Compromised Hosts
Prerequisites
Blacklist and Whitelist Authorization has been completed.
Context
Huawei Qiankun determines whether a threat event is a compromised host based on the following rules:
- If a host in the user-trusted zone initiates attacks, the host is considered as a compromised host. For details about the user-trusted zone, see Configuring Device Security Zones.
- If a host whose IP address is in the global whitelist initiates attacks, the host is considered as a compromised host. For details about the global whitelist, see Configuring a Global Whitelist.
- If a host whose IP address is an untrusted intranet IP address initiates attacks, the host is not considered as a compromised host. For details about the untrusted intranet IP address, see Configuring Untrusted Intranet Addresses.
- If a host whose IP address belongs to the default private network segment initiates attacks, the host is considered as a compromised host. The default private network segments are 10.0.0.0 to 10.255.255.255, 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.555, and 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255.
Based on the compromise types, security operations experts can classify compromised hosts into the following types: Ransomware, Mining, Worm, C&C, Vulnerability Attack, and Insecure Configurations. Those whose compromise types are not identified are classified into Other.
For a compromised host, Huawei Qiankun sends an SMS or email alarm to the tenant and sets the status of the compromised host to Unhandled. Tenants need to handle the threat event by isolating the compromised host or marking the event status (manually handled or ignored).
In addition, for the compromised hosts detected after malicious domain name detection events are analyzed, Huawei Qiankun sends SMS and email alarms to tenants and automatically delivers the domain name blacklist. Users' access to the domain names in the blacklist will be blocked.
- Border Protection and Response Service Standard and automatic blocking
- Border Protection and Response Service Trial
- Border Protection and Response Service Advanced
Procedure
- Log in to the Huawei Qiankun console, and choose .
- Click Threat Events in the menu bar.
- Check the overview of compromised hosts, and click a number or View More to view details.
Figure 1 Overview of compromised hosts
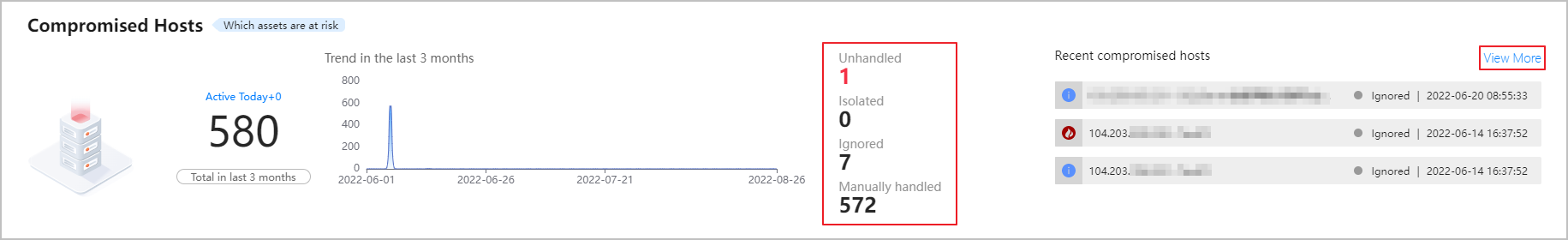
- Handle compromised hosts.
- Isolate a compromised host.
If no service is running on a compromised host or services will not be affected after the compromised host is isolated, click Isolate Host in the Operation column to deliver the IP address blacklist.
After receiving the IP address blacklist from Huawei Qiankun, the Qiankun Shield devices block traffic sent by and to the blacklisted IP address.
Devices can work in hot standby mode. If two devices are onboarded and bound to work in hot standby mode but the active device cannot work properly, the standby device will take over services from the active device. When you isolate a host on the By Event tab page, the IP address blacklist is delivered to both the devices working in hot standby mode, and you can see two records in the Historical IP Blacklist.
Figure 2 Isolating a host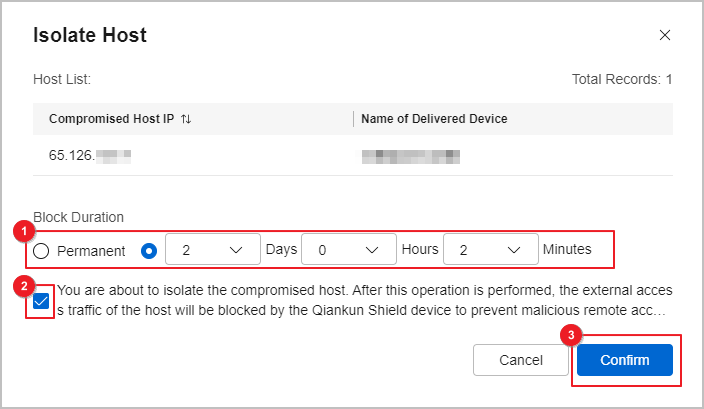
If the handling status of the compromised host is marked
 , the host isolation is cancelled.
, the host isolation is cancelled. - Mark the event status.
- Manually handled
A tenant manually handles compromised hosts, for example, scanning for and removing viruses on the compromised host. After confirming that the host has no security risk, the tenant can mark the compromised host status as Manually handled in the Operation column.
- Ignored
If an event does not need to be handled or is a false positive, set the compromised host to Ignored in the operation column.
- Manually handled
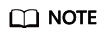
- The handling suggestion may contain the link of a reference manual for you to handle the threat event.
- If you do not know how to handle the problem or the problem persists after you handle it, contact the corresponding Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP) or channel partner.
- Isolate a compromised host.
Follow-up Procedure
- On the Compromised Hosts page, you can click the IP address of a compromised host to view details about the compromised host.
Figure 3 Compromised host list
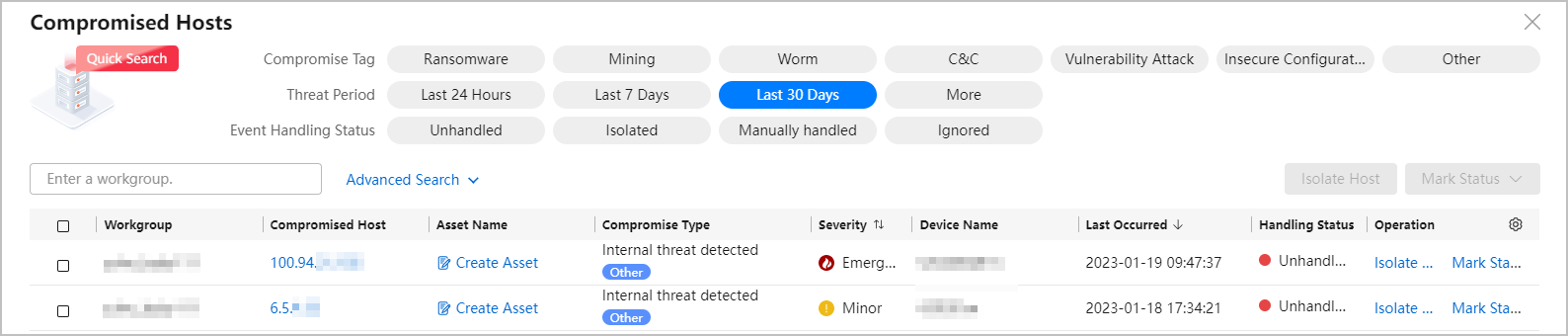
- The compromised host details page displays information such as handling suggestions, handling records, compromise type analysis, and associated alarm event list.
- You can click Export to export details about a compromised host to a Word file.
