Configuring a Same-Region Backup Policy
Scenarios
When you create an RDS instance, an automated backup policy is enabled by default. For security purposes, the automated backup policy cannot be disabled. After the DB instance is created, you can customize the automated backup policy as required and then RDS backs up data based on the automated backup policy you configure.
RDS backs up data at the DB instance level, rather than the database level. If a database is faulty or data is damaged, you can restore it from backups. Backups are saved as packages in OBS buckets to ensure data confidentiality and durability. Since backing up data affects database read and write performance, the automated backup time window should be set to off-peak hours.
After an automated backup policy is configured, full backups are created based on the time window and backup cycle specified in the policy. The time required for creating a backup depends on how much data there is in the instance. Backups are stored for as long as you specified in the backup policy.
You do not need to set an interval for incremental backup because RDS automatically backs up incremental data every 5 minutes or when a certain amount of incremental data is generated. Incremental backups can be used to restore data to a specific point in time.
Video Tutorial
Differences Between Standard Backup and Sparse Backup
|
Item |
Standard Backup |
Sparse Backup |
|---|---|---|
|
Function description |
RDS for MySQL uses standard backup by default. Standard backup backs up all instance data based on the specified time window and backup cycle. A backup file is generated each time a backup is complete, and is stored for the retention period you set. |
If you want to retain backups for a long time, you can enable sparse backup to reduce costs. Compared with the default backup policy, sparse backup reduces the backup frequency while maintaining the same retention period for the backups. To enable sparse backup, submit a service ticket to request required permissions. After sparse backup is enabled, a standard backup policy is displayed by default. You can add sparse backup policies as needed. |
|
Number of backup policies |
An instance has only one backup policy, which cannot be deleted. The default policy is weekly backup. Select at least one day in a week. The backups can be retained for 1 to 732 days. |
The default policy cannot be deleted, but the manually added sparse backup policies can be deleted. After enabling sparse backup, you can also add sparse backup policies alongside the default backup policy.
|
|
Time window |
A one-hour period the backup will be scheduled within 24 hours, such as 01:00-02:00 or 12:00-13:00 |
A one-hour period the backup will be scheduled within 24 hours, such as 01:00-02:00 or 12:00-13:00 |
|
CBR backup |
Supported |
Supported |
Constraints
- For primary/standby instances, if the standby instance is faulty or the replication delay of the standby instance exceeds one day, backups will be performed on the primary instance.
- When you delete a DB instance, its automated backups are also deleted but its manual backups are retained.
- Rebooting the instance is not allowed during full backup. Exercise caution when selecting a backup time window.
- The system verifies the connection to the DB instance when starting a full backup task. If either of the following conditions is met, the verification fails and a retry is automatically performed. If the retry fails, the backup will fail.
- DDL operations are being performed on the DB instance.
- The backup lock failed to be obtained from the DB instance.
- Performing a full backup may decrease instance throughput and increase replication delay because it occupies node resources, especially disk bandwidth.
- CBR backups depend on the Cloud Backup and Recovery (CBR) service. For details, see What Is CBR?
- Enabling CBR backup will incur fees. CBR backups are billed by actual vault usage, which is calculated by CBR.
- The backup time is proportional to how much data your instance has. Too much data can decrease the backup efficiency. If you have large amounts of data and want to speed up the backup process, submit a service ticket to enable CBR snapshot backup.
- After CBR is enabled, snapshot backup is used. Existing automated and manual backups can still be used to restore data.
- When you delete a DB instance, its automated backups are also deleted but its manual backups are retained.
- DDL operations cannot be performed when a CBR snapshot is being created. If a DDL operation is being performed, a snapshot will be created after the DDL operation is complete.
- After CBR is enabled, the next full backup is a snapshot backup. You can use the snapshot backup to restore data.
Billing
Backups are saved as packages in OBS buckets. For the billing details, see How Is RDS Backup Data Billed?
After CBR is enabled, the free backup space is unavailable. You are billed for database server backup vaults on a pay-per-use basis. For details, see How Is CBR Billed?
Procedure
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the target instance name.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Backups & Restorations.
