Graph Keywords
|
Parameter |
Description |
Mandatory (M) or Optional (O) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
graph_id |
- |
Graph ID, which is a positive integer |
O |
|
priority |
- |
Priority, which does not need to be adjusted |
O |
|
device_id |
- |
Device ID. Different graphs can run on one or more chips or on the chips of different PCIe cards. If they run on different chips, the device_id field has to be added to the graph configuration file to specify the device ID on which the graphs are running. If device_id is not specified, the graphs are running on the chips of device 0 by default. The value of device id ranges from 0 to N-1 (N indicates the number of devices). |
O |
|
engines
NOTE:
You are advised to configure multiple engines for multi-channel decoding. One engine corresponds to one thread. If one engine corresponds to multiple threads, the sequence cannot be ensured during decoding. |
id |
Engine ID |
M |
|
engine_name |
Engine name |
M |
|
|
side |
Target for the engine to run. The value can be HOST or DEVICE, which is determined based on service requirements. |
M |
|
|
so_name |
During engine running, you need to copy the dynamic library file in .so format from the host to the device. If FrameworkerEngine running depends on a third-party library file or user-defined library file, the dependent .so file must be configured in the graph file. (Replace xxx in the following example with the actual name of the dependent library.) so_name: "./libFrameworkerEngine.so" so_name: "./libxxx.so" so_name: "./libxxx.so" |
O |
|
|
thread_num |
Number of threads. You are advised to set this parameter to 1 for multi-channel decoding. If the value of thread_num is greater than 1, the decoding sequence of threads cannot be ensured. |
M |
|
|
thread_priority |
Thread priority. The value ranges from 1 to 99. This parameter is used to set the priority of the data processing thread corresponding to the engine. A higher priority is configured for the corresponding engine according to the SCHED_RR scheduling policy. |
O |
|
|
queue_size |
Queue size. The default value is 200. The parameter value needs to be adjusted based on the service load fluctuation, size of data received by the engine, and system memory. |
O |
|
|
ai_config |
Configuration example:
ai_config{
items{
name: "model_path"
value: "./test_data/model/resnet18.om"
}
}
|
O |
|
|
ai_model |
Configuration example:
ai_model{
name: "" // model name
type:"" // model type
version:"" // model version
size:"" // model size
path:"" // model path
sub_path:"" // auxiliary model path
key:"" // model key
sub_key: "" // auxiliary model key
frequency:"UNSET" // device frequency. Value UNSET or 0 indicates that the setting is canceled. Value LOW or 1 indicates low frequency. Value MEDIUM or 2 indicates medium frequency. Value HIGH or 3 indicates high frequency.
device_frameworktype:"NPU" // type of the device on which a model is running. The value is NPU, IPU, MLU, or CPU.
framework: "OFFLINE" // execution framework. The value is OFFLINE, CAFFE, or TENSORFLOW.
}
|
O |
|
|
oam_config |
Mode of dumping algorithm data. If the inference is inaccurate, you can view the algorithm execution results of some or all layers.
Configuration example:
oam_config{
items{
model_name: "" // relative path+model name+suffix
is_dump_all: "" // whether to dump all data. The value is true or false.
layer: "" // layer
}
dump_path:"" // dump path
}
|
O |
|
|
internal_so_name |
Dynamic library file embedded on the device. You can directly use the file without copying it from the host to the device. |
O |
|
|
wait_inputdata_max_time |
Maximum timeout of waiting for the next piece of data after the current data is received
|
O |
|
|
is_repeat_timeout_flag |
Whether to perform cyclic timeout processing (wakeup) when the engine does not receive data. This parameter is used together with wait_inputdata_max_time. The options are as follows:
|
O |
|
|
holdModelFileFlag |
Whether to retain the model file of the engine. The options are as follows:
|
O |
|
|
connects |
src_engine_id |
ID of the source engine |
M |
|
src_port_id |
Sending port number of the source engine. The port number starts from 0. The number of ports is defined by the HIAI_DEFINE_PROCESS macro in the corresponding header file. The implementation code is as follows: #define SOURCE_ENGINE_INPUT_SIZE 1
#define SOURCE_ENGINE_OUTPUT_SIZE 1
class SrcEngine : public Engine {
HIAI_DEFINE_PROCESS(SOURCE_ENGINE_INPUT_SIZE, SOURCE_ENGINE_OUTPUT_SIZE)
} |
M |
|
|
target_engine_id |
ID of the target engine |
M |
|
|
target_port_id |
Receive port number of the target engine |
M |
|
|
target_graph_id |
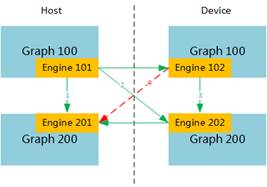
ID of the target graph. Engines can be connected across graphs. In this scenario, the target_graph_id field needs to be added to the connection configuration file to indicate the graph ID at the receive end. If target_graph_id is not specified, engines are connected within the same graph by default. When multiple Ascend 310 chips are available, you can enable models to run on different Ascend 310 chips by connecting engines across graphs. Therefore, you are advised to place the same type of models on the same chip for inference, which avoids unnecessary memory consumption. Scenario description:
|
O |
|
|
receive_memory_without_dvpp |
|
O |
|
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot