plan management
The execution plan of the same statement varies with the change of database parameter settings, version, and data. As a result, the execution performance deteriorates. Plan management can bind a specified plan to a statement to prevent performance deterioration caused by plan changes.
Plan management includes generating unique IDs for plans, generating sql_hash and plan_hash for statements and plans, saving and using plans, and invalidating plans.
Generating a Unique Plan ID
If you want to specify a fixed plan for a statement, each statement and its plan must have a unique identifier, that is, sql_hash and plan_hash.
Enable the GUC parameter enable_generate_plan_hash to generate a unique plan_hash for outlines.
Plans Applicable for Generating an Outline
Except for FQS strong quantitative plans for CNs, outlines will be generated for other plans.
Saving and Using an Outline
The following figure shows the process of saving and using an outline during statement execution.

Saving an outline
Saving an outline stores the plan's auto-generated structure in the SQL_OUTLINE system catalog so it can link to future SQL statements.
- If an outline specified in outline_name does not exist in the corresponding sql_hash statement, the outline is saved. If an outline specified in outline_name already exists, the outline is not saved again.
- The outline is saved only after the statement is correctly executed. If an error occurs during the execution, it will not be saved.
You can set GUC parameter planmgmt_options to save outlines.
- Set planmgmt_options to plan_save_mode_outline, plan_save_level_topsql so that the outline of the Top SQL statement is saved only when the statement meets the requirements.
Or
- Set planmgmt_options to plan_save_mode_outline, plan_save_level_all to save the outline.
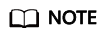
Although plan management can ensure stable statement execution performance, enabling plan management also consumes performance. It is not applicable to simple statements that are not resource-consuming. Setting planmgmt_options to plan_save_mode_outline, plan_save_level_topsql to avoid saving the plan of simple statements.
Using an outline
After using the pgxc_bind_plan function to bind an outline to a statement, you can set planmgmt_options to plan_save_mode_outline, plan_save_level_topsql, enable_plan_baseline so that the bound outline can be used when the statement is executed.

plan management automatically extracts these hints: join sequence (leading hint), join mode, scan mode, skew columns (skew hint), and distribution modes (stream hint).
The purpose of using plan management to bind an outline to statements to fix the plan is fixing the plan using the hints in the outline. The hint types that can be automatically extracted from an outline are limited. Therefore, the restrictions are as follows:
- If hints that are not supported in an outline are manually added to, deleted from, or modified in SQL statements, the plan may not be fixed after the outline is bound.
- no merge hint: SQL 1 includes a no merge hint, while SQL 2 does not. Both SQL 1 and SQL 2 share the same sql_hash. When binding outlines, both queries are included. However, if the outline from SQL 1 is applied, it will not work for SQL 2 due to the missing no merge hint. This is because no merge hint restricts the promotion of subqueries. The levels of statement blocks are different, and the statement blocks used in hints in the generated outline are different when subqueries are promoted and not promoted. As a result, the corresponding table in the hint cannot be found after outline binding, and the hint cannot take effect.
- GUC hint: similar to no merge hint
- You can manually modify the automatically generated outline and add hints that do not support automatic extraction to fix the plan.
Example of Using Plan Management
- Enable plan management.
SET resource_track_cost=0; SET resource_track_duration=0; SET enable_generate_plan_hash = on; SET planmgmt_options='plan_save_mode_outline,plan_save_level_topsql,enable_plan_baseline';
- Connect to the database and create tables and indexes.
1 2 3 4
CREATE TABLE t1(a1 int, b1 int, c1 serial) DISTRIBUTE BY hash(a1); INSERT INTO t1(a1, b1) VALUES(generate_series(1, 10), generate_series(1, 8)); CREATE INDEX idx_t1_b1 on t1(b1); CREATE TABLE t2(a2, b2, c2) AS SELECT * FROM t1;
- View the plans of two statements, one uses indexes and the other do not use.
View the plan of the statement that does not use indexes:
1EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select count(*) from t1, t2 where b1 = 1 and a1 = a2;

