Shared Responsibility Model
Huawei Cloud prioritizes security compliance above all. Both Huawei Cloud and its customers share this responsibility. To define each party's role in protecting cloud security, Huawei Cloud has defined a shared responsibility model for security, as shown in the following figure.
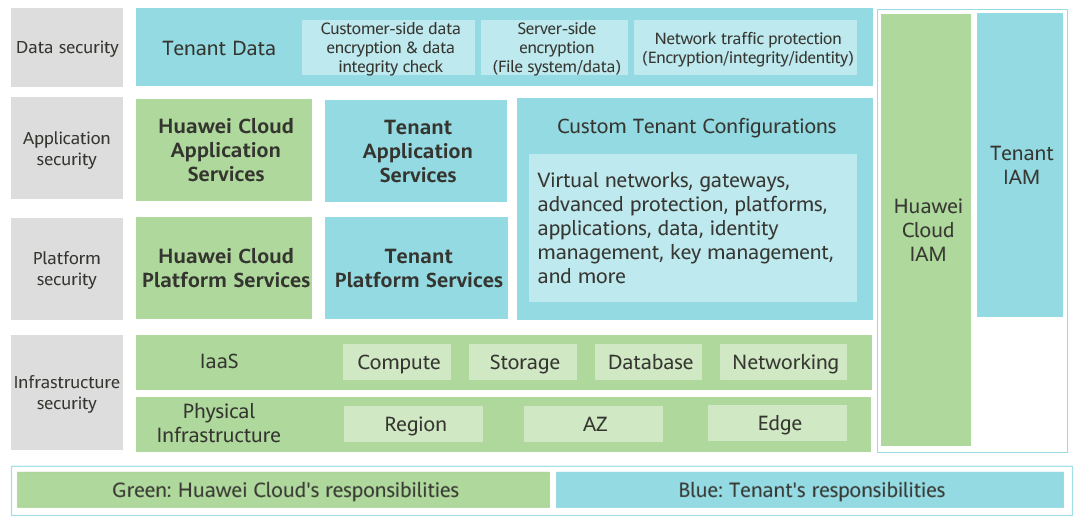
Huawei Cloud is responsible for security of its cloud platform and cloud services, as well as the physical environments of Huawei Cloud data centers where the IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS operate. Huawei Cloud is responsible for providing secure and efficient, and ensuring secure O&M of, cloud infrastructure and services, and responsible for complying with relevant compliance requirements.
- Huawei Cloud securely develops, configures, and deploys cloud technologies. It also provides secure O&M by quickly detecting, isolating, and responding to incidents to restore cloud services promptly. Meanwhile, Huawei Cloud uses an effective vulnerability management system for its cloud services. The system promptly responds to cloud service security vulnerabilities, ensures fast updates during CSP O&M windows, and maintains uninterrupted service for users. The approaches involve optimizing default security settings for cloud services, prioritizing patch installation over R&D, and streamlining patch release schedules. In addition, Huawei Cloud is developing easy-to-use cloud native security services that are competitive in the market.
- Huawei Cloud takes infrastructure security and privacy protection as the top priority of secure O&M. The infrastructure primarily consists of the physical environment for deploying cloud services, including Huawei-developed software and hardware and all types of cloud service system facilities for O&M such as computing, storage, networking, databases, platforms, applications, and security, for example, IAM and high-level security services. In addition, Huawei Cloud integrates third-party security technologies or services and is responsible for their secure O&M.
- Huawei Cloud is also responsible for the security configuration and version maintenance of the cloud services it supports.
- Huawei Cloud provides tenants with comprehensive data protection functions such as privacy, integrity, availability, durability, authentication, authorization, and non-repudiation, and is responsible for the security of related functions. Huawei Cloud keeps the data, but tenants retain full ownership and control of their information. Huawei Cloud never allows O&M personnel to access tenant data without authorization. Huawei Cloud stays up-to-date with internal and external compliance requirements, complies with security laws and regulations required for running Huawei Cloud services, evaluates security standards of the industries it served, and shares compliance practices with tenants.
- Huawei Cloud works with cloud security partners to provide consulting services for tenants. For example, Huawei Cloud assists tenants in configuring security settings for virtual networks and VMs (including host VMs and guest VMs), managing security patches for systems and databases, customizing configurations for virtual network firewalls, API gateways, and advanced security services, and performing DoS/DDoS attack defense drills, emergency response to security incidents, and disaster recovery drills.
Tenants of Huawei Cloud are responsible for the secure and effective management of the configurations of cloud services including IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. This includes but is not limited to virtual networks, the OSs of guest VMs and host VMs, virtual firewalls, API gateways, advanced security services, all types of cloud services, tenant data, identity accounts, and key management.
- Tenant-specific security responsibilities are ultimately based on the cloud services that tenants use. These responsibilities are tied to the specific default or customized security configurations they apply. Huawei Cloud offers the necessary resources, features, and performance for tenants to perform security tasks. Tenants must configure security settings for their resources.
- Tenants need to: (1) Configure policies for firewalls, gateways, and advanced security services of their virtual networks. (2) Manage security settings, including updates and patches, for virtual networks, host VMs, guest VMs, and cloud services like containers. Manage container security, including configuring access control for container clusters, nodes, and containers. Configure security policies for the big data analysis platform. (3) Configure other security policies for cloud services they lease. (4) Manage security of any applications or tools they deploy on Huawei Cloud.
- Tenants are responsible for testing security configurations before deploying services to their production environment to prevent negative impacts on their applications and businesses. For the security of most cloud services, tenants only need to control account access to resources and keeps credentials secure. A few cloud services require other tasks to achieve the desired security. There are many security configurations in monitoring, management, and advanced security services. Tenants can seek technical support from Huawei Cloud and its partners to complete these configurations and ensure security.
- Let's take Huawei Cloud MapReduce Service (MRS) as an example. Tenants need to (1) Configure EIP and virtual network firewalls for the MRS big data cluster they purchase. (2) Control access to the big data cluster, for example, by only allowing trusted networks or hosts to access the EIP port. (3) Manage big data cluster users, configure security policies for big data components, and properly keep related account credentials. (4) Manage the security of applications deployed on the big data cluster.
- Let's take a database service as an example. Tenants need to manage the lifecycle and security of their database engines, including (1) using the latest instance version by default and upgrading the version in a timely manner based on the official website prompt and vulnerability notice; (2) sorting out asset categories and formulating database instance protection policies, such as designing active/standby instances or clusters, planning data backup and recovery, configuring VPCs and security groups, managing internet access, encrypting connections, setting database authentication and authorization policies, enabling the audit service, and applying other necessary security settings.
- Regardless of which Huawei Cloud service is used, tenants are always the owners and controllers of their data. Tenants are responsible for configuring data security, and ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, and authenticating and authorizing data access. For example, when using Identity and Access Management (IAM) and Data Encryption Workshop (DEW) services, tenants are responsible for keeping their service accounts, passwords, and keys safe, and shall comply with industry best practices in configuring, updating, and resetting passwords and keys. Tenants need to set up personal accounts and multi-factor authentication (MFA), properly use secure transfer protocols to communicate with Huawei Cloud resources, and set up user activity logs for monitoring and auditing.
- Tenants are responsible for ensuring compliance of applications and services deployed on Huawei Cloud that are not provided by Huawei Cloud, and evaluating the security standards of the industries they serve.
Note that the security responsibilities depend on the service type (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS), service mode (cloud service or cloud software), and the security service provider. In 2024, Huawei Cloud and China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT) jointly released the Shared Responsibility Model for Cloud Security in 2024. This white paper introduces the shared responsibility for cloud security 2.0 in detail and offers guidance for applying this model effectively.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





