the DR instance will become abnormal due to insufficient space.
- The primary and DR instances in a DR relationship must run the same DB engine version (V2.0-2.0 or later).
- When creating the primary and DR instances, their Table Names in M-compatible Databases configuration must be the same. By default, this parameter is set to Case-sensitive. If the settings differ between the primary and DR instances, the DR relationship cannot be created.
- When Replica Consistency Protocol is set to Paxos, only instances in the 1 primary + 1 standby + 1 log deployment model can create DR relationships.
- You can create a DR relationship only when both the primary and DR instances are in the Normal state. The DR relationship can be stopped from the primary instance only if the primary instance is in the Normal state and the DR instance has been promoted to primary.
- If the DR instance is in a state other than Normal or Degraded, it cannot be promoted to primary and cannot provide DR services. In this case, you must repair or rebuild the DR instance.
- After a DR relationship is created, the DR instance does not support full backup, incremental backup, and differential backup. Only the primary instance supports these backup types. If you want to restore data of the primary instance to itself, stop the DR relationship first. After the restoration is complete, re-create the DR relationship.
- Parameter changes cannot be synchronized between the primary and DR instances in a DR relationship.
- When data is restored from the primary instance to a new instance, the DR user is not automatically deleted. You must manually delete the DR user from the new instance.
- When switching the roles of the primary and DR instances, if the original primary instance breaks down, you must manually start the DR instance to restore it to a normal state and resume services.
Prerequisites
- A GaussDB instance has been created in each of the two regions, with one serving as the primary instance and the other as the DR instance. For details about how to create an instance, see Buying a GaussDB Instance.
- The VPCs in the two regions can communicate with each other. To enable this communication, submit a service ticket to Direct Connect to request the creation of a direct connection between the VPCs in both regions. Additionally, you have configured the firewall rules for your instances. The following tables describe the firewall rules for different instance types.
Table 1 Firewall rules for distributed instances Source Device
Source Port
Destination Port (Listening)
Protocol
Port Description
CNs of the primary and DR instances
1024–65535
Database CN port number + 1
Default: 8001
TCP
Port for the CN of the DR instance to communicate with the CN of the primary instance.
Main standby DN and cascaded standby DNs in the DR instance
1024–65535
Database DN port number + 1
Default: {40001, 40021, 40041, ..., 40001 + (n – 1) x 20} (n indicates the number of database shards.)
TCP
Port for the DNs of the DR instance to communicate with the DNs of the primary instance.
Primary and standby DNs
1024–65535
Database DN port number + 5
Default: {40005, 40025, 40045, ..., 40005 + (n – 1) x 20} (n indicates the number of database shards.)
TCP
Port for heartbeat connection requests between the primary and DR instances.
DNs of the primary and DR instances
1024–65535
12016
TCP
Port for communication between the Agents on the primary and DR instances.
Ping-based connectivity check
/
/
ICMP
Used for checking connectivity between the primary and DR instances.
Table 2 Firewall rules for centralized instances (using the Quorum protocol) Source Device
Source Port
Destination Port (Listening)
Protocol
Port Description
Main standby DN and cascaded standby DNs in the DR instance
1024–65535
Database DN port number + 1
Default: 8001
TCP
Port for the DNs of the DR instance to communicate with the DNs of the primary instance.
Primary and standby DNs
1024–65535
Database DN port number + 5
Default: 8005
TCP
Port for heartbeat connection requests between the primary and DR instances.
DNs of the primary and DR instances
1024–65535
12016
TCP
Port for communication between the Agents on the primary and DR instances.
Ping-based connectivity check
/
/
ICMP
Used for checking connectivity between the primary and DR instances.
Table 3 Firewall rules for centralized instances (using the Paxos protocol) Source Device
Source Port
Destination Port (Listening)
Protocol
Port Description
Primary and standby DNs
1024–65535
Database DN port number + 6
Default: 8006
TCP
Port for cascaded standby DNs of the DR instance to connect to the main standby DN to synchronize data in the streaming replication-based remote DR solution, and port for heartbeat connection requests between the primary and standby DNs.
DNs of the primary and DR instances
1024–65535
12016
TCP
Port for communication between the Agents on the primary and DR instances.
Ping-based connectivity check
/
/
ICMP
Used for checking connectivity between the primary and DR instances.
Creating a DR Relationship
- Log in to the management console.
- Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose .
in the upper left corner of the page and choose . - Click
 in the upper left corner and select the region where the primary instance is located.
in the upper left corner and select the region where the primary instance is located. - On the Instances page, click the name of the primary instance to go to the Basic Information page. In the Network Information area, locate the Subnet field to obtain the CIDR block of the primary instance.
Figure 2 CIDR block of the primary instance

- Click
 in the upper left corner and select the region where the DR instance is located.
in the upper left corner and select the region where the DR instance is located. - On the Instances page, click the DR instance name to go to the Basic Information page. In the Configuration area, locate the DR IP Address field to obtain the DR IP address of the DR instance. In the Network Information area, locate the Subnet field to obtain its CIDR block.
Figure 3 DR IP address and CIDR block of the DR instance

- On the Basic Information page of the DR instance, go to the Configuration area. In the DR IP Address field, click Reset Configuration. In the displayed dialog box, enter the CIDR block of the primary instance obtained in 4, and click OK.
- On the Basic Information page of the primary instance, go to the Configuration area. In the DR IP Address field, click Reset Configuration. In the displayed dialog box, enter the CIDR block of the DR instance obtained in 6, and click OK.
- Go to the Instances page in the console of the primary instance. In the navigation pane on the left, choose Disaster Recovery. On the displayed page, click Create DR Relationship.
- Configure required parameters and select the confirmation information.
Table 4 Parameters for creating a DR relationship Parameter
Description
DR Type
Type of the disaster recovery.
Only streaming DR is supported.
Primary Instance
Instance for which the DR relationship is created.
DR Instance IP Address
You can obtain the DR IP address from the Basic Information page of the DR instance. For details, see 6.
DR Instance DB User
DB user of the DR instance, which is used to authenticate the primary and DR instances during DR. The default username is root.
DR Instance User Password
Administrator password of the DR instance.
- Click OK to submit the request. To check the task status, go to the Disaster Recovery page. If the task status is Available, the DR relationship is established.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





