Como ativar e exibir o binlog da minha instância de TaurusDB?
Esta seção descreve como ativar e exibir o binlog e o impacto no desempenho de TaurusDB após a ativação do binlog.
- Ativação do binlog
- Visualização de arquivos de binlog
- Impacto da ativação do binlog no desempenho de TaurusDB
Ativação do binlog
Binlog não pode ser ativado para réplicas de leitura de TaurusDB.
- Faça logon no console de gerenciamento.
- Clique em
 no canto superior esquerdo e selecione uma região e um projeto.
no canto superior esquerdo e selecione uma região e um projeto. - Clique em
 no canto superior esquerdo da página e escolha Databases > TaurusDB.
no canto superior esquerdo da página e escolha Databases > TaurusDB. - Clique no nome da instância para acessar a página Basic Information.
- No painel de navegação, escolha Parameters.
- Configure os parâmetros da seguinte forma:
- Se a versão do kernel for anterior a 2.0.45.230900, procure o parâmetro log-bin, selecione ON na caixa de listagem suspensa na coluna Value e clique em Save. O valor do parâmetro modificado é aplicado somente após a reinicialização da instância de banco de dados. Para obter detalhes sobre o impacto e as precauções da reinicialização de uma instância de BD, consulte Reinicialização de uma instância de BD.
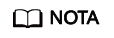 Para exibir a versão do kernel, clique no nome da instância para acessar a página Basic Information. Na área Configuration, verifique o campo Kernel Version.Figura 1 Visualização da versão do kernel
Para exibir a versão do kernel, clique no nome da instância para acessar a página Basic Information. Na área Configuration, verifique o campo Kernel Version.Figura 1 Visualização da versão do kernel
- Se a versão do kernel for 2.0.45.230900 ou posterior, pesquise o parâmetro rds_global_sql_log_bin, selecione ON na caixa de listagem suspensa na coluna Value e clique em Save. O valor do parâmetro modificado é aplicado imediatamente. Você não precisa reinicializar a instância de BD.
Depois que esse parâmetro for alterado, conecte-se ao banco de dados e execute o seguinte comando para verificar se o binlog está ativado para todos os threads:
select @@session.rds_sql_log_bin_inconsistent_count;
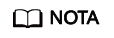
rds_sql_log_bin_inconsistent_count indica o número de usuários cujo valor de sql_log_bin é inconsistente com o valor de rds_global_sql_log_bin.
- Se a saída do comando for 0, o binlog está ativado com sucesso para todos os threads e todas as instruções podem ser registradas no binlog. Em seguida, um backup completo pode ser realizado.
- Se o comando de saída não for 0, execute o seguinte comando para verificar os IDs dos threads para os quais o binlog não está ativado:
As instruções executadas nos IDs de thread consultados não podem ser registradas no binlog temporariamente.
Verifique seus serviços com base nos IDs de thread obtidos (por exemplo, 53 em Figura 2), envie ou reverta transações e execute novas transações (por exemplo, SELECT 1;) em tempo hábil com base nos requisitos de serviço ou desconecte conexões ociosas e reconecte-as.
- Se a versão do kernel for anterior a 2.0.45.230900, procure o parâmetro log-bin, selecione ON na caixa de listagem suspensa na coluna Value e clique em Save. O valor do parâmetro modificado é aplicado somente após a reinicialização da instância de banco de dados. Para obter detalhes sobre o impacto e as precauções da reinicialização de uma instância de BD, consulte Reinicialização de uma instância de BD.
Visualização de arquivos de binlog
- Conecte-se a uma instância de BD. Para obter detalhes, consulte Conexão a uma instância de BD.
- Execute o seguinte comando para exibir arquivos de binlog:
SHOW BINLOG EVENTS [IN 'log_name'] [FROM pos] [LIMIT [offset,] row_count];
Se uma mensagem indicando que as permissões da conta são insuficientes, use a conta root.
Impacto da ativação do binlog no desempenho de TaurusDB
A ativação do binlog não afeta as operações de SELECT, mas afeta INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE e outras operações de gravação.
Não há diferenças significativas entre binlog de TaurusDB e binlog do MySQL de código aberto. A sintaxe de binlog do TaurusDB é totalmente compatível com a do MySQL de código aberto.