- In the upper right corner of the page, choose Modify Backup Policy > Configure Same-Region Backup Policy. On the displayed page, you can view the existing backup policy. If you want to modify the policy, adjust the values of the following parameters:
Figure 1 Modifying a backup policy
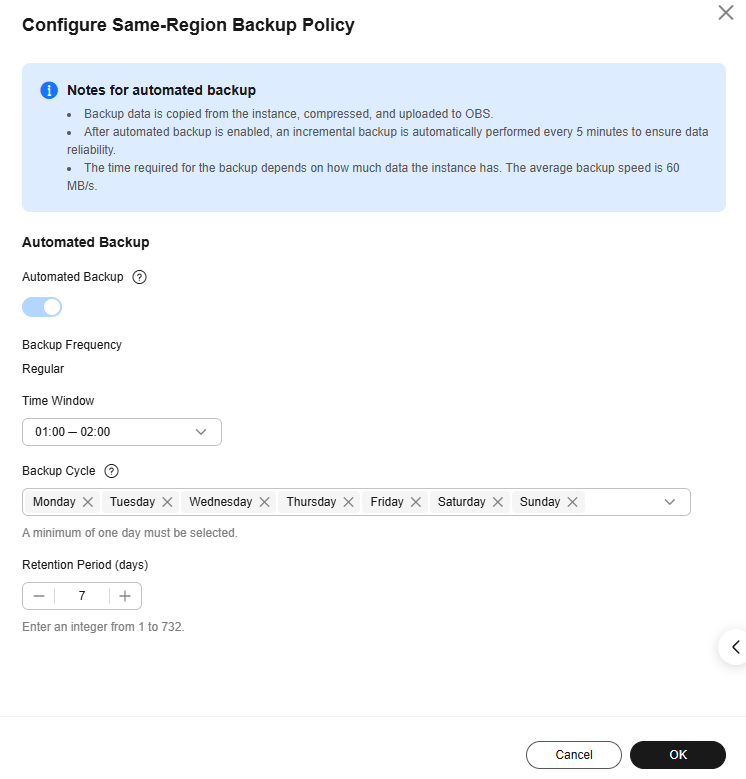
- Retention Period: How many days your automated full backups and binlog backups can be retained. The retention period is from 1 to 732 days and the default value is 7.
- Extending the retention period improves data reliability.
- Reducing the retention period takes effect for existing backups. Any backups (except manual backups) that have expired will be automatically deleted. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
Policy for automatically deleting automated full backups:
To ensure data integrity, even after the retention period expires, the most recent backup will be retained, for example, if Backup Cycle was set to Monday and Tuesday and Retention Period was set to 2:
- The full backup generated on Monday will be automatically deleted on Thursday because:
The backup generated on Monday expires on Wednesday, but it is the last backup, so it will be retained until a new backup expires. The next backup will be generated on Tuesday and will expire on Thursday. So the full backup generated on Monday will not be automatically deleted until Thursday.
- The full backup generated on Tuesday will be automatically deleted on the following Wednesday because:
The backup generated on Tuesday will expire on Thursday, but as it is the last backup, so it will be retained until a new backup expires. The next backup will be generated the next Monday and will expire on the next Wednesday. So the full backup generated on Tuesday will not be automatically deleted until the next Wednesday.
- Time Window: A one-hour period the backup will be scheduled for each day, such as 01:00-02:00 or 12:00-13:00. The backup time window indicates when the backup starts. The backup duration depends on the data volume of your instance.

To minimize the potential impact on services, set the time window to off-peak hours. The backup time window is saved in the UTC time zone of the local browser. It changes with the time zone during the switch between the DST and standard time.
- Backup Cycle: Daily backups are selected by default, but you can change it. At least one day must be selected.
- Retention Period: How many days your automated full backups and binlog backups can be retained. The retention period is from 1 to 732 days and the default value is 7.
- Click OK.
To use this function, submit a service ticket to request required permissions.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the target instance name.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Backups & Restorations.
- In the upper right corner of the page, choose Modify Backup Policy > Configure Same-Region Backup Policy. You can see the configured backup policy. To modify the backup policy, adjust the parameter values as needed.
