Creating an Elasticsearch Cluster (New Version)
You can use Elasticsearch clusters created in CSS for purposes like log analytics, data search, real-time data analytics, and more.
You can create an Elasticsearch cluster in either of the following ways:
- Method 1: Create an Elasticsearch cluster on the CSS management console. This topic provides the operation guide for the default UI (that is, the new UI). For the operation guide for the old UI, see Creating an Elasticsearch Cluster (Old Version).
To improve efficiency in creating clusters, CSS has made several enhancements on the cluster creation page in terms of ease-of-use. Being more intuitive, the new UI streamlines cluster creation procedures.
- Method 2: Create an Elasticsearch cluster using CSS APIs. For details, see Creating a Cluster.
Prerequisites
- You have planned the Elasticsearch cluster configuration by following the guidelines in Elasticsearch Cluster Planning Suggestions, including the cluster size, node configuration, and storage capacity requirements.
- You have created a VPC, subnet, and security group beforehand, or you can create them when creating the cluster. For more information, see Virtual Private Cloud User Guide.
- If you are going to enable automatic snapshot creation for the cluster, make sure you have created an OBS bucket for storing snapshots. The OBS bucket must be in the same region as the Elasticsearch clusters, and the storage class must be Standard or Warm.
Impact on Billing
- If you enable automatic snapshot creation, automatically created snapshots will be stored in standard OBS buckets, and you will need to pay extra for the storage. For more information, see Billing Overview.
- VPC endpoints, if created for the cluster, will incur extra fees, depending on the resource usage. For details, see VPC Endpoint Billing.
Video Tutorial
This video demonstrates how to create a pay-per-use Elasticsearch cluster with the security mode enabled.
Opening the Create Cluster Page
- Log in to the CSS management console.
- In the navigation pane on the left, choose Clusters > Elasticsearch.
- In the upper right corner, click Create Cluster. The new-version UI for creating a cluster is displayed by default.
Figure 1 Create Cluster (new version)
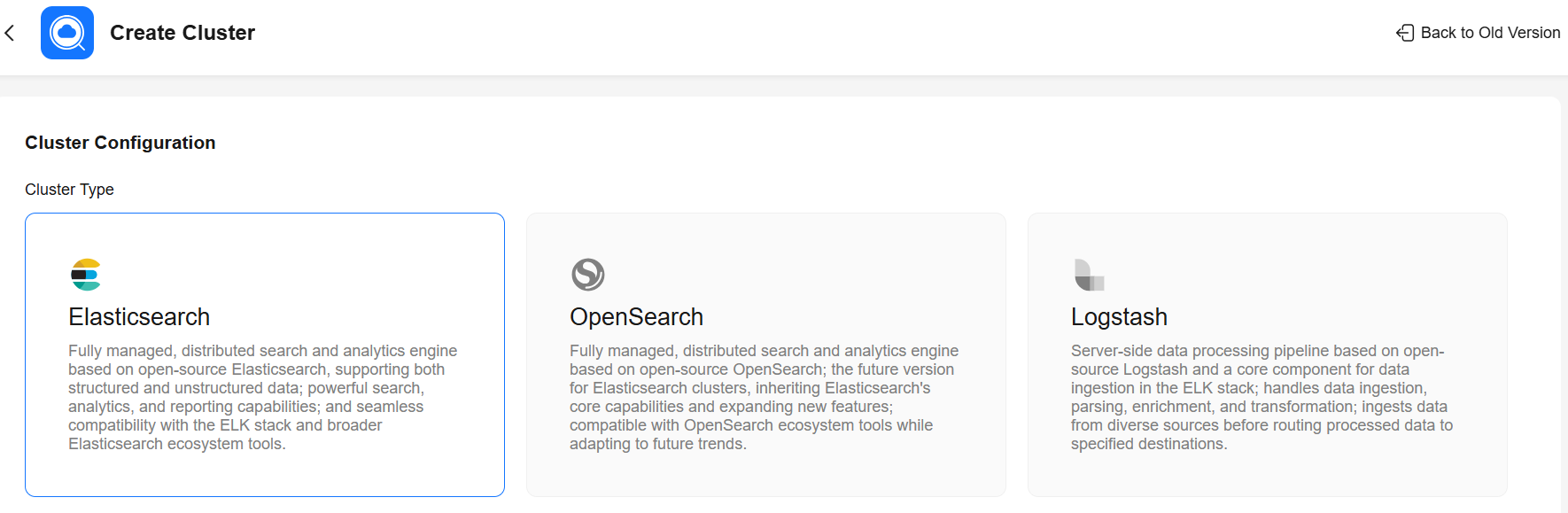
Cluster Configuration
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Cluster Type |
Select Elasticsearch. |
|
Cluster Version |
Select a cluster version from the drop-down list. |
Basic Settings
Select the region, billing mode, and AZ of the cluster.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Region |
Select the region where the cluster is located. A region is the location of a physical data center. Regions are defined based on their geographical location and network latency. For lower network latency and quicker resource access, select the nearest region. |
|
AZ |
Select one or more AZs associated with the cluster region. An AZ is a physical region where resources use independent power supplies and networks. AZs are physically isolated but interconnected through an internal network. A maximum of three AZs can be configured. For details about the use of multiple AZs, see Suggestions on Multi-AZ Deployment. |
|
Billing Mode |
Billing mode for the cluster, which can be Yearly/Monthly or Pay-per-use.
|
Data Nodes
Configure the cluster's data nodes.
- If the cluster has no client nodes, the data nodes will need to handle the additional task of query request distribution and data analysis.
- If the cluster has no master nodes, the data nodes will also need to handle cluster management.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CPU Architecture |
Select the CPU architecture of the data nodes. x86 and Kunpeng nodes are supported. The architectures actually supported may vary depending on the regional environment. |
|
Node Specifications |
Select the specifications of the data nodes. Click Available. On the displayed page, select a flavor that suits your needs. The nodes may use either local or EVS disks. For more information about different node specifications, see ECS Types. In the node flavor list, vCPUs | Memory indicate the number of vCPUs and memory capacity available for each flavor, and Recommended Storage indicates the supported storage capacity range. The node flavors available may vary depending on the region you select.
WARNING:
|
|
Node Storage Type and Capacity |
Select the storage type and capacity of the data nodes.
|
|
Nodes |
Set the number of data nodes for the cluster.
If the number of data nodes in your cluster is not evenly divisible by the number of AZs, data distribution may become unbalanced across nodes. This will negatively impact both query and write performance. |
Master Nodes
Configure master nodes for the cluster. By default, master nodes are not enabled. To enable master nodes, select Master Node, and configure the node settings.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CPU Architecture |
Select the CPU architecture of the master nodes. x86 and Kunpeng nodes are supported. The architectures actually supported may vary depending on the regional environment. |
|
Node Specifications |
Select the specifications of the master nodes. Click Available. On the displayed page, select a flavor that suits your needs. Master nodes support EVS disks only. For more information about different node specifications, see ECS Types. In the node flavor list, vCPUs | Memory indicate the number of vCPUs and memory capacity available for each flavor. The node flavors available may vary depending on the region you select. |
|
Node Storage Type and Capacity |
Select the storage type and capacity of the master nodes.
|
|
Nodes |
Set the number of master nodes for the cluster. The value can be 3, 5, 7, or 9. |
Client Nodes
Configure client nodes for the cluster. By default, client nodes are not enabled. To enable client nodes, select Client Node, and configure the node settings.
Client nodes route and coordinate search and index requests, offloading processing from data nodes for enhanced query performance and cluster scalability when there are heavy loads.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CPU Architecture |
Select the CPU architecture of the client nodes. x86 and Kunpeng nodes are supported. The architectures actually supported may vary depending on the regional environment. |
|
Node Specifications |
Select the specifications of the client nodes. Click Available. On the displayed page, select a flavor that suits your needs. Client nodes support EVS disks only. For more information about different node specifications, see ECS Types. In the node flavor list, vCPUs | Memory indicate the number of vCPUs and memory capacity available for each flavor. The node flavors available may vary depending on the region you select. |
|
Node Storage Type and Capacity |
Select the storage type and capacity of the client nodes.
|
|
Nodes |
Set the number of client nodes for the cluster. Value range: 1 to 64 |
Cold Data Nodes
Configure cold data nodes for the cluster. By default, cold data nodes are not enabled. To enable cold data nodes, select Cold Data Node, and configure the node settings.
