Modifying HBase Parameters to Optimize Cluster Performance
Scenario
A CloudTable HBase cluster has many HBase parameters related to read/write performance. You can modify the HBase parameters to tune cluster performance under different read/write request loads. You need to restart the cluster to make changes take effect.
Constraints
- Restart the CloudTable HBase cluster after parameter configuration modification. Otherwise, services will be interrupted.
- Do not modify cluster parameters when the CloudTable HBase cluster is being restarted.
Prerequisites
No task is running in the cluster.
Procedure
- Log in to the CloudTable console.
- Select a region in the upper left corner.
- In the navigation pane, click Cluster Management.
- Click the name of a cluster for which you want to modify HBase parameters to access the cluster details page.
- In the Parameter Configuration area, click the Parameter Configuration tab to modify HBase parameters.
For details about the HBase parameters you can modify, see HBase Parameters.
- Select the target parameter and click
 in the Value column.
in the Value column. - Enter a new value in the text box, and then click
 . The parameter value has been successfully changed if the system prompts "The parameter changed to xx successfully. Save the modified value." The new parameter value is marked with a red asterisk (*).
. The parameter value has been successfully changed if the system prompts "The parameter changed to xx successfully. Save the modified value." The new parameter value is marked with a red asterisk (*).
If you want to cancel it, click
 .Figure 1 Modifying HBase parameters
.Figure 1 Modifying HBase parameters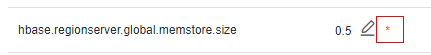
- Click Save Changes in the upper left corner above the parameter list. A dialog box is displayed.
- In the Save Changes dialog box, verify whether the parameter settings are correct. Select Restart the cluster immediately and click OK.
Figure 2 Saving the modification
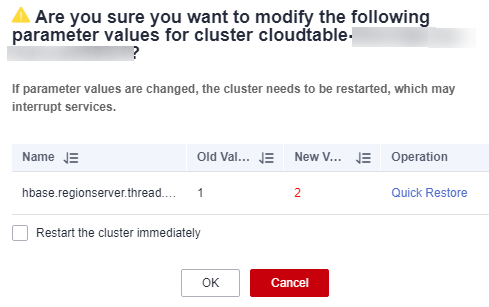
- After you select Restart the cluster immediately and click OK, the cluster restarts immediately. After the cluster restart is complete, the new parameter configurations take effect. Click
 above the parameter list. The system prompts "The new value is applied" in the upper right corner of the parameter list.
above the parameter list. The system prompts "The new value is applied" in the upper right corner of the parameter list. - If you do not select Restart the cluster immediately and click OK in the Save Changes dialog box, the system prompts "The new value is not applied" above the parameter list. In this case, you need to restart the cluster for the changes to take effect. For details about how to restart a cluster, see Restarting an HBase Cluster.
- If the new parameter value is incorrect, click Quick Restore to cancel the modification.
- After you select Restart the cluster immediately and click OK, the cluster restarts immediately. After the cluster restart is complete, the new parameter configurations take effect. Click
- Select the target parameter and click
- After modifying parameters, you can click the Change History tab to view the change history.
On the Change History tab page, you can view the following information.
- Name: Name of the changed parameter.
- Old Value: old parameter value
- New Value: new parameter value
- Modified: time when you modify a parameter value
HBase Parameters
Table 1 lists HBase parameters you can modify currently.
The sum of the values of hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size and hfile.block.cache.size cannot exceed 0.8.
|
Parameter |
Value Range |
Default Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
hbase.regionserver.thread.compaction.small |
[1,20] |
1 |
Indicates the number of HFile compaction threads. You can increase the parameter value in heavy-put-load scenarios. |
|
hbase.regionserver.global.memstore.size |
(0,0.8) |
0.4 |
It is recommended that you set this parameter to "hbase.hregion.memstore.flush.size x Number of regions with active writes/RegionServer GC -Xmx". The default value is 0.4, indicating that 40% of RegionServer GC -Xmx is used. |
|
hbase.hstore.blockingStoreFiles |
[1,2147483647] |
60 |
When the HFile number in the column cluster reaches this threshold, all operations in the region are blocked until the compaction is complete. You can increase the parameter value in heavy-put-load scenarios. |
|
hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period |
[1,2147483647] |
60000 |
A client and RegionServer parameter, indicating the scan lease period. It is recommended that you set this parameter to an integral multiple of 60,000 ms, and increase the parameter value in heavy-read-load scenarios. Unit: millisecond |
|
hfile.block.cache.size |
(0,0.8) |
0.2 |
Indicates the data cache percentage in the RegionServer GC -Xmx. You can increase the parameter value in heavy-read-load scenarios, in order to improve cache hit ratio and performance. The default value is 0.2, indicating that 20% of RegionServer GC -Xmx is used. |
|
hbase.regionserver.handler.count |
[1,300] |
100 |
Indicates the number of RPC server instances on the RegionServer. The recommended value ranges from 100 to 300. |
|
hbase.regionserver.metahandler.count |
[1,100] |
50 |
Indicates the number of program instances for processing prioritized requests. The recommended value ranges from 20 to 100. |
|
hbase.hstore.flusher.count |
[1,10] |
2 |
Indicates the number of memstore flush threads. You can increase the parameter value in heavy-put-load scenarios. |
|
hbase.ipc.server.callqueue.read.ratio |
[0,1] |
0.5 |
When used under different load models, it controls the ratio between the numbers of read and write RPC queues. The value ranges from 0 to 1.0, and the default value is 0.5.
|
|
hbase.regionserver.hotregion.handler.count |
[1,65535] |
66 |
Number of RPC listener instances started on RegionServers for hotspot regions. |
|
hbase.ipc.server.hotregion.max.callqueue.length |
[1,65535] |
330 |
Maximum length of the queue for RegionServers to process requests of hotspot regions. Upon receiving a new request, the system checks whether the length of the queue exceeds the threshold. If so, the request is discarded. |
|
hbase.metric.controller.analysis.period |
[1,2147483647] |
60 |
Hotspot analysis period of MetricController, in seconds. |
|
hbase.metric.controller.analysis.threads.max |
[1,100] |
10 |
Maximum number of threads for hotspot analysis in the thread pool. |
|
hbase.metric.controller.collect.threads.max |
[1,100] |
16 |
Maximum number of threads for hotspot analysis in the traffic collection thread pool. |
|
hbase.metric.regionserver.hotspot.threshold |
[1,2147483647] |
20000 |
Hotspot threshold of a RegionServer. Unit: requests per second. |
|
hbase.metric.region.hotspot.threshold |
[1,2147483647] |
10000 |
Hotspot threshold of a single region. Unit: requests per second. |
|
hbase.hotspot.enable |
[true,false] |
true |
Whether to enable hotspot self-healing. The value true means to enable it, and false means to disable it. After this function is enabled, access hotspots will be automatically processed. |
|
hbase.tries.cache.enabled |
[true,false] |
false |
If this parameter is set to true, LoudsTriesLruBlockCache is used to cache index blocks and data blocks. |
|
hbase.write.tries |
[true,false] |
false |
If this parameter is set to true, the succinct tries feature is enabled. In this case, a new data structure is used to improve the utilization of index blocks. |
|
hbase.hfile.hsync |
[true,false] |
false |
Specifies whether to enable the HFile durability to make data persistence on disks. If this parameter is set to true, the performance is affected because each Hfile file is synchronized to the disk. |
|
hbase.wal.hsync |
[true,false] |
false |
Specifies whether to enable WAL file durability to make the WAL data persistence on disks. If this parameter is set to true, the performance is affected because each WAL file is synchronized to the disk. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





