Running Shell Commands
This action aims to run the Shell commands in a host in a specified environment.
Configuring Deployment Actions
- Create an application by referring to Creating an Application.
- On the Deployment Actions page, add this deployment action based on the service scenario.
- Configure the action using the parameters described in the table below.
Table 1 Parameters Parameter
Description
Action Name
Custom action name. Enter 1 to 128 characters. Do not start or end with a space. Use letters, digits, spaces, and these special characters: -_,;:./()
Environment
Deployment object. Select an environment whose resource type is host cluster.
Shell Commands
Bash scripts to run.
Action Control
Whether to enable the settings.
- Keep running on failure: Continue the task even if this action fails.
- Execute this action with the sudo permission: Use the sudo permission to deploy this action.
Example: Using Shell Commands to Check Service Logs
After application deployment is complete, you can run the shell commands to view the service startup or execution logs.
Preparations
- Ensure that you are an authorized user of a host. Only authorized users have the permissions required to view service startup or execution logs.
- Obtain the full path of the service startup log. For example, the full path of the startup log of Tomcat is as follows:
/usr/local/tomcat/apache-tomcat-8.5.38/logs/catalina.out
Procedure
- Run the tail command to query the service startup or execution logs.
- Run the following command to query the last 20 lines of the log. The following figure shows the command output.
tail -n 20 /usr/local/tomcat/apache-tomcat-8.5.38/logs/catalina.out
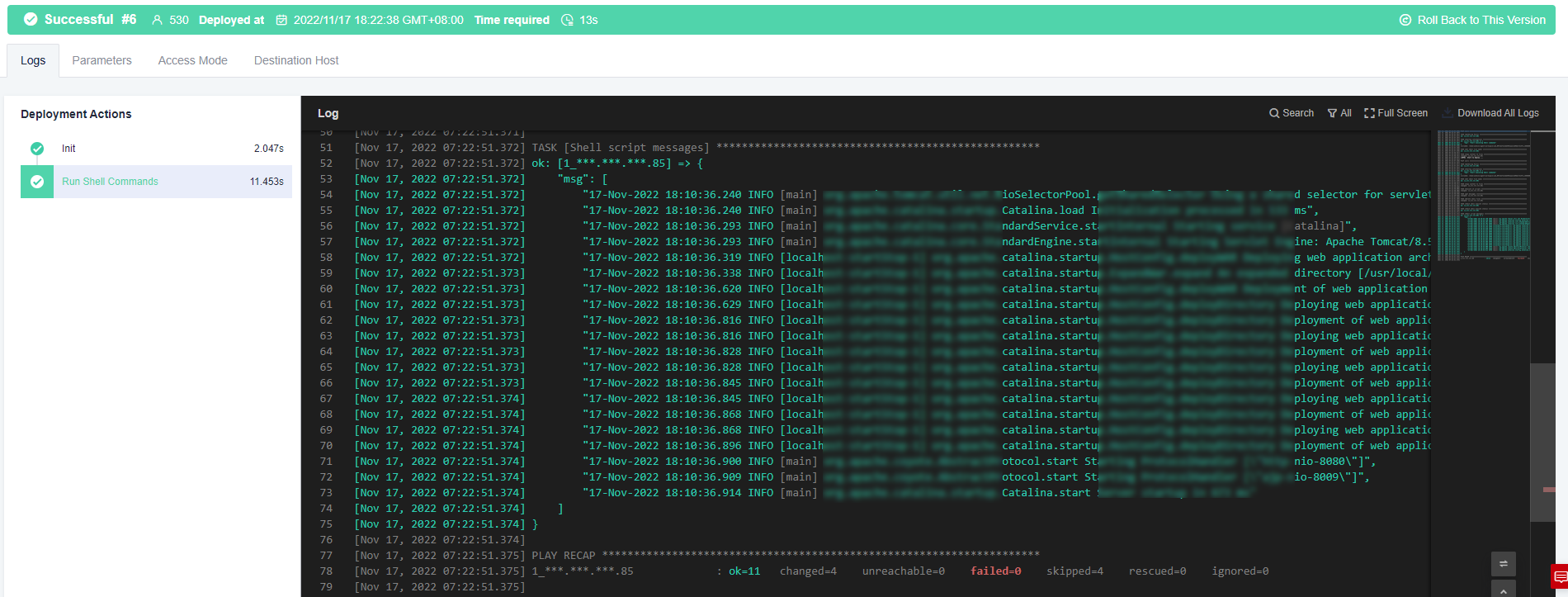
Do not run the cat command when running the shell command to check files. If the log file is too large, it may take some time to load data. Do not use the tail –f command.
If the shell command to be executed contains more than 10,240 characters, you are advised to Run Shell Script extension.
Helpful Links
If you encounter any problem during deployment, see Running Shell Commands.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





