Preparing Virtualized GPU Resources
CCE uses xGPU virtualization technologies to dynamically divide the GPU memory and computing power. A single GPU can be virtualized into a maximum of 20 virtual GPU devices. This section describes how to implement GPU scheduling and isolation capabilities on GPU nodes.
Prerequisites
|
Item |
Supported Version |
|---|---|
|
Cluster version |
v1.23.8-r0, v1.25.3-r0, or later |
|
OS |
Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0 with the kernel version of 5.10 or later |
|
GPU type |
Tesla T4 and Tesla V100 |
|
Driver version |
535.216.03, 535.54.03, 510.47.03 (EOL), and 470.57.02 (EOL)
NOTE:
CCE AI Suite (NVIDIA GPU) of versions later than v2.7.84 are no longer compatible with GPU drivers that have reached EOL. Upgrade the drivers in use to supported versions. |
|
CUDA version |
CUDA 12.2.0 to 12.8.0 |
|
Runtime |
containerd |
|
Add-on |
The following add-ons must be installed in the cluster:
|
Step 1: Enable GPU Virtualization
Both CCE AI Suite (NVIDIA GPU) and Volcano Scheduler must be installed in the cluster.
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Settings.
- Switch to the Heterogeneous Resources tab and enable GPU Virtualization. You can configure GPU virtualization by cluster or by node pool.
- Cluster-level GPU virtualization:
- Enable GPU Settings > GPU Virtualization. After this function is enabled, GPU virtualization is enabled globally by default, and the compute power and GPU memory of a single GPU can be split.
- In Default Cluster Driver, select a driver that supports GPU virtualization.
- In the lower right corner of the page, click Confirm Settings.
Figure 1 Enabling cluster-level GPU virtualization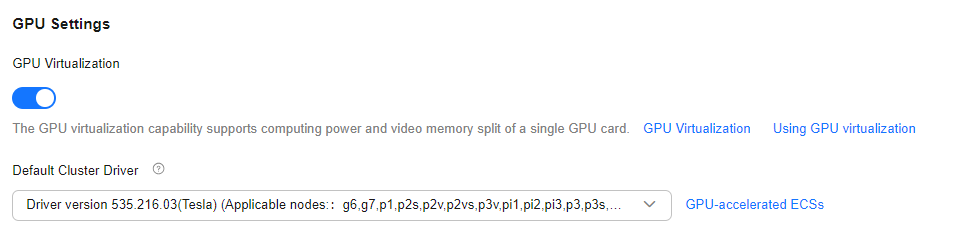
- Node pool-level GPU virtualization: If CCE AI Suite (NVIDIA GPU) of version 2.7.2 or later is installed, GPU virtualization can be configured by node pool.
- In Node Pool Configurations under GPU Settings, click Add.
- In the Node Pools list, select the node pool where you want to enable GPU virtualization and choose a driver that supports GPU virtualization from Driver. After you customize a GPU driver for a node pool, nodes in that pool will preferentially use the custom driver. Nodes for which no driver is specified will use the cluster's default driver.

- The specified driver version will be installed for new nodes added to the pool. This configuration does not affect existing nodes in the pool.
- An updated driver version applies only to new nodes added to the node pool. Existing nodes must be restarted to apply the changes.
- Click
 under GPU Virtualization to enable GPU virtualization for the node pool. To configure GPU virtualization for multiple node pools, click Add.
under GPU Virtualization to enable GPU virtualization for the node pool. To configure GPU virtualization for multiple node pools, click Add. - In the lower right corner of the page, click Confirm Settings.
Figure 2 Enabling node pool-level GPU virtualization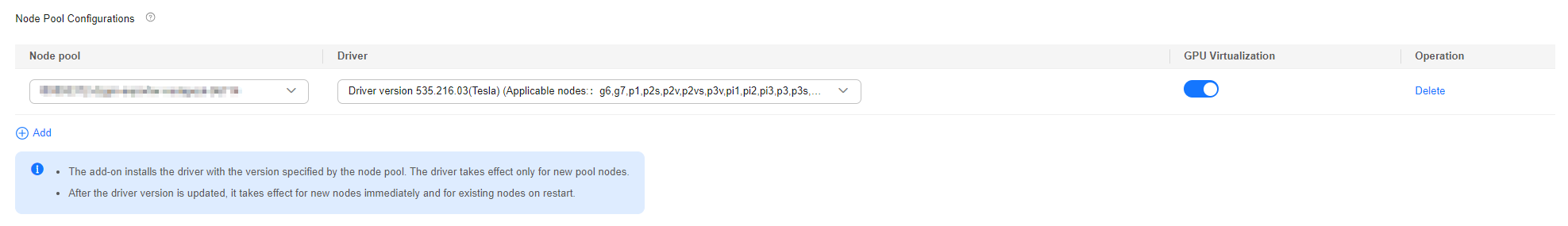
- Cluster-level GPU virtualization:
- After configuring GPU virtualization, verify the settings.
In the navigation pane, choose Cluster > Nodes. In the right pane, click the Nodes tab and find the node where GPU virtualization has been configured. In the Operation column of the target node, choose More > View YAML. If the node-status.volcano.sh/nvidia value in the YAML file is {"enableXGPU":true}, GPU virtualization has been configured on the node.
Figure 3 Verifying GPU virtualization
Step 2: Create a GPU Node
Create nodes that support GPU virtualization in the cluster to use the GPU virtualization function. For details, see Creating a Node or Creating a Node Pool. If there are GPU nodes in your cluster that meet the prerequisites requirements, skip this step.

Step 3 (Optional): Modifying the Volcano Scheduling Policy
The default scheduling policy of Volcano for GPU nodes is Spread. If the node configurations are the same, Volcano selects the node with the minimum number of running containers, so that containers can be evenly allocated to each node. In contrast, the bin packing policy attempts to schedule all containers to one node to avoid resource fragmentation.
If the bin packing policy is required when the GPU virtualization feature is used, you can modify the policy in the advanced settings of the Volcano add-on. The procedure is as follows:
- Log in to the CCE console and click the cluster name to access the cluster console. In the navigation pane, choose Settings.
- On the Scheduling tab, switch from kube-scheduler to Volcano in the Default Scheduler area, locate the expert mode, and click Refresh.

- Modify the Volcano scheduling configuration.
- In the nodeorder add-on, add the arguments parameter and set leastrequested.weight to 0. That is, set the priority of the node with the fewest allocated resources to 0.
- Add the bin packing add-on, and customize the weights of virtualized GPU resources (volcano.sh/gpu-core.percentage and volcano.sh/gpu-mem.128Mi).
Example:... default_scheduler_conf: actions: allocate, backfill, preempt tiers: - plugins: - name: priority - enablePreemptable: false name: gang - name: conformance - plugins: - enablePreemptable: false name: drf - name: predicates - name: nodeorder arguments: leastrequested.weight: 0 # Set the priority of the node with the least allocated resources to 0. - plugins: - name: cce-gpu-topology-predicate - name: cce-gpu-topology-priority - name: xgpu - name: binpack # Add the bin packing add-on and specify the weights of virtualized GPU resources. arguments: binpack.resources: volcano.sh/gpu-core.percentage,volcano.sh/gpu-mem.128Mi binpack.resources.volcano.sh/gpu-mem.128Mi: 10 binpack.resources.volcano.sh/gpu-core.percentage: 10 - plugins: - name: nodelocalvolume - name: nodeemptydirvolume - name: nodeCSIscheduling - name: networkresource ... - Click Save.
Helpful Links
To create a workload that uses GPU virtualization, see Using GPU Virtualization.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





