Uploading/Obtaining a Debian Package Using Linux Commands
This practice describes how to use Linux commands to upload a private package to a Debian repository and obtain a dependency from the repository.
Prerequisites
- You have a Debian package available.
- You have a Linux host that can connect to the public network available.
- You have created a Debian repository in the self-hosted repo.
- You have permissions for the current repository. For details, see Managing Repository Permissions.
Releasing a Package to a Debian Repository
- Use your Huawei Cloud account to access self-hosted repos.
- Select a Debian repository. Click Tutorial on the right of the page.
- In the displayed dialog box, click Download Guide File.
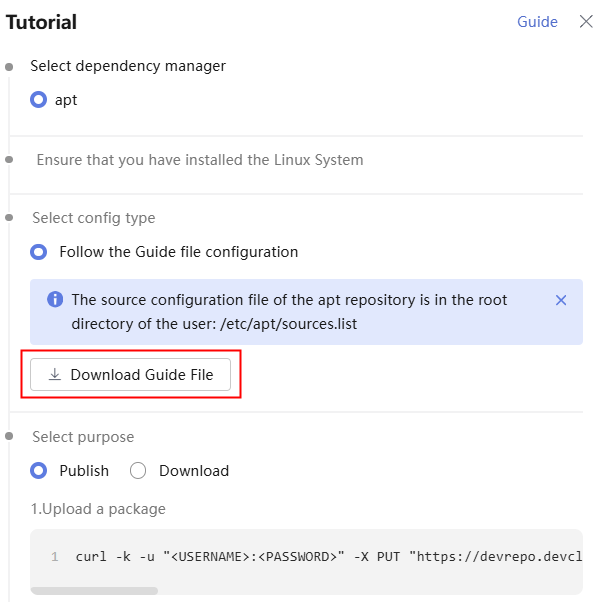
- On the Linux host, run the following command to upload a Debian package:
curl -u <USERNAME>:<PASSWORD> -X PUT "https:// <repoUrl>/<DEBIAN_PACKAGE_NAME>;deb.distribution=<DISTRIBUTION>;deb.component=<COMPONENT>;deb.architecture=<ARCHITECTURE>" -T <PATH_TO_FILE>
In this command, USERNAME, PASSWORD, and repoUrl can be obtained from the Debian upload command in the configuration file downloaded in 3.
- USERNAME: username used for uploading files, which can be obtained from the Debian configuration file. For details, see the example figure.
- PASSWORD: password used for uploading files, which can be obtained from the Debian configuration file. For details, see the example figure.
- repoUrl: URL used for uploading files, which can be obtained from the Debian configuration file. For details, see the example figure.

DEBIAN_PACKAGE_NAME, DISTRIBUTION, COMPONENT, and ARCHITECTURE can be obtained from the Debian package to be uploaded.
The a2jmidid_8_dfsg0-1_amd64.deb package is used as an example.
- DEBIAN_PACKAGE_NAME: software package name, for example, a2jmidid_8_dfsg0-1_amd64.deb.
- DISTRIBUTION: release version, for example, trusty.
- COMPONENT: component name, for example, main.
- ARCHITECTURE: system architecture, for example, amd64.
- PATH_TO_FILE: local storage path of the Debian package, for example, /root/a2jmidid_8_dfsg0-1_amd64.deb.
The following figure shows the complete commands.

- After the commands are successfully executed, go to the self-hosted repo page and find the uploaded Debian package.
Obtaining a Dependency from a Debian Repository
The following procedure uses the Debian package released in Releasing a Package to a Debian Repository as an example to describe how to obtain a dependency from a Debian repository.
- Download the public key file of the Debian repository by referring to Releasing a Package to a Debian Repository.
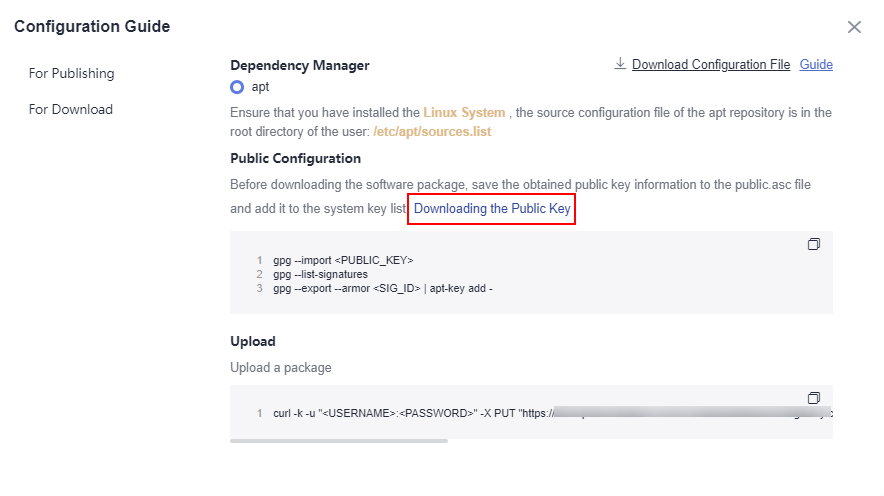
- Import the gpg public key.
gpg --import <PUBLIC_KEY_PATH>
PUBLIC_KEY_PATH: local path for storing the Debian public key, for example, artifactory.gpg.public.

- Add the public key to the list of keys used by apt to authenticate packages.
gpg --export --armor <SIG_ID> | apt-key add -

- Add the apt repository source.
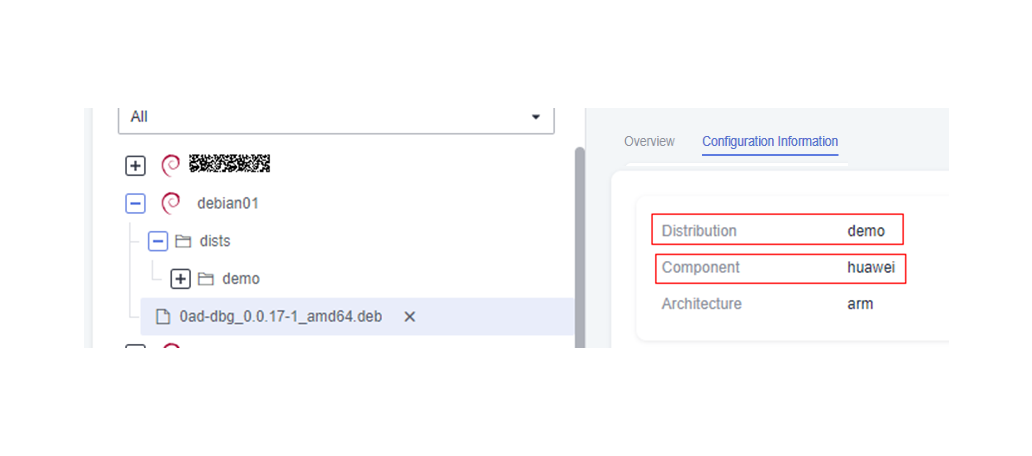
Open the configuration file (for details about how to obtain the file, see Releasing a Package to a Debian Repository), replace all DISTRIBUTION fields with the value of COMPONENT (for example, main) used for uploading the Debian file, and add the repository source based on the downloaded configuration file sources.list.
- After the repository source is added, run the following command to update the repository source:
apt-get update

- Run the following command to download the Debian package: Replace a2jmidid with the actual value of PACKAGE.
apt download a2jmidid
To obtain <PACKAGE>, perform the following steps:
Download the Packages source data of the Debian package. The following uses the a2jmidid package as an example.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





