Setting a Local Retention Period for RDS for MySQL Binlogs
Scenarios
RDS for MySQL deletes local binlogs after they are backed up to OBS. You can set the local retention period for binlogs as required.
In addition to the retention period, you can also configure other items such as the maximum storage space usage, maximum number of files to be retained, and automatic storage space protection. To use these items, submit a service ticket to request required permissions.
Constraints
- Binary logging is enabled for RDS by default and uses row-based logging.
- On the RDS console, you can set the binlog retention period only for the primary instance. The binlog retention period for read replicas is the same as that of the primary instance.
- If there are abnormal read replicas or standby instances, local binlogs will not be cleared. This prevents replication failures on the read replicas or standby instances.
- If the retention period is set to 0, the binlogs of your DB instance will be deleted once they are synchronized to the standby instance and read replicas and successfully backed up to OBS. If the retention period is set to a value greater than 0, for example, 1, the binlogs will be retained for one day after they are synchronized to the standby instance and read replicas from the primary instance and successfully backed up to OBS. After the retention period expires, the binlogs will be automatically deleted. For details about how to view binlogs, see Downloading a Binlog Backup.
- The binlog retention period is measured in hours on the console. However, the values of expire_logs_days (MySQL 5.7) and binlog_expire_logs_seconds (MySQL 8.0) are measured in days when you query the binlog retention period by running a command, which cannot be used as a reference. To check how long the binlogs can be retained, view the binlog retention period on the console.
Differences Between Local Binlogs and Binlog Backups
|
Item |
Local Binlogs |
Binlog Backups |
|---|---|---|
|
Overview |
Local binlogs are used to set up a primary/standby architecture and subscribe to data. |
RDS automatically backs up data modifications made after the most recent full or incremental backup every 5 minutes or when a certain amount of incremental data is generated. You can use binlog backups to restore instance data to a point in time. |
|
Status |
This function is enabled by default and cannot be disabled. The default retention period is 0, which means that local binlogs will be deleted upon they are backed up. For details about how to customize the retention period, see Procedure. |
This function is enabled by default and cannot be disabled. |
|
Billing |
N/A |
If the free space RDS provides is used up, the additional space required will be billed. For the billing details, see How Is RDS Backup Data Billed? |
|
Storage space |
Local binlogs occupy the storage space of your instance. You can view the storage space occupied by binlogs on the DBA Assistant page. For details, see Managing Storage Capacity. |
Binlog backups do not occupy the storage space of your instance. Backups are saved as packages in OBS buckets. They occupy the OBS backup space. To query data in a backup, see Downloading a Binlog Backup. |
Procedure
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region.
in the upper left corner and select a region. - Click
 in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service.
in the upper left corner of the page and choose Databases > Relational Database Service. - On the Instances page, click the target instance name to go to the Summary page.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Backups & Restorations. On the Binlog Backups page, click Set Binlog Retention Period.
- In the displayed dialog box, set required parameters and click OK.
Figure 1 Setting the binlog retention period (default settings)
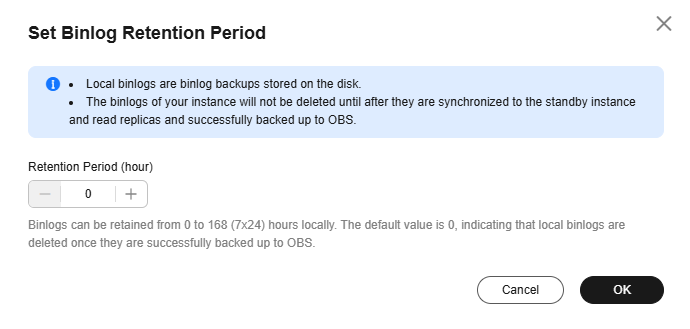 Figure 2 Setting the binlog retention period (advanced settings)
Figure 2 Setting the binlog retention period (advanced settings)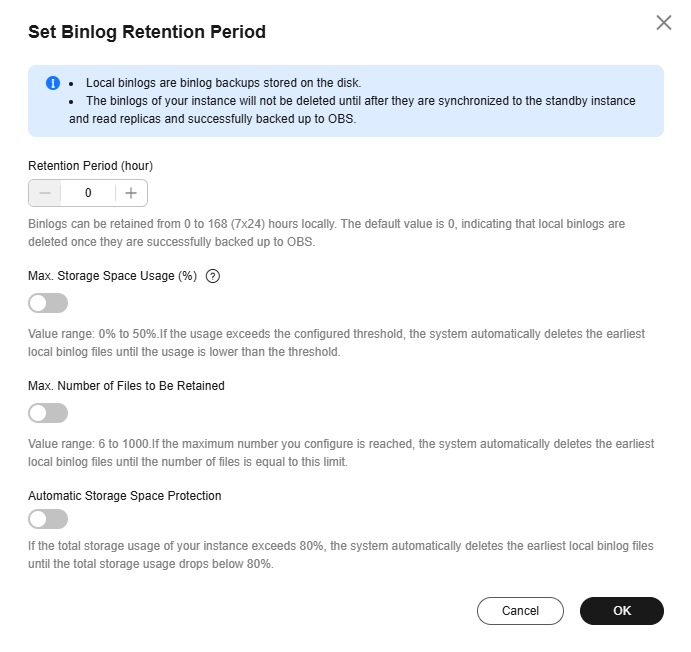
Table 2 Parameter description Parameter
Description
Retention Period (hour)
The value range is from 0 to 168 (7 x 24). The default value is 0, indicating that local binlogs will be deleted once they are backed up to OBS.
Max. Storage Space Usage (%)
Storage usage = Size of local binlog files/Total storage of the instance
The value range is from 0 to 50. If the usage exceeds the configured threshold, the system automatically deletes the earliest local binlog files until the usage is lower than the threshold.
Max. Number of Files to Be Retained
The value range is from 6 to 1000. If the maximum number you configure is reached, the system automatically deletes the earliest local binlog files until the number of files is equal to this limit.
Automatic Storage Space Protection
If the total storage usage of your instance exceeds 80%, the system automatically deletes the earliest local binlog files until the total storage usage drops below 80%.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