Figure 4 Compromised Host details page
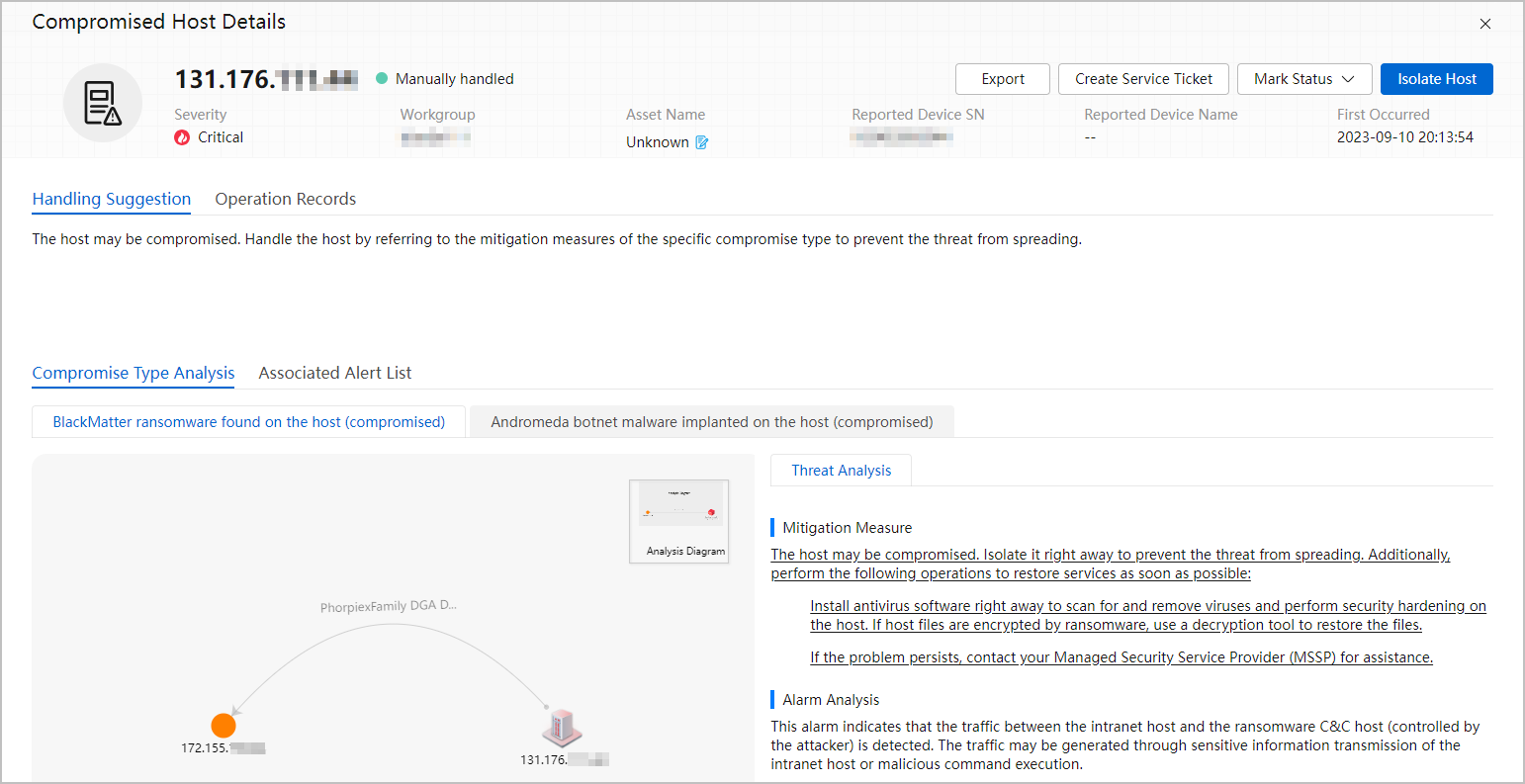
After the export is complete, click your account in the upper right corner and click Download to download the corresponding file.
Figure 5 Download center
- You can click an event name in the associated threat event list on the details page of compromised hosts to check details about the event.
