Syntax of RBAC Policies
Policy Structure
An RBAC policy consists of a Version, a Statement, and Depends.

Policy Syntax
Click  to view the details of a policy. The DDS Administrator policy is used as an example to describe the syntax of RBAC policies.
to view the details of a policy. The DDS Administrator policy is used as an example to describe the syntax of RBAC policies.
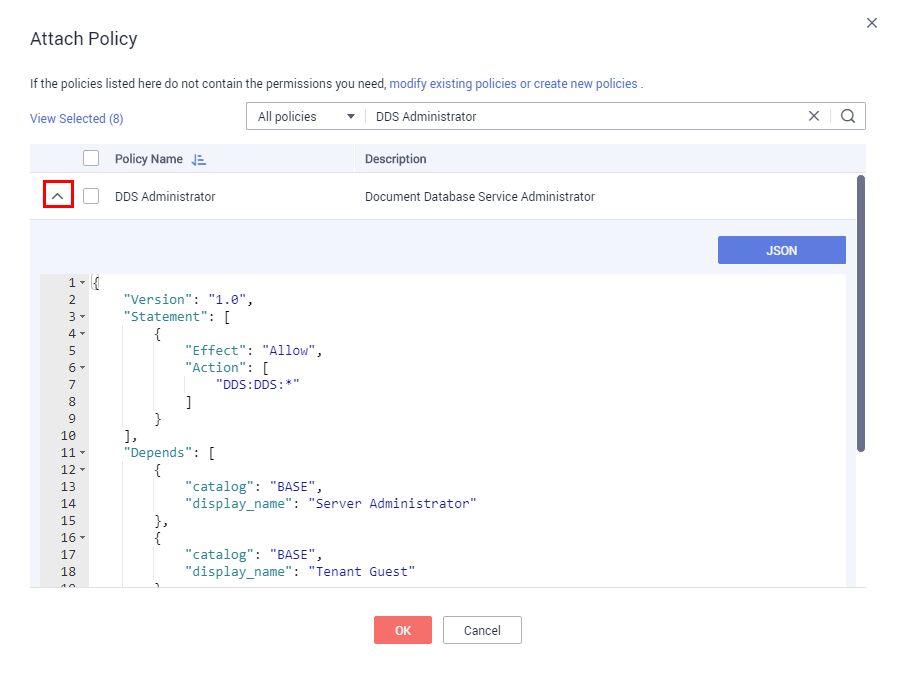
{
"Version": "1.0",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"DDS:DDS:*"
],
"Resource": [
"DDS:*:*:instanceName:dds-*"
],
}
],
"Depends": [
{
"catalog": "BASE",
"display_name": "Server Administrator"
},
{
"catalog": "BASE",
"display_name": "Tenant Guest"
}
]
}
|
Parameter |
Meaning |
Value |
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Version |
Policy version |
The value is fixed at 1.0. |
|
|
Statement |
Action |
Operations to be performed on DDS. |
Format: Service name:Resource type:Operation DDS:DDS:*: Permissions for performing all operations on all resource types in DDS. |
|
Effect |
Determines whether the operation defined in an action is allowed. |
|
|
|
Resource |
Defines resource authentication. |
This parameter is optional. DDS:*:*:instanceName:dds-* indicates that the user has the configured action permissions on all instances whose names start with dds-. If this parameter is not specified, the user has the permissions on all instances by default. |
|
|
Depends |
catalog |
Name of the service to which dependencies of a policy belong |
Service Name Example: BASE |
|
display_name |
Name of a dependent policy |
Permission name Example: Server Administrator |
|