View the plan of the statement that uses indexes:
1EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select /*+ indexscan(t1 idx_t1_b1) */ count(*) from t1, t2 where b1 = 1 and a1 = a2;

- View the plan saved in the sql_outline table.
1SELECT sql_hash, plan_hash, outline_name, outline FROM dbms_om.sql_outline WHERE outline like '%public.t1%public.t2%';

Use sql_hash, plan_hash, and outline_name for sql_6e8591b8291c3b458b26ce7419fd3704, plan_00df934ed2620cb09c5f51a33f1945fd, and outline_ae16ae6300416c3efc96378c7b3a7e7b, respectively.
- Bind a plan that uses an index to a statement.
1 2 3 4 5
SELECT pgxc_bind_plan('sql_6e8591b8291c3b458b26ce7419fd3704', 'outline_ae16ae6300416c3efc96378c7b3a7e7b'); pgxc_bind_plan ---------------- t (1 row)
- Check whether the statement uses the bound index plan.
1EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select count(*) from t1, t2 where b1 = 1 and a1 = a2;

The preceding plan shows that the bound index plan is used.
- Unbind a plan from a statement.
SELECT pgxc_unbind_plan('sql_6e8591b8291c3b458b26ce7419fd3704'); pgxc_unbind_plan ------------------ t (1 row) - View the execution plan after the plan is unbound.
1EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select count(*) from t1, t2 where b1 = 1 and a1 = a2;

The preceding figure shows that the index plan is no longer used.
- Rebind the plan and delete indexes.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
SELECT pgxc_bind_plan('sql_6e8591b8291c3b458b26ce7419fd3704', 'outline_ae16ae6300416c3efc96378c7b3a7e7b'); pgxc_bind_plan ---------------- t (1 row) DROP INDEX idx_t1_b1;
- View the statement execution plan after the plan becomes invalid.
EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select count(*) from t1, t2 where b1 = 1 and a1 = a2;

According to the preceding plan, although the bound outline is used, the index hint in the bound outline does not take effect because the index is deleted.
- View the plan of the statements that contain no merge hint.
EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select * from t1 where a1 in (select /*+ no merge */ a2 from t2 where b2 < 10);
- View the plan for statements that does not contain no merge hint.
EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select * from t1 where a1 in (select a2 from t2 where b2 < 10);

- Check the outlines for statements with and without no merge hint.
SELECT sql_hash, plan_hash, outline_name, outline FROM dbms_om.sql_outline WHERE sql_hash = 'sql_14150502dc61e290b4c81c5c43d7446c';

- Attach an outline to statements with no merge hint.
SELECT pgxc_bind_plan('sql_14150502dc61e290b4c81c5c43d7446c', 'outline_a2cdc54106b991174cc0a35b8e0f0b29'); pgxc_bind_plan ---------------- t (1 row) - Apply the attached outline to a statement without no merge hint. The subquery remains promoted.
EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select * from t1 where a1 in (select a2 from t2 where b2 < 10);

- Edit the attached outline by adding no merge hint to it, and update it in dbms_om.sql_outline.
CREATE OUTLINE outline_nomerge for sql_14150502dc61e290b4c81c5c43d7446c using '/*+ begin_outline_data no merge@"sel$2" TableScan(@"sel$1" public.t1@"sel$1") TableScan(@"sel$2" public.t2@"sel$2") end_outline_data */' - Attach the updated outline that contains no merge hint.
SELECT pgxc_bind_plan('sql_14150502dc61e290b4c81c5c43d7446c', 'outline_nomerge'); pgxc_bind_plan ---------------- t (1 row) - Apply the attached outline to a statement without no merge hint. Now, the subquery stays unpromoted.
EXPLAIN (verbose on, blockname on, outline on) select * from t1 where a1 in (select a2 from t2 where b2 < 10);

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





