Obtaining a Long-Term Login or Image Push/Pull Command
Scenarios
When you use a container engine client to push or pull images, you can use a temporary or long-term command to connect to SWR.
- For Docker, you can obtain a long-term login command. If you just push or pull images occasionally, a temporary command will be enough for you.
- For containerd, you can obtain a long-term pull/push command. If you just push or pull images occasionally, a temporary command will be enough for you.

Keep the long-term login command of Docker containers and the long-term push/pull command of containerd containers secure to prevent information leakage.
For details, see What Are the Differences Between Long-Term and Temporary Login Commands?
This section describes how to obtain a long-term Docker login command and containerd push or pull command.
A temporary login command will expire in six hours. If the command expires, clear the browser cache before you generate a new one.
To be better compatible with the new IAM console, enhanced commands are introduced. To distinguish from them, existing commands are renamed as standard commands. An enhanced command simplifies permission control by removing SWR-based authorization. Only IAM-based authorization is used for easier but more comprehensive permission control over image push and pull. For more information, see Table 1.
|
Difference |
Standard Login Command |
Enhanced Login Command |
|---|---|---|
|
Scope |
Unlimited |
Available only on the new IAM console. |
|
Validity period |
There are temporary and long-term login commands. For details about their differences, see What Are the Differences Between Long-Term and Temporary Login Commands? |
For security purposes, only temporary login commands are provided, with a validity period of 24 hours. |
|
Permissions control |
IAM-based permission control. For details, see Configuring Permissions in IAM. SWR-based permission control. For details, see Configuring Permissions in SWR. |
Only IAM-based permission control is provided. For details, see Configuring Permissions in IAM. For enhanced login commands, IAM condition keys are enhanced. For details, see Table 2. |
|
Interconnection with log auditing |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Condition keys |
See Table 2. |
See Table 2. |
|
Condition Key |
Standard Login Command |
Enhanced Login Command |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Temporary Login Command |
Long-Term Login Command |
||
|
g:CalledVia |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:CalledViaFirst |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:CalledViaLast |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:PrincipalTag/tag-key |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
g:MFAAge |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
g:MFAPresent |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
g:SourceIdentity |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
g:TokenIssueTime |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
g:ViaService |
No |
No |
Yes |
|
g:DomainId |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
g:DomainName |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalAccount |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalUrn |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalIsService |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalIsRootUser |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalServiceName |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalType |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalId |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:UserName |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:UserId |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalOrgPath |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalOrgId |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:PrincipalOrgManagementAccountId |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:ResourceOrgId |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:ResourceOrgPath |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:Referer |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:SecureTransport |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:SourceIp |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:SourceVpc |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:SourceVpce |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:UserAgent |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:RequestedRegion |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:RequestTag/tag-key |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:ResourceAccount |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
g:ResourceTag/tag-key |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:TagKeys |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:EnterpriseProjectId |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:SourceAccount |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:SourceUrn |
No |
No |
No |
|
g:CurrentTime |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
How to Obtain
Perform the following operations to obtain a long-term Docker login command and containerd push or pull command.
- Obtain the programming access permission. (If you already have the programming access permission, skip this step.)
- Log in to the IAM console as an administrator.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - In the user list, search for the user you want to grant programmatic access to.
- Click the user to go to its details page. Click
 next to Access Type. Select Programmatic access. (You can also select both.)
Figure 1 Changing the access type
next to Access Type. Select Programmatic access. (You can also select both.)
Figure 1 Changing the access type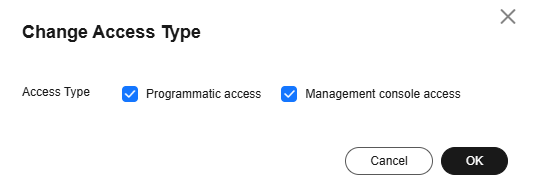
- Obtain an AK/SK. (If you already have an AK/SK, skip this step.)
Ensure that you have permission to access the IAM service. For details about the authorization, see Creating a User Group and Assigning Permissions.
- Log in to the IAM console, hover the cursor over the username, and click My Credentials.
- In the navigation pane, choose Access Keys and click Create Access Key.
- Enter a description, and click OK.
- In the displayed dialog box, click Download.
- After the credential is downloaded, obtain the AK and SK from the credentials.csv file.
Table 3 Example of credentials.csv Username
Access Key ID
Secret Access Key
a*****
RVHVMX******
H3nPwzgZ******
Each credential file can be downloaded only once. Keep it secure.
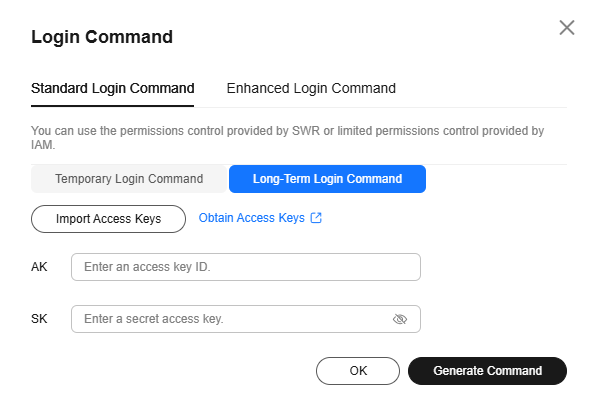
- Log in to the SWR console.