Figure 6 Threat event details
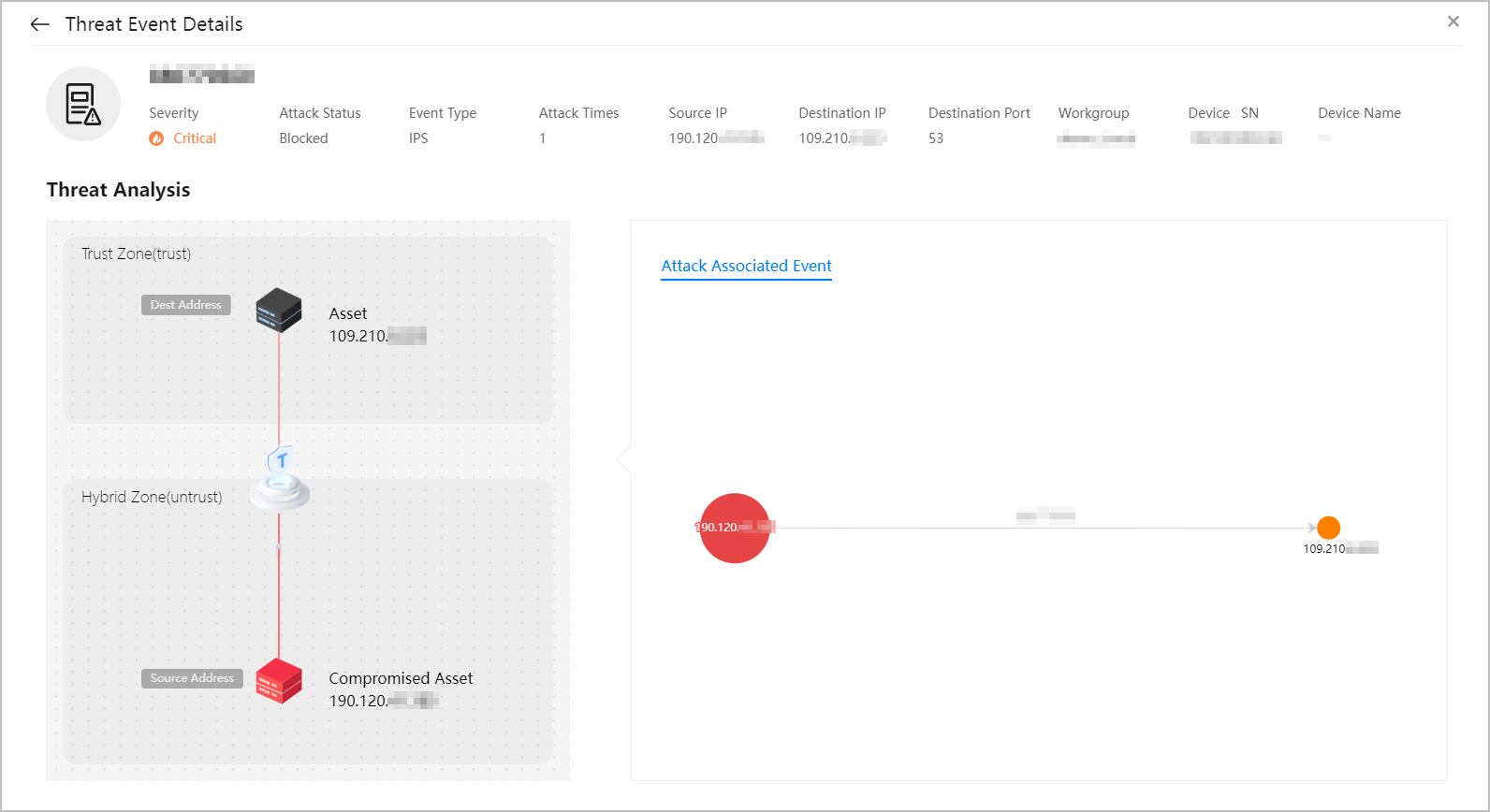
The details page of compromised hosts may contain public IP addresses, which are used only to display event information to help you learn about threat events. The service does not proactively initiate connections to these public IP addresses.
- You can click Export to export details about a compromised host to a Word file.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot






