Parallel File System Overview
What Is Parallel File System?
Parallel File System, a sub-product of OBS, provides high-performance file systems for big data scenarios where OBS is used as the unified data lake storage. It features access latency in milliseconds, TB/s-level bandwidth, millions of IOPS, and high compatibility, performance, scalability, and reliability.
Different from the bucket structure, each directory in the access path of a parallel file system is independent. For example, /dir01/dir02/example.txt is a file and /dir01/ and /dir01/dir02/ are directories. In a hierarchical directory structure, you can rename a single directory. You do not need to list and modify all files with a specific directory prefix. This hierarchical structure makes the data organization of a parallel file system basically the same as that of Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). The big data analysis framework that uses HDFS as the data access layer can access data in a parallel file system through the OBSFileSystem plug-in (OBSA-HDFS). For details, see About PFS.
Performance
Every time when a volume created from a parallel file system is mounted to a workload, there will be a resident process at the backend for the volume. When a workload uses too many parallel file system volumes or reads and writes a large number of parallel file systems, resident processes will consume a significant amount of memory. Table 1 list the used memory in some scenarios. To ensure that the workload can run normally, the number of parallel file system volumes used depends on the requested memory. For example, if the workload requests 4 GiB of memory, the workload can have no more than 4 parallel file system volumes.
|
Test Item |
Used Memory (MiB) |
|---|---|
|
Long-term stable operation |
About 50 |
|
Concurrent write to a 10-MB file from two processes |
About 110 |
|
Concurrent write to a 10-MB file from four processes |
About 220 |
|
Write to a 100-GB file from a single process |
About 300 |
Prerequisites
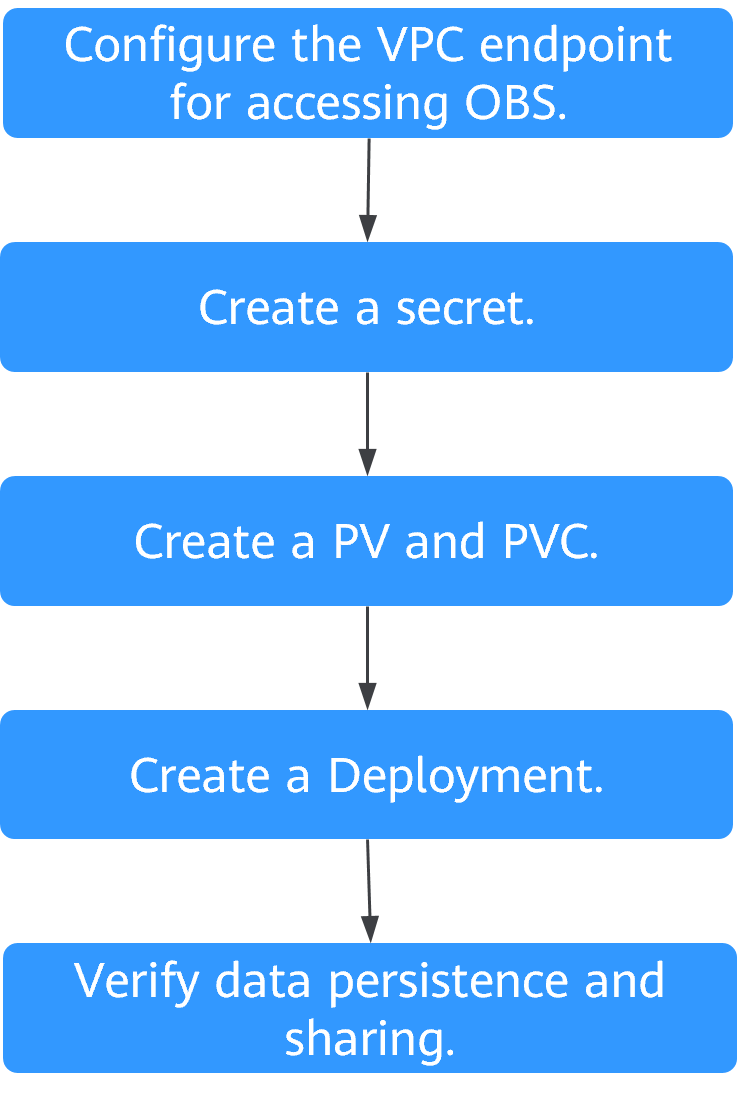
Before using a parallel file system for persistent data storage, you have configured a VPC endpoint for accessing OBS. Otherwise, the volume created from the parallel file system may fail to be mounted. You are advised to create all possible VPC endpoints for OBS at a time to avoid repeated operations when creating volumes from existing parallel file systems. For details about VPC Endpoint, see What Is VPC Endpoint? For details about how to create a VPC endpoint, see Purchasing VPC Endpoints. You can submit a service ticket or contact OBS O&M personnel to obtain the name of each VPC endpoint for OBS.
Scenarios
Only existing parallel file systems can be mounted to workloads as volumes. You need to use an existing parallel file system to create a PV and then mount the PV to a workload through a PVC. For details, see Creating a Volume from an Existing Parallel File System.
Process Flowchart
Billing
For details about the billing, see OBS Billing.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