- Click Generate Login Command. Click Standard Login Command. On the Long-Term Login Command tab, click Import Access Keys to upload credentials.csv or enter the Access Key ID and Secret Access Key contained in credentials.csv that is obtained in 2. Then click Generate Command. If your console does not have the Long-Term Login Command tab, skip this step and manually concatenate a long-term login command by taking the following steps.
- Obtain the project name and image registry address.
- Log in to the IAM console.
- Hover the cursor over the username in the upper right corner.
- Choose My Credentials from the drop-down list.
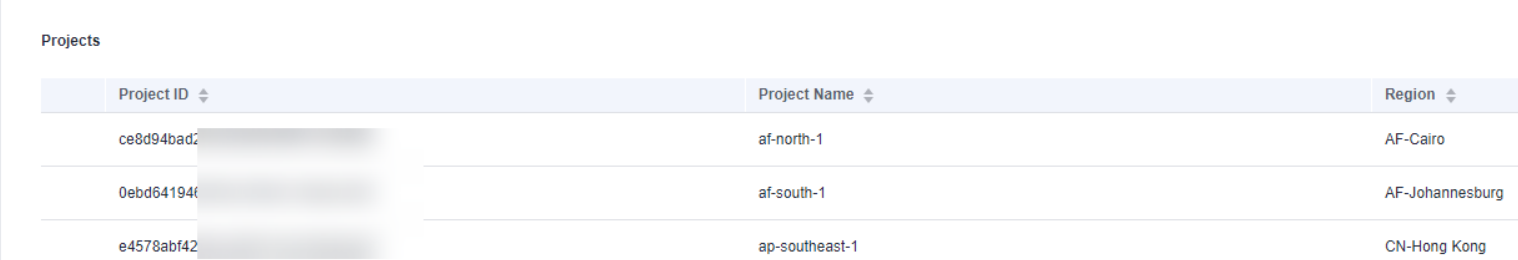
- In the project list, find the region and project your VM belongs to.
Figure 2 Region and project
- Log in to a Linux PC and run the following command to obtain a login key:
printf "$AK" | openssl dgst -binary -sha256 -hmac "$SK" | od -An -vtx1 | sed 's/[ \n]//g' | sed 'N;s/\n//'
Replace AK with the access key ID and SK with the secret access key in the credentials file obtained in 2.
Example:
printf "RVHVMX******" | openssl dgst -binary -sha256 -hmac "H3nPwzgZ******" | od -An -vtx1 | sed 's/[ \n]//g' | sed 'N;s/\n//'
After the command is executed, the following login key is obtained:
cab4ceab4a1545***************
The login key is an example only.
- Use all the information you obtained to generate a long-term login command in the following format:
docker login -u [project-name]@[AK] -p [login-key] [image-registry-address]
The project name and registry address are obtained in 5, the AK in 2, and the login key in 6.
Example:
docker login -u ap-southeast-3@RVHVMX****** -p cab4ceab4a1545*************** swr.ap-southeast-3.myhuaweicloud.com
If "Login Succeeded" is displayed, the login is successful.
- The login key is encrypted and cannot be decrypted. So, other users cannot obtain your SK from -p.
- The login command can be executed on other Docker clients.
- (Optional) When you log out of the registry, run the following commands to delete your authentication information:
cd /root/.docker/ rm -f config.json
- (Optional) Run history -c to delete the operation records.
- Gain programmatic access. If you already have it, skip this step.
- Log in to the IAM console as an administrator.
- Click
 in the upper left corner and select a region and a project.
in the upper left corner and select a region and a project. - In the user list, search for the user you want to grant programmatic access to.
- Click the user to go to its details page. Click
 next to Access Type. Select Programmatic access. (You can also select both.)
Figure 3 Changing the access type
next to Access Type. Select Programmatic access. (You can also select both.)
Figure 3 Changing the access type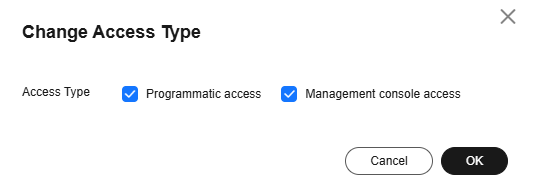
- Obtain an AK/SK. If you already have it, skip this step.
Ensure that you have permission to access the IAM service. For details about the authorization, see Creating a User Group and Assigning Permissions.
- Log in to the IAM console, hover the cursor over the username, and click My Credentials.
- In the navigation pane, choose Access Keys and click Create Access Key.
- Enter a description, and click OK.
- In the displayed dialog box, click Download.
- After the credential is downloaded, obtain the AK and SK from the credentials.csv file.
Table 4 Example of credentials.csv Username
Access Key ID
Secret Access Key
a*****
RVHVMX******
H3nPwzgZ******
Each credential file can be downloaded only once. Keep it secure.
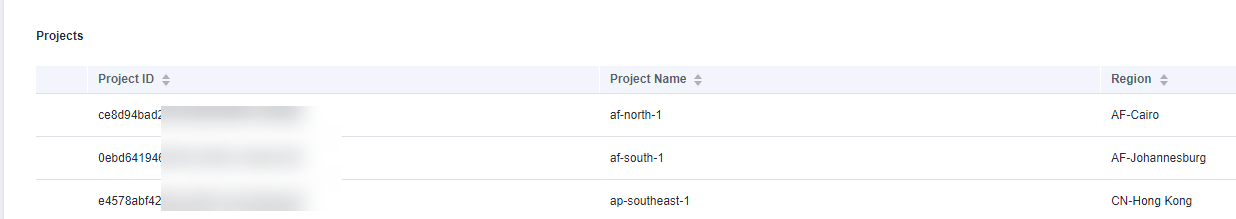
- Obtain the project name and image registry address.
- Log in to the IAM console.
- Hover the cursor over the username in the upper right corner.
- Choose My Credentials from the drop-down list.
- In the project list, find the region and project your VM belongs to.
Figure 4 Region and project
- Use the project information you obtained to generate an image registry address in the format of swr.project-name.myhuaweicloud.com.
For example, if the VM of user a***** belongs to AP-Singapore, the image registry address will be swr.ap-southeast-3.myhuaweicloud.com.
- Log in to a Linux PC and run the following command to obtain a login key:
printf "$AK" | openssl dgst -binary -sha256 -hmac "$SK" | od -An -vtx1 | sed 's/[ \n]//g' | sed 'N;s/\n//'
Replace AK with the access key ID and SK with the secret access key in the credentials.csv file in 2.
Example:
printf "RVHVMX******" | openssl dgst -binary -sha256 -hmac "H3nPwzgZ******" | od -An -vtx1 | sed 's/[ \n]//g' | sed 'N;s/\n//'
After the command is executed, the following login key is obtained:
cab4ceab4a1545***************
The login key is an example only.
- Concatenate the obtained information to form a long-term containerd command.
1. Image pull command
ctr image pull --user [project-name]@[AK]:[login-key] [image-repository-address]/{organization-name}/{image-name}:{tag}
In the command, the project name and image registry address are obtained in 3, the AK is the Access Key Id field in the credentials.csv file obtained in 2, and the login key is the execution result in 4.
2. Image push command
ctr image push --user [project-name]@[AK]:[login-key] [image-repository-address]/{organization-name}/{image-name}:{tag}
In the command, the project name and image registry address are obtained in 3, the AK is the Access Key Id field in the credentials.csv file obtained in 2, and the login key is the execution result in 4.
- The login key is encrypted and cannot be decrypted into an SK.
- The commands can be executed on other servers running containerd to pull and push images.
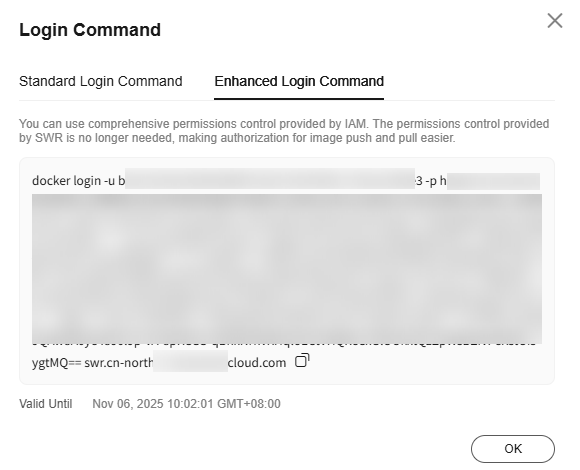
Obtaining an Enhanced Login Command for Docker
- Log in to the SWR console.
- Click Login Command. On the Enhanced Login Command tab, click the copy icon next to the command to copy the login command.
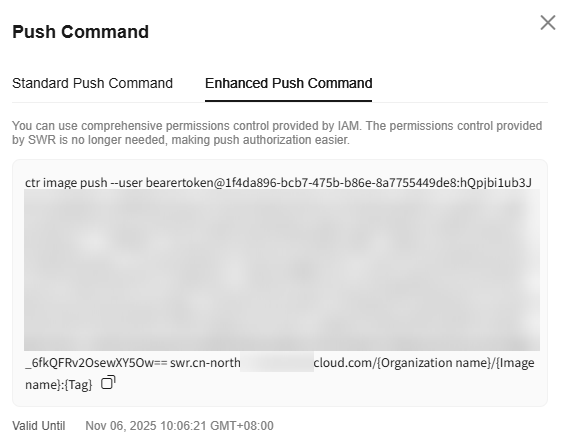
Obtaining Enhanced Upload and Download Commands for containerd
- Log in to the SWR console.
- In the navigation pane, choose My Images. Then click the name of the target image.
- On the image details page, click the Pull/Push tab, and click Push Command or Pull Command. On the Enhanced Push Command or Enhanced Pull Command tab, click copy icon next to the command to copy the login command.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





