Drive Hints
Function
When generating a query plan, the optimizer uses the dynamic planning or genetic algorithm to enumerate possible join paths and selects the optimal path. When the number of join tables increases, the search space may expand greatly. In this case, you can use a drive hint to specify the fact table in the query and use heuristic search to narrow the search range. This hint takes effect only when the GUC parameter join_search_mode is set to heuristic.
Syntax
1
|
[no] drive (table) |
Description
- no indicates that the table specified by the hint is not a drive table.
- table specifies the table specified by the hint. You can specify only one table. Use a table alias (if any) instead of a table name.
Example
Create tables t1, t2, and t3.
1 2 3 |
create table t1(a1 int,b1 int,c1 int,d1 int); create table t2(a2 int,b2 int,c2 int,d2 int); create table t3(a3 int,b3 int,c3 int,d3 int); |
The original statement is as follows:
1
|
explain select * from t1,t2,t3 where t1.b1=t2.b2 and t1.c1=t3.c3 and t2.d2=t3.d3; |
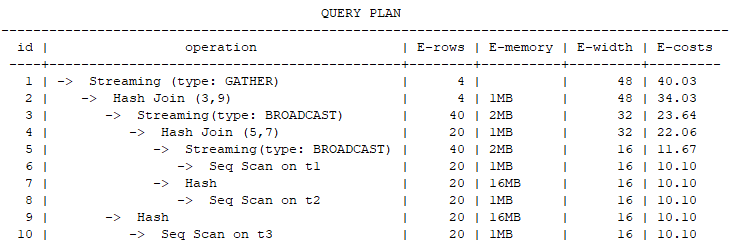
explain select /*+ drive(t3) */ * from t1, t2, t3 where t1.b1=t2.b2 and t1.c1=t3.c3 and t2.d2=t3.d3;
After hints are used:
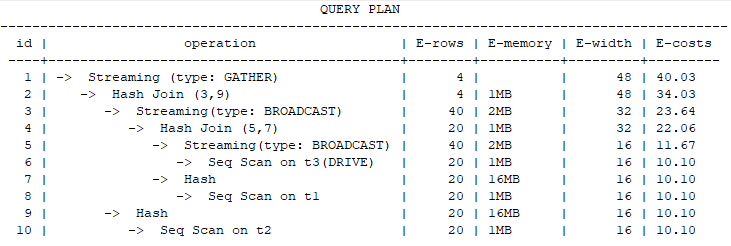

If the GUC parameter join_search_mode is set to heuristic and the number of joined tables exceeds the value of from_collapse_limit, the optimizer automatically identifies drive tables and displays them in the plan. If the final drive selected by the optimizer is incorrect, you can use no drive hint to correct the selection.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