Figure 2 Configuring a sparse backup policy
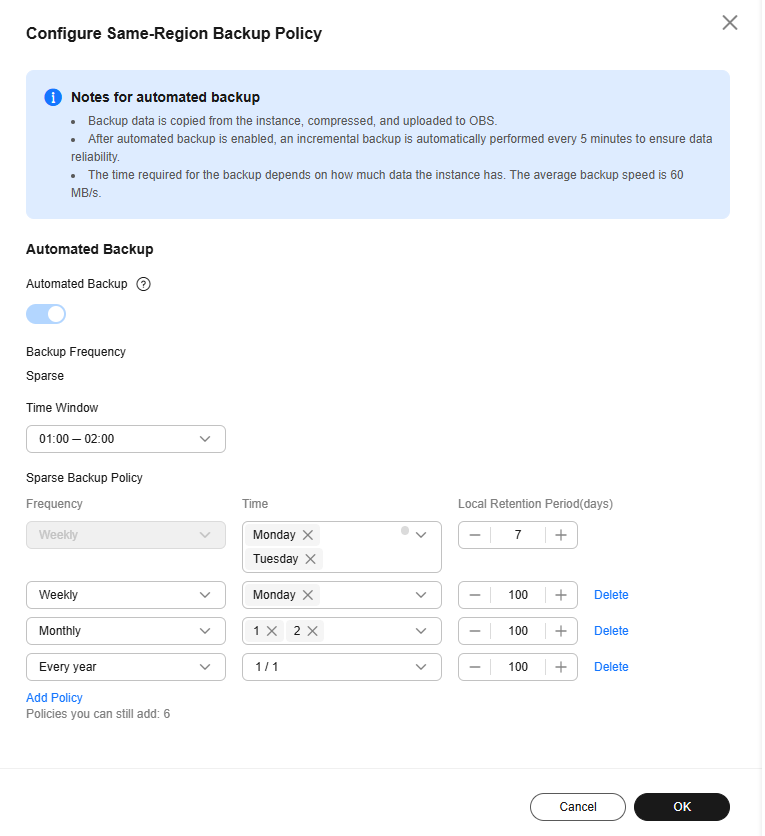
- Time Window: Set it to a one-hour period the backup will be scheduled for each day, such as 01:00-02:00 or 12:00-13:00. The backup time window indicates when the backup starts. The backup duration depends on the data volume of your instance.

To minimize the potential impact on services, set the time window to off-peak hours. The backup time window is saved in the UTC time zone of the local browser. It changes with the time zone during the switch between the DST and standard time.
- Sparse Backup Policy
The default backup policy is weekly backup. Select at least one day in a week. The backups can be retained for 1 to 732 days.
You can add more backup policies to back up data by week, month, or year.Table 2 Configuring sparse backup policies Frequency
Time
Retention Period
Every week
Select at least one day in a week.
The retention period is the number of days for storing full automated backups and binlog backups. It can be set to 1 to 732 days.- Extending the retention period improves data reliability.
- Reducing the retention period takes effect for existing backups. Any backups (except manual backups) that have expired will be automatically deleted. Exercise caution when performing this operation.
Every month
Select at least one day in a month.
Every year
Select a specific day in a year.
- If multiple sparse backup policies need to create backups on the same day, the system generates only one backup on that day and retains the backup based on the longest retention period.
- After sparse backup policies are configured, if no backup is generated in the specified backup window of a day (the backup conflicts with other operations or the backup fails), the backup will be skipped.
- If sparse backup policies are deleted and the backups that have been generated cannot match any existing policy, they will still be kept for the original retention period.
- Time Window: Set it to a one-hour period the backup will be scheduled for each day, such as 01:00-02:00 or 12:00-13:00. The backup time window indicates when the backup starts. The backup duration depends on the data volume of your instance.
- Click OK.
FAQ
- Why Has Automated Backup of My RDS Instance Failed?
- Q: How Do I Clear Automated Backups?
A: Automated backups cannot be manually deleted. To delete them, you can adjust the retention period specified in your automated backup policy. Retained backups will be automatically deleted at the end of the retention period.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





