What Can I Do If Services Cannot Be Accessed After a Policy Is Configured on CFW?
Symptom
After you configure a protection policy on CFW, the service traffic is abnormal. For example:
- An EIP cannot access the Internet.
- A server cannot be accessed.
- A certain domain name cannot be accessed.
Troubleshooting Methods
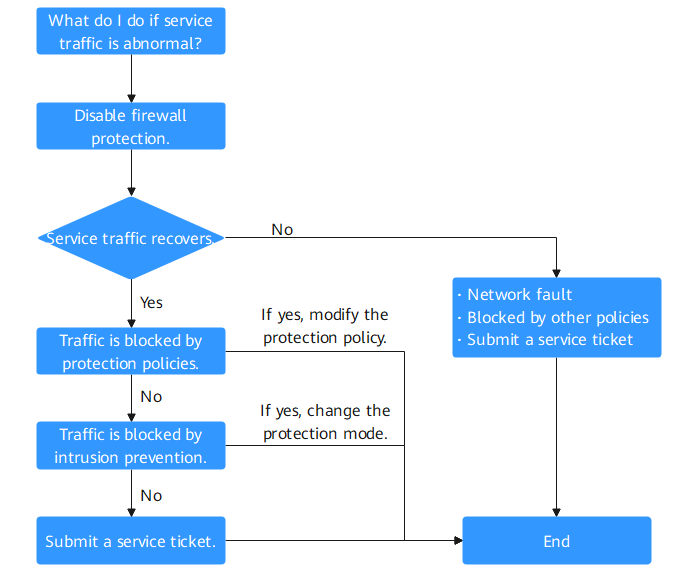
Cause 1: Traffic Interruption Not Caused by CFW
Log in to the CFW console and perform the following steps:
- Disable protection.
- EIP traffic fault: Disable the CFW protection in EIPs whose services are interrupted. For details, see Disabling EIP Protection.
- SNAT or inter-VPC access failure: Disable the VPC border firewall. For details, see Disabling a VPC Border Firewall.
- Observe the service running status.
- If the service is restored, it indicates traffic was blocked by CFW. Rectify the fault by referring to Cause 2: Traffic Blocked by Protection Policies and Cause 3: Traffic Blocked by Intrusion Prevention.
- If the fault persists, the traffic interruption is not caused by CFW. Possible fault causes include:
- Network fault: The route configuration is incorrect, or the NE is faulty.
- Policy-based interception: Interception caused by incorrect configurations of other security services, network ACLs, or security groups.
If you need assistance from Huawei Cloud, you can create a service ticket.
Cause 2: Traffic Blocked by Protection Policies
Traffic is blocked probably because a blocking rule is configured in the access control policy, or the normal services are blacklisted. In this case, CFW blocks related sessions, causing service loss.
You can take the following measures:
In the Access Control Logs tab, search for logs about the blocked IP address or domain name.
- If no records are found, see cause 3 in Table 1.
- If a record is found, click the Rule column to go to the matched blocking policy.
- The blacklist is blocked. You can select either of the following methods:
- Method 1: Delete the blacklist policy.
- Method 2: Add a whitelist policy for the IP address/domain name. (The whitelist takes precedence over the blacklist. After the whitelist policy is added, the blacklist policy will be invalid and the traffic is directly permitted.)
- The protection rule is blocked. You can perform either of the following operations:
- Method 1: Find the blocking rule of the IP address or domain name in the access control rule list and disable the policy.
- Method 2: Modify the matching condition of the blocking policy and remove the IP address or domain name information.
- Method 3: Add a protection rule whose Action is Allow and Priority is Pin on top. For details, see Adding a Protection Rule.
- The blacklist is blocked. You can select either of the following methods:
Case
Handling process: Detect a fault -> Disable protection -> View logs -> Modify a policy -> Restore protection -> Confirm logs
The network O&M personnel of a company found that an ECS cannot access the Internet through the bound EIP xx.xx.xx.94.
The firewall administrator took the following measures:
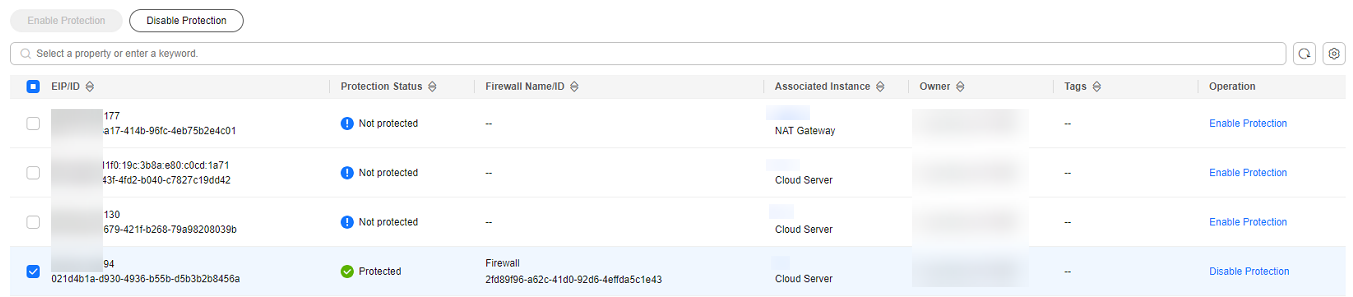
- To ensure that the IP address can be used for external communication during fault locating, the firewall administrator logged in to the firewall console, chose , and disables protection for the EIP.
After the firewall is disabled, the traffic of the EIP is not processed and related logs are not displayed.Figure 2 EIPs
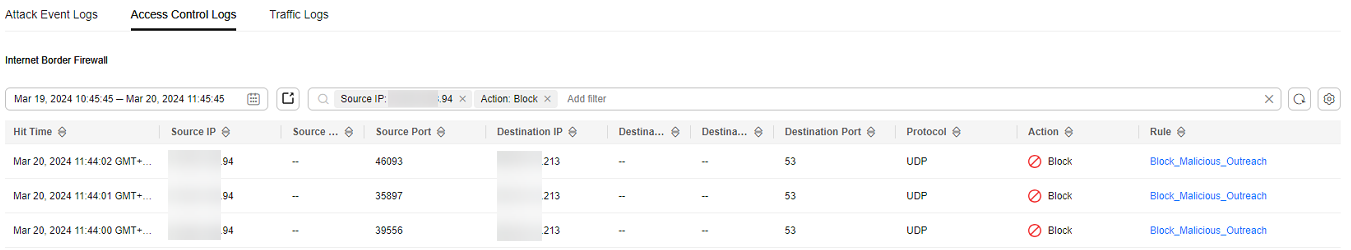
- The administrator chose and clicked the Access Control Logs tab. He searched for the blocking logs of the access source IP address xx.xx.xx.94. A blocking rule named Block-Malicious-Outreach was found. This rule blocked the traffic from the attack source IP address to the Internet.
Figure 3 Filtering access control logs
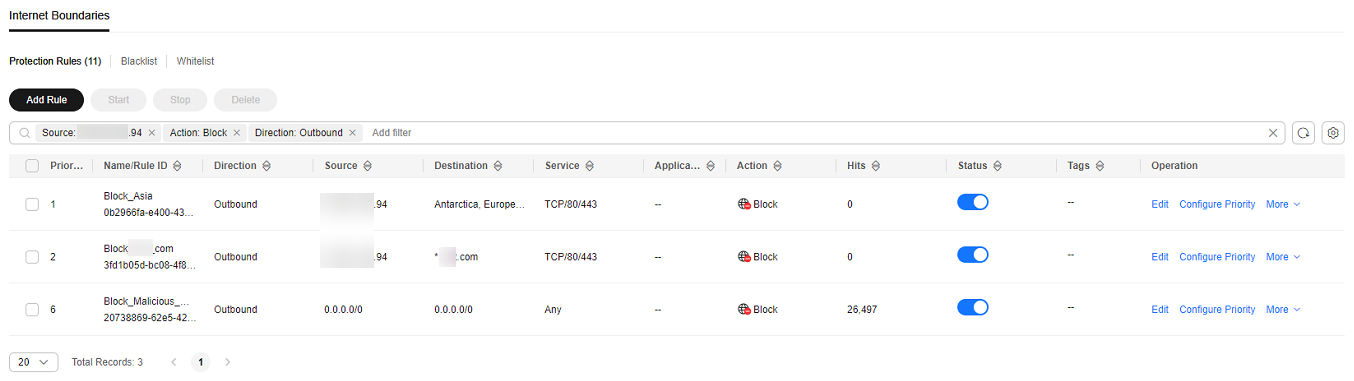
- The administrator searched for "Source: xx.xx.xx.94; Action: Block; Direction: Outbound; Status: Enabled" in the access control policy list. Three available policies that contain the IP address were found.
The policy contained the Block-Malicious-Outreach blocking rule. According to the value of the Hits column, a large number of sessions have been blocked.

According to Figure 4, there were three valid rules whose source IP addresses contain xx.xx.xx.94, including Block-xxx-com (with the highest priority), Block-Malicious-Outreach, and Allow-Asia (with the lowest priority). Besides the blocking rule Block-Malicious-Outreach, the administrator checked whether the two other two rules may intercept normal services.
Finally, it is found that the EIP accessed suspicious IP addresses so that an administrator configured a blocking rule it, but the configured destination was incorrect. As a result, all external traffic is blocked by mistake (see the second protection rule in Figure 4).
- The administrator changed the destination address to a specific IP address that needs to be blocked, and enabled protection for the EIP on the page of the firewall console. After protection was restored, the traffic of the EIP was normally forwarded by CFW.
- The administrator viewed the external connection logs related to the IP address in the traffic logs and confirmed that the service was restored.
Cause 3: Traffic Blocked by Intrusion Prevention
The protection mode of intrusion prevention functions, such as IPS, is too strict, blocking normal traffic.
You can take the following measures:
- If no records are found, submit a service ticket to troubleshoot the problem.
- If a record is found, perform either of the following operations:
- Copy the rule ID. In the corresponding module (such as IPS), set the protection mode of the rule with that ID to Observe. For details about the intrusion prevention module, see Configuring Intrusion Prevention.
