Configuring RDS
To store application data permanently, you need to use Relational Database Service (RDS). Based on the cloud computing platform, CAE provides RDS for MySQL which is reliable, scalable, easy to manage, and ready for use. RDS for MySQL enables you to easily set and scale relational databases on the cloud. Using the RDS service, you can perform nearly all necessary tasks without programming. This service simplifies operation procedures and reduces routine O&M workloads, so that you can focus on application and service development.
You can bind a cloud database in component configuration. Then, you can read environment variables to obtain MySQL information during application running to access MySQL.
The cloud database to be bound must be in the same VPC as the environment.
Prerequisites
You have created an RDS MySQL DB instance. For details, see Buying an RDS for MySQL DB Instance.
Procedure
- Log in to CAE.
- Choose Component Configurations.
- Select the target component from the drop-down list in the upper part of the page.
Figure 1 Selecting a component
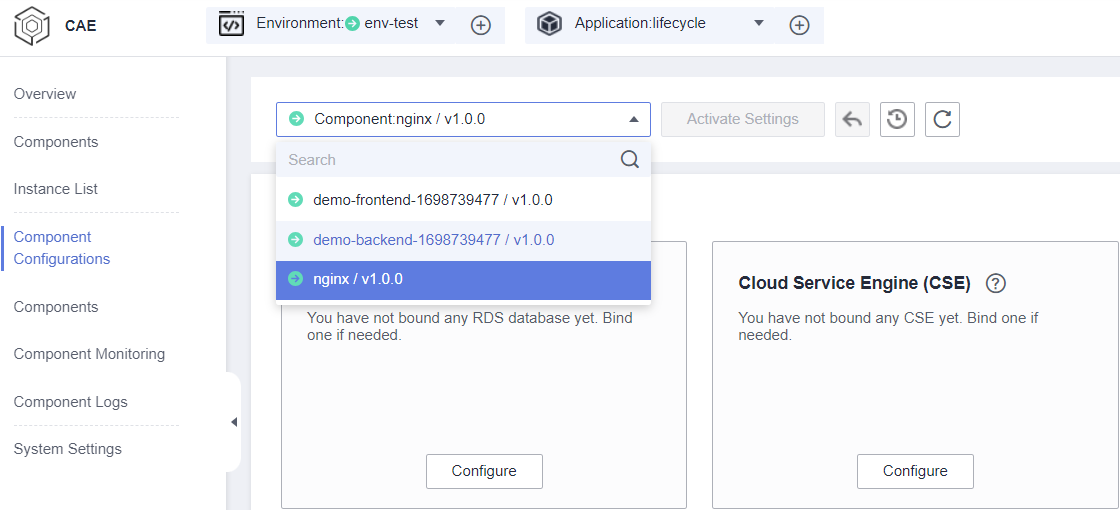
- Click Configure in the Relational Database Service (RDS) module.
- You need to set RDS environment variables in your code when configuring an RDS instance for the first time. Available variables:
Variable
Description
RDS_ADDRESS
Private IP address of the RDS database instance
RDS_DB_NAME
Database name
RDS_USER_NAME
Database username
RDS_PASSWORD
Database password
RDS_PORT
Database port
After the configurations take effect, user code can obtain RDS database parameters through environment variables and use these parameters to connect to the databases for adding, deleting, modifying, and querying data.
For example, use GORM to connect to postgreg:func initDB() (*gorm.DB, error) { // Obtain parameters from environment variables. dbAddress := os.Getenv("RDS_ADDRESS") dbName := os.Getenv("RDS_DB_NAME") dbUserName := os.Getenv("RDS_USER_NAME") dbPassword := os.Getenv("RDS_PASSWORD") dbPort := os.Getenv("RDS_PORT") // Use the obtained parameters to build DSN. dbDSN := fmt.Sprintf("host=%s port=%s user=%s dbname=%s sslmode=disable password=%s",dbAddress, 5432, dbUserName, dbName, dbPassword) // Connect to a database. instance, err := gorm.Open("postgres", dbDSN) if err != nil { log.Println("connect db failed : " + err.Error()) return nil, err } return instance, nil } - In the right pane, select an RDS instance.
If the existing RDS instances do not meet service requirements:
- Click Go to RDS Console to create an RDS instance.
- Click Buy DB Instance and configure the instance.
- Set the parameters by referring to Table 1.
Table 1 Configuring RDS Parameter
Description
RDS Instance
You can select an RDS database instance in the same VPC as CAE.
Database
Select the target database.
Database Username
Select a user under the database.
Database Password
Enter a database password. The password is mandatory.
Confirm Password
Enter the password again.
Database Port
Enter a database port.
- Click Save.
- Make the configurations take effect.
- If the component has been deployed, click Activate Settings in the upper part of the page. In the dialog box displayed on the right, confirm the configurations and click OK for the configurations to take effect.
- If the component has not been deployed, click Set and Deploy Component in the upper part of the page. In the dialog box displayed on the right, click OK. After the deployment is complete, the configurations take effect.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