Cold data nodes are used to store and query large quantities of latency-insensitive data. They offer an effective way to manage large datasets while cutting storage costs. When cold data nodes are enabled, you can switch between cold and hot data storage. For details, see Switching Between Hot and Cold Storage for an Elasticsearch Cluster. If there are no cold data nodes, we recommend that you use decoupled storage and compute, which can also cut storage costs. For details, see Configuring Decoupled Storage and Compute for an Elasticsearch Cluster.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
CPU Architecture |
Select the CPU architecture of the cold data nodes. x86 and Kunpeng nodes are supported. The architectures actually supported may vary depending on the regional environment. |
|
Node Specifications |
Select the specifications of the cold data nodes. Click Available. On the displayed page, select a flavor that suits your needs. The nodes may use either local or EVS disks. For more information about different node specifications, see ECS Types. In the node flavor list, vCPUs | Memory indicate the number of vCPUs and memory capacity available for each flavor, and Recommended Storage indicates the supported storage capacity range. The node flavors available may vary depending on the region you select.
WARNING:
|
|
Node Storage Type and Capacity |
Select the storage type and capacity of the cold data nodes.
|
|
Nodes |
Set the number of cold data nodes for the cluster. Value range: 1 to 32 If the number of cold data nodes in your cluster is not evenly divisible by the number of AZs, data distribution may become unbalanced across nodes. This will negatively impact both query and write performance. |
Network Settings
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
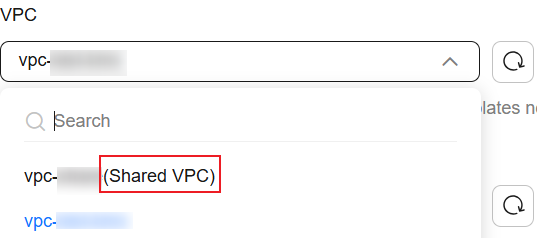
VPC |
Select a VPC for the cluster for proper network isolation. You can select a shared VPC, which is indicated by Shared VPC in the VPC name. To create a CSS cluster in a shared VPC, the default vpc subnet statement permission is required.
VPC sharing allows you to centrally manage resources across multiple accounts, helping to improve resource management efficiency and reduce O&M costs. For more information about shared VPCs, see VPC Sharing. If none of the existing VPCs meets your requirements, click Create VPC to create one. (Make sure you have the permission to create VPCs.) For details, see Creating a VPC and Subnet. |
|
Subnet |
Select a subnet for the cluster. A subnet improves network security by providing exclusive network resources that are isolated from other networks. Select a subnet in the current VPC. Or you can select a subnet under a shared VPC. The owner of a VPC can share the VPC to specified users. If no existing subnets meet your requirements, click Create Subnet to create a new subnet. For details, see Creating a VPC and Subnet. |
|
IPv4 Address |
Assign IPv4 addresses to cluster nodes.
|
|
Security Group |
Select a security group for the cluster. A security group serves as a virtual firewall that provides access control policies for clusters. To select a security group that meets your requirements, click View Security Group to go to the security group list, where you can check the details of each security group. The selected security group must allow port 9200 in the inbound direction. Otherwise, the cluster may be inaccessible to external services. Furthermore, to enable Kibana private network access, port 5601 must also be allowed. If none of the existing security groups meets your requirements, click Create Security Group to create one. (Make sure you have the permission to create security groups.) For details, see Creating a Security Group. |
Security Mode
Configure the cluster's security mode and access methods. The security mode is enabled by default when you create a cluster. To disable it, deselect Security Mode.
- Disabling the security mode: Use when creating a cluster for internal testing or workloads that have a low security standard. When the security mode is disabled, HTTP is used, data is transmitted in plaintext, and no user authentication is required for cluster access. Make sure the cluster is deployed in a secure environment. Do not expose the cluster's network interface to the public network.
- Security mode + HTTP: Use to balance security and performance. In this setting, user authentication is required for cluster access, yet data is transmitted via HTTP.
- Security mode + HTTPS: Use when security takes precedence over performance. In this setting, user authentication is required for cluster access, and data is transmitted via HTTPS in ciphertext.

HTTPS, public network access, and Kibana public network access can be enabled only when the security mode is enabled.
Cluster Management
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Cluster Name |
User-defined cluster name. The cluster name must start with a letter and can contain 4 to 32 characters. Only letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_) are allowed. |
|
Add Description |
Add a description for the cluster for easy recognition. Click + Add Description and then enter a description of the cluster. The value can contain 0 to 128 characters. |
|
Enterprise Project |
Associate the cluster with an enterprise project. An enterprise project groups cloud resources, so you can manage resources and members by project. The default project is default. If enterprise projects are enabled, you can select an enterprise project from the drop-down list. You can click View Enterprise Projects to go to the Enterprise Project Management Service console and check enterprise project details. For more information, see Accessing the Enterprise Center. |
|
Tags |
Adding tags to clusters helps you identify and manage your cluster resources. Click + Add. You can select existing tag keys and values from the drop-down lists or enter new ones. If you want to use the same tag to identify multiple cloud resources for better resource grouping, we recommend that you predefine tags in Tag Management Service (TMS). For details, see Predefined Tags. Each cluster can have a maximum of 20 tags. If your organization has configured tag policies for CSS, add tags to clusters based on these policies. If a tag does not comply with the tag policies, cluster creation may fail. Contact the administrator to learn more about tag policies. |
Automatic Snapshot Creation
 to expand More Settings and configure automatic snapshot creation. Automatic snapshot creation is disabled by default. To enable it, select Automatic Snapshot Creation, and configure the necessary settings. You are advised to enable automatic snapshot creation to have data backed up periodically, thus improving cluster reliability. If you choose not to enable it, enable replicas when creating indexes to prevent data loss.
to expand More Settings and configure automatic snapshot creation. Automatic snapshot creation is disabled by default. To enable it, select Automatic Snapshot Creation, and configure the necessary settings. You are advised to enable automatic snapshot creation to have data backed up periodically, thus improving cluster reliability. If you choose not to enable it, enable replicas when creating indexes to prevent data loss.

If you enable automatic snapshot creation, automatically created snapshots will be stored in standard OBS buckets, and you will need to pay extra for the storage. For more information, see Billing Overview.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
OBS Bucket |
From the drop-down list, select an OBS bucket for storing snapshots. If no OBS buckets meet your requirements, click Create Bucket to go to the OBS console and create one. For details, see Creating a Bucket. To grant an IAM user access to an OBS bucket, you need to grant the GetBucketStoragePolicy, GetBucketLocation, ListBucket, and ListAllMyBuckets permissions to that user. |
|
Backup Path |
Snapshot storage path in the OBS bucket.
The backup path cannot:
CAUTION:
Only standard OBS storage can be used to store snapshots. Do not apply OBS lifecycle rules to the backup path. |
|
Maximum Backup Rate (per Second) |
The parameter sets the maximum backup rate per node. When it is exceeded, flow control is triggered to prevent excessive resource usage and ensure system stability. The actual backup rate may not reach the configured value, as it depends on factors such as OBS performance and disk I/O.
Value format: number + unit
Default value: 40 MB The value 0MB means there is no limit on how fast data is backed up to snapshots. An overly high backup rate may lead to excessive resource usage, which may impact cluster stability. Therefore, set this parameter carefully. |
|
Maximum Recovery Rate (per Second) |
The parameter sets the maximum recovery rate per node. When it is exceeded, flow control is triggered to prevent excessive resource usage and ensure system stability. The actual recovery rate may not reach the configured value, as it depends on factors such as OBS performance and disk I/O.
Value format: number + unit
Default value:
An overly high recovery rate may lead to excessive resource usage, which may impact cluster stability. Configure this parameter carefully to maintain optimal performance.
For Elasticsearch clusters later than 7.6.2, the recovery rate is also limited by the indices.recovery.max_bytes_per_sec parameter.
NOTE:
|
|
IAM Agency |
Select an IAM agency to grant the current account the permission to access and use OBS. To store snapshots to an OBS bucket, you must have the required OBS access permissions.
