Supported and Unsupported Scenarios
Scenarios Supported by Parallel Query
|
Supported Scenario |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Scans |
Full table scans, index scans, index range scans, index reverse scans, index point queries, and index pushdown |
|
Queries |
Single-table queries, multi-table joins, views, subqueries, and some CTE queries, non-partitioned table queries, single-partition queries of partitioned tables, and UNION/UNION ALL queries |
|
Joins |
BNL JOIN, BKA JOIN, HASH JOIN, NESTED LOOP JOIN, SEMI JOIN, ANTI JOIN, and OUTER JOIN |
|
Subqueries |
Conditional subqueries, scalar subqueries, some correlated subqueries, non-correlated subqueries, and derived tables |
|
Data types |
Integer, Character, Floating Point, and time |
|
Expression calculation |
Arithmetic expressions (+, -, *, %, /, |, and &) and conditional expressions (<, <=, >, >=, <>, BETWEEN/AND, and IN) |
|
Logical operations |
OR, AND, and NOT |
|
General functions |
Character, Integer, and Time functions |
|
Aggregate functions |
COUNT, SUM, AVG, MIN, and MAX
CAUTION:
If you want a SQL statement containing the COUNT aggregate function to use parallel query, instead of InnoDB parallel query, set innodb_parallel_select_count to OFF. |
|
Sorting, grouping, pagination, and filtering |
ORDER BY, GROUP BY/DISTINCT, LIMIT/OFFSET, WHERE/HAVING, and column projection |
|
EXPLAIN statements |
EXPLAIN FORMAT=TREE, EXPLAIN ANALYZE (supported in 2.0.60.241200 and later), and EXPLAIN FORMAT=JSON introduced in MySQL 8.0 and traditional EXPLAIN statements |
Scenarios Unsupported by Parallel Query
|
Unsupported Scenario |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Statements |
|
|
Triggers |
Triggers |
|
Indexes |
|
|
Functions |
Window functions |
|
Spatial functions (such as SP_WITHIN_FUNC) |
|
|
User-defined functions |
|
|
REF functions (VIEW_REF, OUTER_REF, and AGGREGATE_REF) |
|
|
User-related functions (such as user, current_user, session_user, and system_user) |
|
|
Spatial relationship functions (such as MBRContains, MBRCoveredBy, MBRCovers, MBRDisjoint, MBREquals, MBRIntersects, MBROverlaps, MBRTouches, and MBRWithin) |
|
|
Functions starting with ST_ |
|
|
Spatial functions (GIS): GeomCollection, GeometryCollection, LineString, MultiLineString, MultiPoint, MultiPolygon, Polygon, ST_Distance, and Point |
|
|
Encryption and hash functions: SHA, SHA1, SHA2, and MD5 |
|
|
Lock and synchronization functions: get_lock, is_free_lock, is_used_lock, release_lock, release_all_locks, and sleep |
|
|
Other functions:
|
Incompatibility Between Parallel Queries and Serial Queries
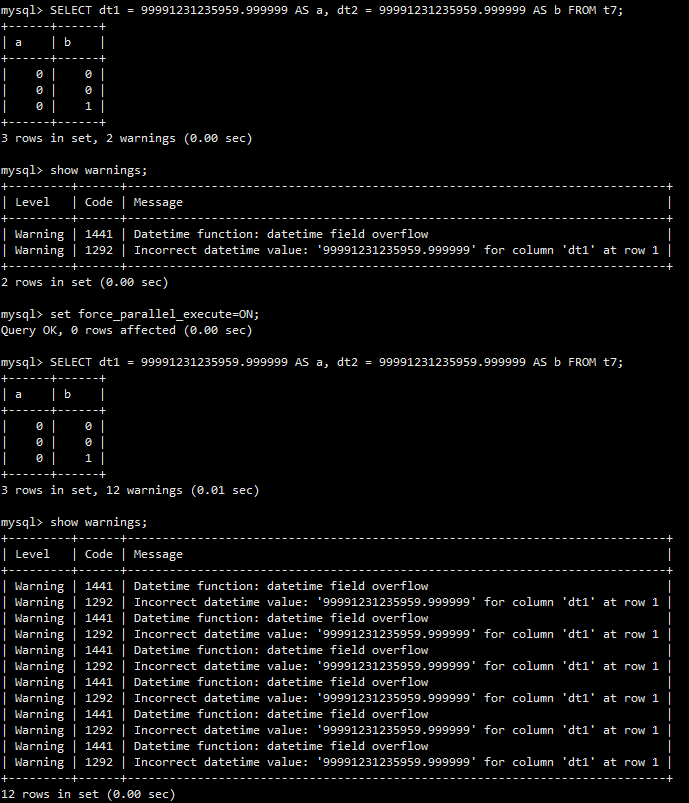
- Number of errors or alarms
If an error or alarm message is displayed during serial queries, the error or alarm message will be displayed in each worker thread during the parallel queries. As a result, the total number of error or alarm messages increases.
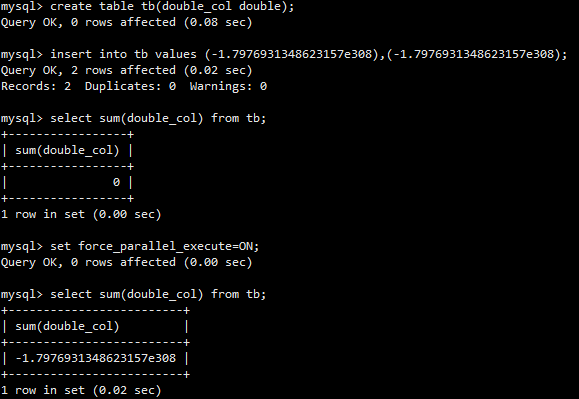
- Precision
During parallel queries, if there is a function type in a SELECT statement, additional stored procedures will be generated in the intermediate results. As a result, compared with serial queries, the precision of the floating point part in parallel queries may be different, and the final results may be slightly different.
- Truncation
During the parallel queries, if there is a function type in a SELECT statement, additional stored procedures will be generated in the intermediate results. In this process, the calculation result of the function needs to be cached, and data truncation may occur (generally due to data type conversion, for example, covering a floating-point value to a character string). As a result, the final result is different from the serial queries.
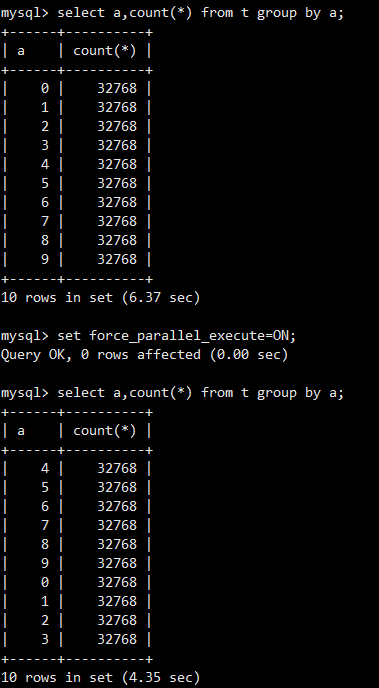
- Sequence of result sets
Because tasks are executed by multiple worker threads during parallel queries, the sequence of the returned result set may not be consistent with that of serial queries. In the case of a query with LIMIT, this problem is more likely to occur. If fields of GROUP BY are invisible characters, the sequence of the returned result set is also different.
- UNION ALL result sets
UNION ALL ignores sort operators. The sequence of the returned result set in parallel execution may be different from that in non-parallel execution. In the case of a query with LIMIT, the result sets are different.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