- Add the IP addresses that do not need to be protected by CFW to the whitelist. For details about how to configure the whitelist, see Adding an Item to the Blacklist or Whitelist.
Case
Handling process: Detect a fault -> Change the protection status -> View logs -> Confirm services -> Modify the policy -> Restore the protection status -> Confirm logs
The O&M personnel of a company found that a service on the server whose IP address was xx.xx.xx.90 cannot be accessed. It was suspected that the service was blocked by the firewall.
The firewall administrator took the following measures:
- To quickly recover the service, the administrator logged in to the firewall console, chose , and changed the protection mode from Intercept mode - strict to Observe.
During this period, the firewall did not intercept attack traffic but only logged the attack traffic.
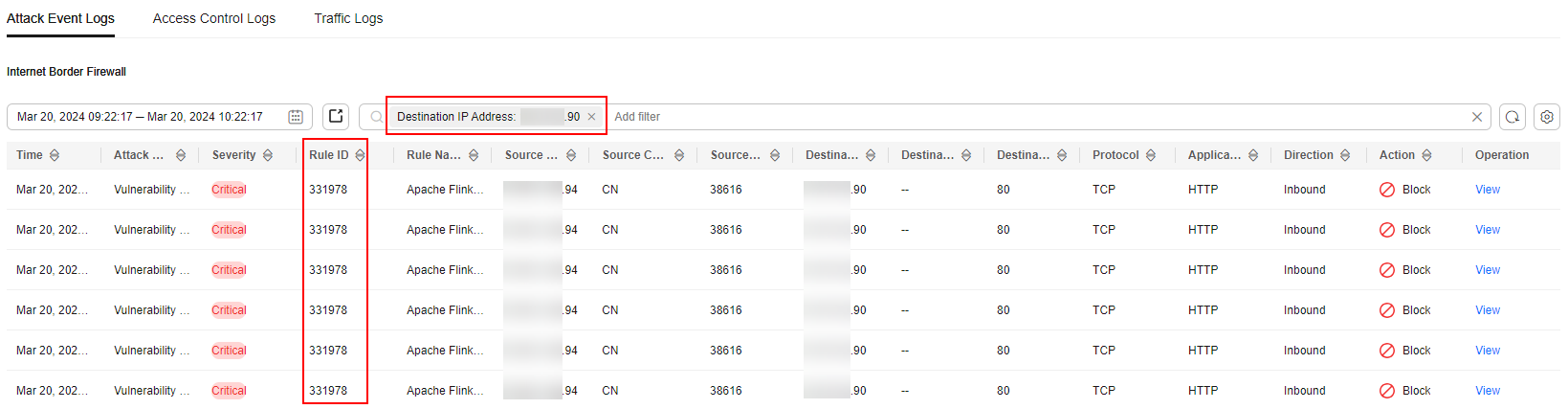
- The administrator chose and clicked the Attack Event Logs tab. The logs about the access to the destination IP address xx.xx.xx.90 were displayed. The IPS rule whose ID was 331978 blocked the traffic.
Figure 5 Filtering attack event logs
- The administrator clicked Details in the Operation column, clicked Payload Content on the displayed page, and created a packet capture task to verify that the service was normal. The administrator searched for the rule whose ID is 331978 from the list on the Basic Protection tab page by referring to Modifying the Action of a Basic Protection Rule.
Figure 6 Rule 331978
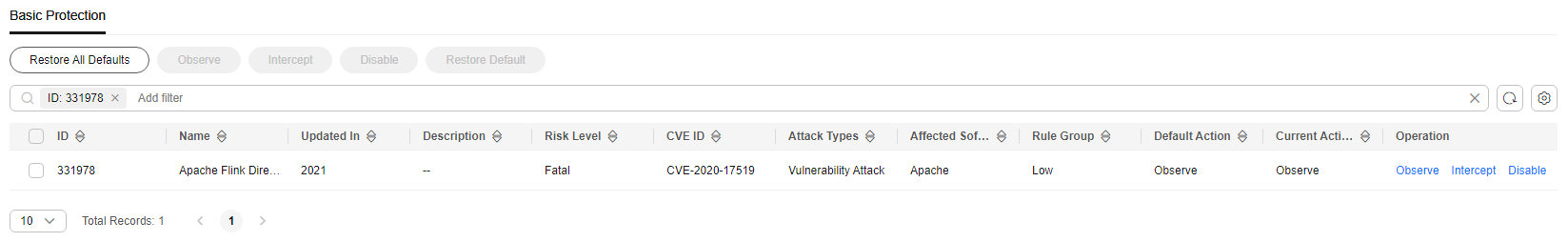
- The administrator clicked Observe in the Operation column. This rule did not block the traffic matching the signature but only logged the traffic.
- The administrator set the protection mode to Intercept mode - strict and went to the Basic Protection tab to confirm that the Current Status of the rule 331978 was still Observe.
- In the Attack Event Logs tab, after the service session matched the rule, the Action of the log was Allow. The service was recovered.
Submitting a Service Ticket
If the preceding methods cannot solve your problem, submit a service ticket.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot