Managing Namespaces
A namespace is a collection of resources and objects. Multiple namespaces can be created in a single CCE cluster with the data isolated from each other. This enables namespaces to share the services of the same cluster without affecting each other.
For example, you can deploy workloads in a development environment into one namespace, and deploy workloads in a testing environment into another namespace.
Table 1 describes the namespace types.
|
Creation Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Created by a cluster by default |
When a cluster is started, the default, kube-public, kube-system, and kube-node-lease namespaces are created by default.
|
|
Created manually |
You can create namespaces to serve separate purposes. For example, you can create three namespaces, one for a development environment, one for joint debugging environment, and one for testing environment. You can also create one namespace for login services and one for game services. |
This section describes how to create and delete a namespace, and manage namespace resource quotas.
Prerequisites
A CCE cluster has been bound to the environment. For details, see Binding a CCE Cluster.
Creating a Namespace
- Log in to ServiceStage.
- On the Environment Management page, click the target environment.
- In the Resource Settings area, choose Cloud Container Engine from Compute.
- Click Namespace > Create Namespace.
- Set the parameters by referring to the following table. Parameters marked with an asterisk (*) are mandatory.
Parameter
Description
*Namespace
Namespace name.
Namespace description
Description about the namespace.
Figure 1 Setting namespace parameters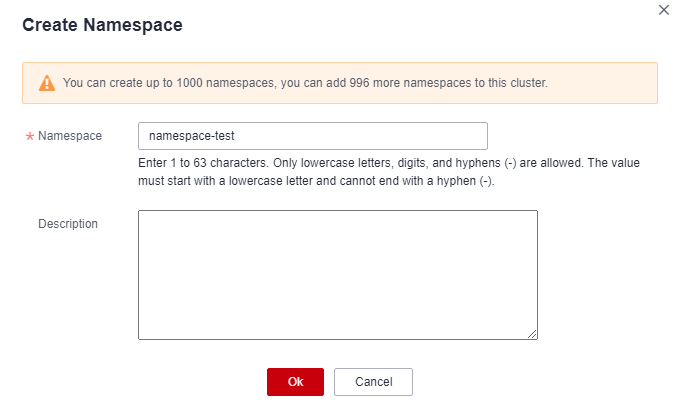
- Click OK.
The created namespace is displayed in the namespace list.
Deleting a Namespace

- If a namespace is deleted, all resources (such as workloads and configuration items) in this namespace will be also deleted. Exercise caution when deleting a namespace.
- The cluster-created namespace default cannot be deleted.
- Log in to ServiceStage.
- On the Environment Management page, click the target environment.
- In the Resource Settings area, choose Cloud Container Engine from Compute.
- Click the Namespace tab.
- To delete a single namespace, locate the target namespace and click Delete in the Operation column.
- To delete namespaces in batches, select the target namespaces and click Delete above the namespaces.
- In the displayed dialog box, enter DELETE and click OK.
Managing Namespace Resource Quotas
By default, pods running in a CCE cluster can use the CPUs and memory of a node without restrictions. This means that pods in a namespace may exhaust all resources of the cluster.
Kubernetes provides namespaces for you to group workloads in a cluster. By setting resource quotas for each namespace, you can prevent resource exhaustion and ensure cluster reliability. You can configure quotas for resources such as CPU, memory, and the number of pods in a namespace. For more information, see Resource Quotas.
User-created namespaces and the cluster-created namespace default support resource quota management.
- Log in to ServiceStage.
- On the Environment Management page, click the target environment.
- In the Resource Settings area, choose Cloud Container Engine from Compute.
- Click the Namespace tab.
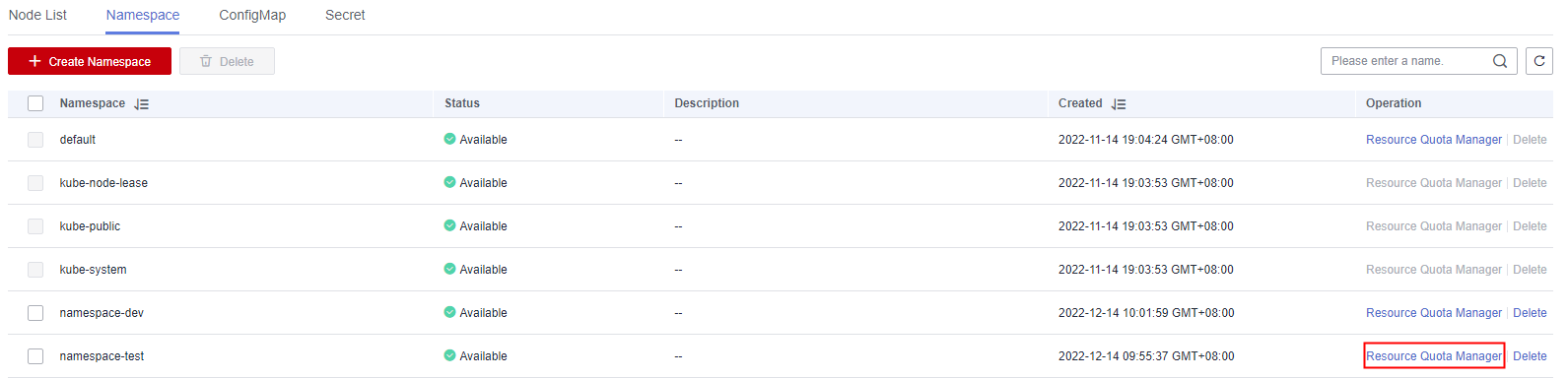
- Locate the target namespace and click Resource Quota Manager in the Operation column.
In the displayed Resource Quota Manager dialog box, view the resource types, total resource quotas, and accumulated quota usage in the namespace.Figure 2 Accessing the Resource Quota Manager page
- Click Edit Quota and set the total quota of each resource type.
- If the usage of a resource type is not limited, enter 0.
- If the usage of a resource type is limited, enter the expected integer.

- Accumulated quota usage includes the resources used by CCE to create default components, such as the Kubernetes Services (which can be viewed using kubectl) created under the default namespace. Therefore, you are advised to set a resource quota greater than expected to reserve resource for creating default components.
- If the total CPU or memory quota in a namespace is limited, you must set the maximum and minimum number of CPU cores and memory (GiB) that can be used by the component when setting resources for the Kubernetes component of this namespace in Creating and Deploying a Component and Upgrading a Single Component. Otherwise, the operation will fail.
- If the total quota of other resource types in a namespace is limited and the remaining usage of this resource type does not meet requirements, the Kubernetes component of this namespace will fail to be deployed.
- Click OK.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





