Adding Request Information (Response Extraction)
If multiple packets exist in the same case, use regular expressions or JSON to extract the output of the previous packet for the input of the next packet.
For example, in an e-commerce flash sale scenario, after you search for a product and purchase it, you can use the response extraction function to extract the product ID obtained from packet search and use the ID as the input parameter of the next purchase packet.
Notes and Constraints
- Cross-case extraction is not supported. That is, the output extracted from case A's packet cannot be used for the input of case B's packet.
- The variables from a response extraction are local variables.
- After an array is extracted from a response variable, the array can only be used as the input of the array variable in the next packet. Each field in the array cannot be used separately.
Video Tutorial
This video demonstrates how to extract responses.
Procedure
- Log in to the CodeArts PerfTest console and choose PerfTest Projects in the navigation pane.
- Click the name of the desired PerfTest project to go to the details page.
- On the Cases tab page, select the desired test case in the case list on the left.
- On the Case Script tab page, select a case, and click Add Request.
- On the Response Extraction tab page, set the basic information by referring to Table 1.
Table 1 Response extraction parameters Parameter
Description
Enable Response Extraction
After response extraction is enabled, if multiple packets exist in the same case, you can use regular expressions or JSON to extract the output of the previous packet for the input of the next packet.
Variable Name
Must be unique. The value of the response extraction is assigned to this variable.
Expected Value
Expected variable value of response extraction.
If you enable this option, the extracted value is compared with the expected value. If they are different from each other, the URL verification will fail.
Extraction Range
Range of the content to be extracted.
The packet content, header, and URL can be extracted using regular expressions.
Regular Expression
A regular expression specifies a type of logical expressions performed on strings. In a regular expression, you use certain predefined strings and a combination of these strings to form a rule string that is used to specify a specific filtering logic.
Parentheses () indicate extraction and are used to enclose content to be extracted. The content in a pair of parentheses forms a sub-expression.
A complete regular expression consists of two types of characters: special characters (also called meta characters) and literal or common text characters (such as letters, digits, and underscores). For details about meta characters, see Regular Expression Metacharacters.
Sequence Number of Matching Item
This parameter indicates the sequence number of the matched content extracted through a regular expression. This parameter cannot be set to 0.
Value range: positive integers
Expression Value
This parameter indicates the sequence number of the parsed sub-expression.
- Value 0 indicates that the entire regular expression is matched.
- Value 1 indicates that the first sub-expression of the regular expression is matched, that is, the content extracted by the first ().
Value range: natural numbers
After extracting content through Regular Expression and Sequence Number of Matching Item, use Expression Value to obtain the final content.
Key Name
Enter the key name to be obtained. This parameter is valid only when Extraction Range is set to Parameter values in .json files.
For example, to extract v42 from {"key":{"key1":"v1","key2":{"key3":"v3"},"key4":[{"key41":"v41","key42":"v42"},{"key41":"v43","key42":"v44"}]}}, enter key.key4[0].key42.
Default Value
Value extracted when a regular expression match or JSON extraction fails.
Condition Expression
This parameter is used together with the Key Name to be obtained.
For example, {"key":{"key1":"v1","key2":{"key3":"v3"},"key4":[{"key41":"v41","key42":"v42"},{"key41":"v43","key42":"v44"}]}}. If you want to describe when key42 is equal to v42, extract the target value v41, you can enter key.key4[].key42=v42 for Condition Expression, and enter key.key4[].key41 for Key Name.
Table 2 Common regular expressions Regular Expression
Description
Example
(\d+)
Matches non-negative integers.
String:
bTivm2wu9jih1LBKR4osZGrjjl
Match results:
2 9 1 4
([A-Za-z]+)
Matches a string of letters.
String:
bTivm2wu9jih1LBKR4osZGrjjl
Match results:
bTivm wu jih LBKR osZGrjjl
([A-Za-z0-9]+)
Matches a string of digits and letters.
String:
bTivm2wu9jih1LBKR4osZGrjjl:asdasd22
Match results:
bTivm2wu9jih1LBKR4osZGrjjl asdasd22
(\w+)
Matches a string of digits, letters, or underscores (_).
String:
bTivm2wu9jih1LBKR4osZGrjjl:asdasd22
Match results:
bTivm2wu9jih1LBKR4osZGrjjl asdasd22
([\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)*@[\w-]+(\.[\w-]+)+)
Matches email addresses.
String:
bTivm2wu9jih1LBKR4osZGrjjl:abc@abc.com
Match results:
abc@abc.com
- (Optional) A request can contain one or more variables. If you need to add multiple variables for a request, click Add Variable and set related parameters.
- When the configuration is complete, click Save.
Examples of Regular Expression Response Extraction
Example 1
The response content of the previous packet is as follows:
"baseInfo" : {
"mobilephone":"xxxxxxxxxxx",
"Telephone":"xxxxxxxxxxx",
"unitGuid":"xx",
"unitName":null,
"address":"xxx",
"gender" : 0,
"imageUrl" :null
},
"UserNotices":null
},
"msgId" : "64xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxf5",
"isUsed" :"1",
"token":"eyxxxxxxxxxxxJ9.eyJzdW1101JYZMiLCJcUbdGUkIJezMT!!zz#z!20TxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxS1611dYQISHTFKifVOsImd1aWQi0ilOODkiLCJleHAiOjEiMzIizNzY1MjZ9.myU5idiASM-11@EP7YQTfTsR_8zsq7?sbYJYoxfRsuf6OZhGL-XWmjnvdaviGauhSdw16ImWOFEvbACSHMXGT1U0ijS5z6ezX@sZePruzFnvcIMgShF8xNPN6zVokQp-uwbyS3W6NpZpDuwsjuiZ7DZTNpKoqCkGHwvPJrHBOrWFR_u6-FBbTiFiqdhQb95U-1gLiLvoZHY_rguzwyrZ-leGRdCG_ZASreoWC-uH)HnqltpgItrChWQToHQyxOABdMSbBSHhNctBBZHgQPMESqQQQTbBiPGvbQDprB7ZBFMUB_ShynS_evtyfEladGEddhOBn-fxxxxxxxxxxx"
},
To extract the token value, use the regular expression "token"\s*:\s*"(.*?)". The configuration of response extraction is shown as follows:
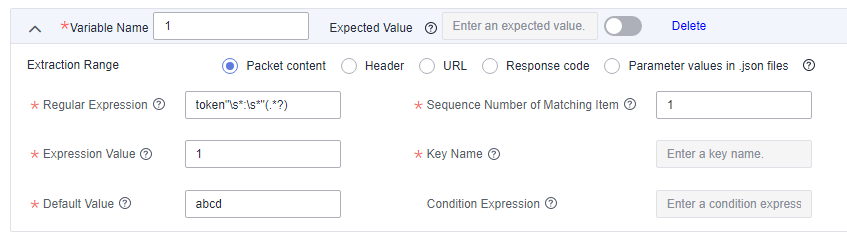
Example 2
The response content of the previous packet is as follows:
javawind:9javawind:12 javawind:16javawind:17 javawind:46javawind:22
To extract the value 16, see the following figure.
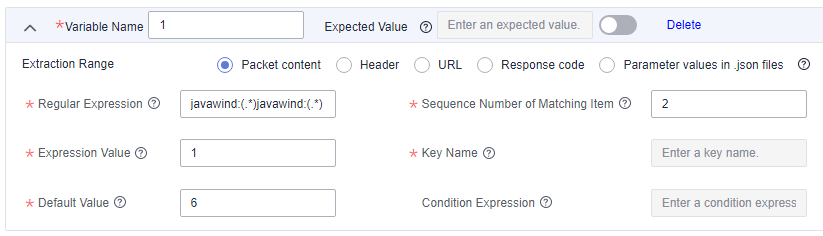
- The following data is extracted using the regular expression javawind:(.*)javawind:(.*).
9 12 16 17 46 22
- The following data is extracted using the second matching item.
16 17
- The following data is extracted using the first expression.
16
Example 3
The packet content is ababdacac.
Response extraction settings:
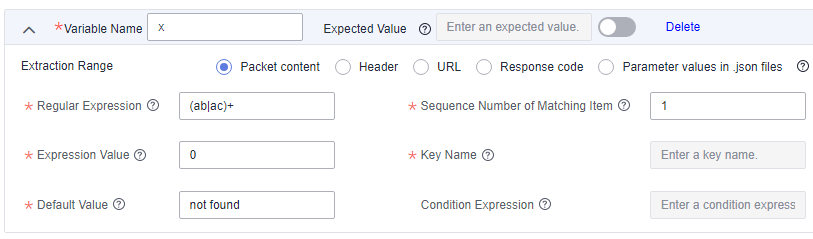
Regular Expression: (ab|ac)+ indicates that multiple ab or ac values are matched.
Sequence Number of Matching Item: 1, indicating that the matching item is matched by ab. 2, indicating that the matching item is matched by ac. 1 may be used to obtain abab and a substring ab, and 2 may be used to obtain acac and a substring ac.
Expression Value: The value 0 indicates that the maximum matching string abab or acac is used. The value 1 indicates that the substring ab or ac is used.
Example 4
The extracted content is Content-Type in the HTTP response header.
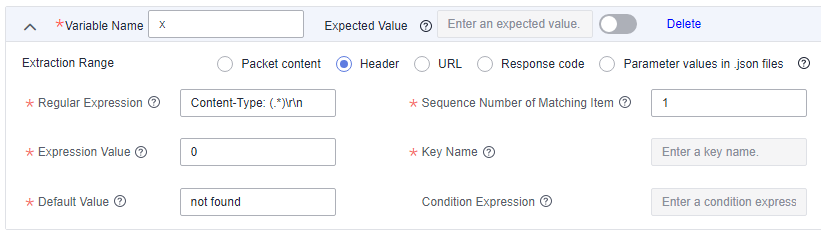
Regular Expression: Content-Type: (.*)\r\n. Note that there is a space after the colon (:) and \r\n is at the end, which is generated based on HTTP specifications.
Sequence Number of Matching Item: 1, because there is only one (.*).
Expression Value: 1, indicating that the expected value is obtained.
Examples of JSON Expression Response Extraction
The sample data is as follows:
{
"name": {
"first": "Tom",
"last": "Anderson"
},
"age": 37,
"children": ["Sara","Alex","Jack"],
"fav.movie": "Deer Hunter",
"friends": [{
"first": "Dale",
"last": "Murphy",
"age": 44,
"nets": ["ig","fb","tw"]
},
{
"first": "Roger",
"last": "Craig",
"age": 68,
"nets": ["fb","tw"]
},
{
"first": "Jane",
"last": "Murphy",
"age": 47,
"nets": ["ig","tw"]
}]
}
Example 1
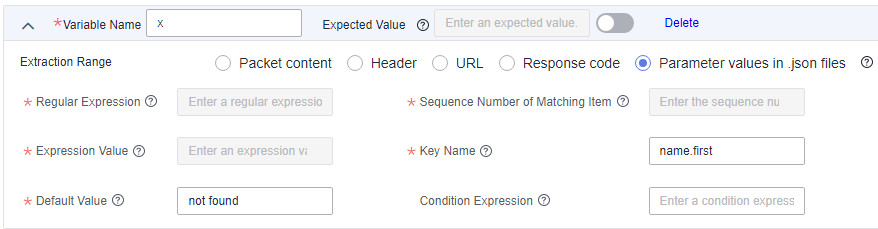
To extract the first name, set Key Name to name.first.
Example 2
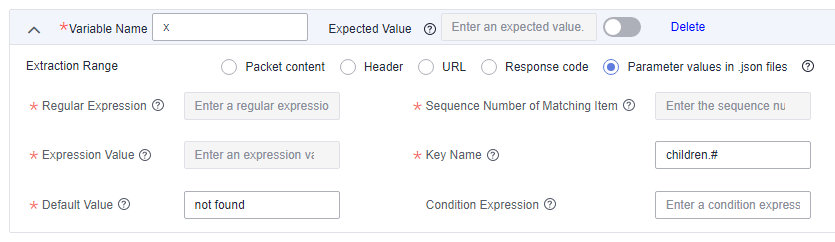
To extract the number of Tom's children, set Key Name to children.#.
Example 3
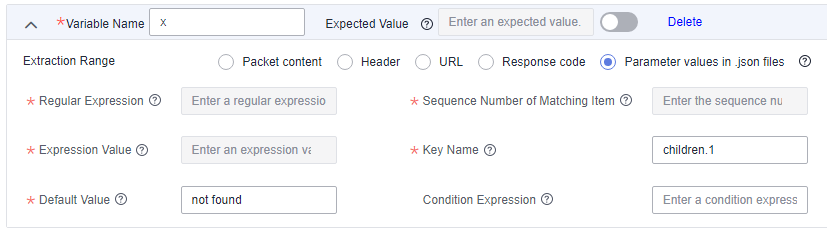
To extract the name of Tom's second child, set Key Name to children.1. (Sequence number starts from 0.)
Example 4
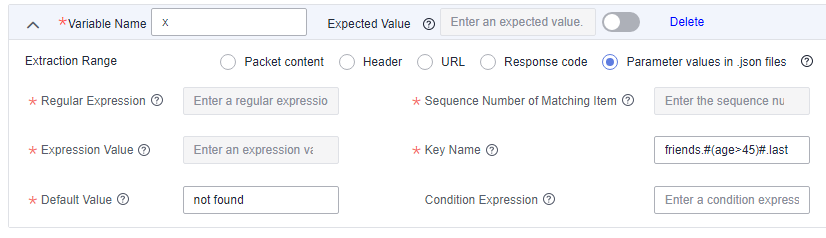
To extract the last names of Tom's friends older than 45, set Key Name to friends.#(age>45)#.last.
Example 5
To extract the first name of Tom's friend whose last name is Murphy, set Key Name to friends.#(last=="Murphy")#.first.
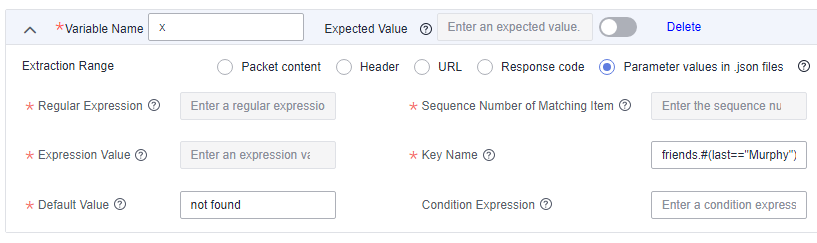
Example 6
To extract the second nickname of Tom's first friend, set Key Name to friends.0.nets.1. (Sequence number starts from 0.)
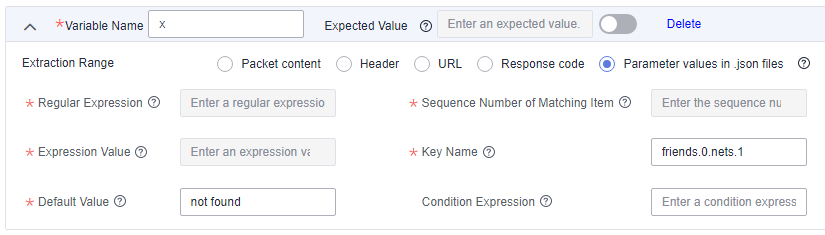
Example 7
To extract the first name of Tom's friend whose nickname is fb, set Key Name to friends.#(nets.#(=="fb"))#.first.
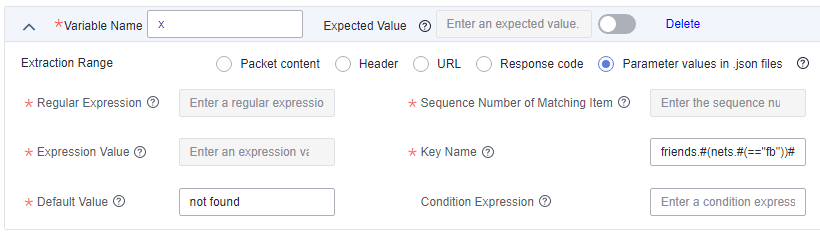
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