WARNING:
The agency name can contain only letters (case-sensitive), digits, underscores (_), and hyphens (-). Otherwise, the backup will fail. |
|
Snapshot Name Prefix |
A snapshot name consists of the snapshot name prefix and timestamp, for example, snapshot-1566921603720. The snapshot name prefix can contain 1 to 32 characters. It must start with a lowercase letter, and it can only contain lowercase letters, digits, hyphens (-), and underscores (_). The default value is snapshot. |
|
Time Zone |
Select a time zone for the backup start time. |
|
Backup Start Time |
Specify the start time of auto backup. Select a value from the drop-down list. The interval can be Daily, Hourly, or weekly (by selecting a specific day of the week), and the backup time can be set to any hour from 00:00 to 23:00 (full hours only). |
|
Retained Snapshots |
Number of automatically created snapshots to be retained. The value ranges from 1 to 90. The system automatically deletes excess snapshots every half hour. (The expiration deletion policy applies only to the snapshots that were automatically created at the same frequency as the current automatic snapshot creation policy.)
NOTE:
If the snapshot creation interval is short or if the data size of indexes is large, the number of automatic snapshots retained may not reach the value set using this parameter. |
VPC Endpoint
Expand More Settings and configure a VPC endpoint for the cluster. VPC endpoint is disabled by default. To enable it, select VPC Endpoint, and configure the necessary settings.

- If a shared VPC and a subnet within this shared VPC were selected earlier for the cluster, VPC Endpoint cannot be enabled.
- VPC endpoints, if created for the cluster, will incur extra fees, depending on the resource usage. For details, see VPC Endpoint Billing.
- You need specific permissions to create VPC endpoints. For details, see VPCEP Permissions.
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Create Private Domain Name |
Whether to create a private domain name for the VPC endpoint.
|
|
Configure Whitelist |
Add accounts that are allowed to access the cluster through the VPC endpoint service. Click Add to add accounts in Account ID.
|
Kibana Public Network Access
Expand More Settings and configure Kibana public network access for the cluster. Kibana public network access is disabled by default. To enable it, select Kibana Public Network Access, and configure the necessary settings.

This parameter is available only when the security mode is enabled for the cluster.
Quantity
|
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Required Duration |
Set the duration of your subscription in the range of 1 month to 3 years. If you plan to use the cluster for more than nine months, you should choose a yearly subscription for a better price. |
|
Auto-renew |
Whether to automatically renew the subscription. By default, auto-renewal is disabled. To enable it, select Auto-renew. When Auto-renew is selected, a yearly/monthly subscription is automatically renewed upon expiry.
For more information, see Auto-Renewal Rules. |
Submit
- In the Configuration Summary panel, review the cluster configuration details.
Any mandatory fields that are missing are displayed in red, and you have to set them in the configuration area.
- Click Create Now.
Cluster creation time depends on the number of nodes. Typically, this process takes less than 60 minutes, though clusters with a large number of nodes may require additional time.
- Return to the cluster list and check the newly created cluster.
If the cluster is created successfully, Cluster Status changes to Available.
Related Documents
- For details about how to check basic cluster information, such as the cluster status, private IP address, and node information, see Viewing Elasticsearch Cluster Information.
- For details about the methods you can use to access an Elasticsearch cluster, see Elasticsearch Cluster Access Methods.
- You can enhance cluster performance by properly planning the number of index shards. For details, see How Do I Plan the Quantity of Index Shards for a Cluster?
- For how to optimize the write and query performance of a cluster and improve cluster utilization, see Optimizing the Write Performance of a Cluster and Optimizing the Query Performance of a Cluster.
- For details about how to migrate data from Elasticsearch clusters elsewhere to Elasticsearch clusters in CSS, see About Elasticsearch Cluster Migration Solutions.
- For details about how to synchronize data from other products to CSS's Elasticsearch clusters, see Using Logstash to Synchronize Data to Elasticsearch.
- For a security-mode cluster, you need to specify the administrator account and password for cluster access. You are advised to create roles and users with the corresponding permissions on the Kibana console. For details, see Creating Users for an Elasticsearch Cluster and Granting Cluster Access.
- If cluster creation fails, follow the guidelines in Why Does Cluster Creation Fail? for troubleshooting.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot