What Should I Do If My Linux ECS Fails to Start Due to Incorrect /etc/fstab File Configuration?
Symptom
For Linux ECSs, their automatic mounting of file systems is configured in the /etc/fstab file. If the automatic mounting information is incorrectly configured or unavailable, the ECS OS may fail to start after the system is restarted.
For details, see /etc/fstab File Introduction.
Possible Causes
- The /etc/fstab file was not modified before the disk is detached or reinitialized. As a result, the /etc/fstab file contains unnecessary automatic mounting information of file systems.
- The device name or UUID of a file system is incorrectly configured.
- The file type of a file system is incorrectly configured.
- The mount parameters are incorrect.
Solution
- Log in to the ECS. For details, see Login Overview (Linux).
- Run the following command to back up the /etc/fstab file before modifying it:
cp /etc/fstab /etc/fstab.bak
- Run the following command to check the content of the /etc/fstab file and ensure that the mount path, device name, or UUID is correct:
cat /etc/fstab
Figure 1 Check results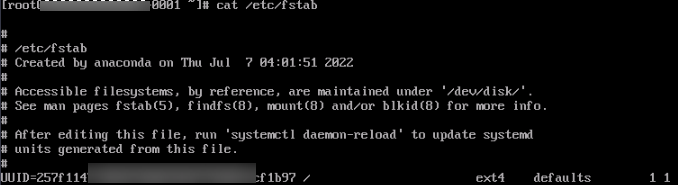
- Check the mount point.
Check that each mount point (for example, /mnt/data) exists and has the correct permissions and owner.
- Check the device or UUID.
You are advised to mount partitions using the UUID to prevent errors in the fstab file caused by device name changes. These changes may occur when an ECS is restarted after specifications are modified or disks mounted or unmounted.
Run the following command to obtain the device UUID and ensure that the device name (for example, /dev/vda1) or UUID exists and is correct:
blkid
Figure 2 Obtaining the device UUID
- Check the mount options.
Check whether the mount option of each mount partition is correct, for example, defaults and rw.
- Check the mount status.
Run the following command to check whether all file systems are correctly mounted:
df -h
Figure 3 Check results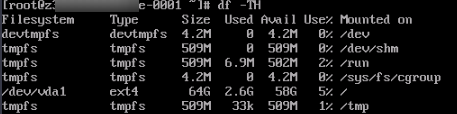
Compare the /etc/fstab file content with the mount point details in the command output, and delete unnecessary configuration lines from the /etc/fstab file.
- Check the mount point.
- Run the following command to test the mount result:
This command automatically mounts the file system based on the configuration in the /etc/fstab file.
- If no error is displayed, the /etc/fstab file is correctly configured. No further action is required.
- If an error is displayed, use a text editor (such as vi or nano) to edit the /etc/fstab file based on the error information, and save the modified file.
- If the /etc/fstab file is modified, run the following command to restart the system to apply the modification.
reboot
/etc/fstab File Introduction
Table 1 lists each field in the /etc/fstab file.
|
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
|
file system |
UUID of the file system of the partition to be mounted. For example, UUID=xxxx-xxxx. |
|
dir |
Mount point. |
|
type |
File system type of the partition to be mounted, for example, ext4 or xfs. |
|
options |
Mount parameter. The defaults parameter is generally used. If multiple parameters are required, separate them with commas (,). Table 2 lists common mount parameters. |
|
dump |
Whether a file system is backed up with dump.
|
|
pass |
Determines the check sequence of the file systems with fsck. A smaller value indicates a higher check priority. Rule:
|
|
Mount Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
defaults |
Uses the default mount parameters of file systems. Separate multiple parameters with commas (,). For example, the default parameters of the ext4 file type are rw,suid,dev,exec,auto,nouser,async. |
|
rw |
Mounts a file system as read/write. |
|
ro |
Mounts a file system as read-only. |
|
auto |
Automatically mounts at startup or when the mount -a command is executed. |
|
noauto |
Requires manual mounting using commands. |
|
suid |
Allows the suid operation and setting of sgid bits. Generally, this parameter is used to temporarily elevate the permissions of common users when they run special tasks. |
|
nosuid |
Prevents the suid operation and sgid bits. |
|
dev |
Parses the block device on the file system. |
|
nodev |
Does not parse the block device on the file system. |
|
exec |
Allows the execution of executable files on mount points. |
|
noexec |
Prevents the execution of executable files on mount points. |
|
nouser |
Only allows the root user to mount file systems. |
|
async |
Asynchronous I/O |
|
sync |
Synchronous I/O |
|
nofail |
If the device does not exist when you start the ECS, the device is ignored. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





