Obtaining the Length of a String
In DWS, you can use the following functions to obtain the length of a string, including the number of bits, bytes, and characters. For details about the differences among bits, bytes, and characters, see Overview of String Processing Functions and Operators.
|
Type |
Description |
Function |
Example |
Usage Difference |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Bits |
Obtain the number of digits in a string. |
|
- |
|||
|
Bytes |
Obtain the number of bytes in all string types. |
|
The functions of octet_length(string) and lengthb(string) are the same. When developing cross-platform databases such as MySQL and DWS, octet_length(string) is preferred. lengthb(string) is a mapping function for compatibility with Oracle and is used only for Oracle migration. lengthb(text/bpchar) is the same as lengthb(string), but its input parameter is of the text or bpchar type. |
|||
|
Obtain the number of bytes in all string types (only for compatibility with Oracle). |
|
|||||
|
Obtain the number of bytes in text and bpchar (only for compatibility with Oracle). |
|
|||||
|
Characters |
Obtain the number of characters in a string. |
|
length(string) is equivalent to char_length(string), but its format is simpler. |
|||
|
Obtain the number of characters in a string in the specified encoding format. |
- |
- |
bit_length(string)
Description: Obtains the number of bits in a string. That is, the number of bytes multiplied by 8. The number of bits in a string depends on the database encoding mode. For example, in GBK, a Chinese character is 2 bytes. In UTF-8 and SQL_ASCII, a Chinese character is 3 bytes.
Return type: integer
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT bit_length('world'); bit_length ------------ 40 (1 row) |
octet_length(string)
Description: Obtains the number of bytes in a string. It is important for processing multi-byte characters (such as UTF-8 characters and special symbols) and can accurately obtain the storage size of a string.
Return type: integer
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT octet_length('data'); octet_length -------------- 4 (1 row) |
lengthb(string)
Description: Obtains the length of a string in bytes. It shares the same functions as octet_length(string) and is only used for compatibility with Oracle. If data is migrated from Oracle, use lengthb(string). However, if workloads need to run across databases (for example, DWS and MySQL), use octet_length(string) because MySQL does not have the lengthb function.
The return result depends on character sets (GBK and UTF-8).
Return type: integer
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT lengthb('hello'); lengthb --------- 5 (1 row) |
lengthb(text/bpchar)
Description: Obtains the number of bytes of a specified string. The input parameter can be text or bpchar (equivalent to CHAR(n)).
- lengthb(text) indicates the byte length of actual characters (without padding spaces), which is suitable for most scenarios.
- lengthb(bpchar) indicates the byte length of a fixed-length string (including padding spaces), which is suitable for strict fixed-length scenarios (such as fixed-length codes and certificate numbers). It is not recommended for daily use (implicit problems may be caused by space padding).
Return type: integer
- For a string containing newline characters, for example, a string consisting of a newline character and a space, the value of length and lengthb in DWS is 2.
- This function returns the number of bytes in a specified string. For multi-byte character encoding, such as UTF-8, one character may occupy multiple bytes.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT lengthb('hello'); lengthb --------- 5 (1 row) |
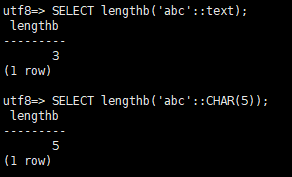
Examples of input parameters of the text and bpchar types:
1 2 3 4 |
-- Case 1: Specify the input parameters as text. SELECT lengthb('abc'::text); -- 'abc' occupies 3 bytes (UTF-8), and the returned value is 3. -- Case 2: Specify the input parameters as bpchar or CHAR(5). SELECT lengthb('abc'::CHAR(5)); -- The value is stored as 'abc..', and the returned value is 5 (each space occupies 1 byte). |
char_length(string) or character_length(string)
Description: Obtains the number of characters in a string.
Return type: integer
For multi-byte character encoding (such as UTF-8), one character may occupy multiple bytes.
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT char_length('hello'); char_length ------------- 5 (1 row) |
length(string)
Description: Obtains the character length (number of characters) of a string. It is equivalent to char_length(string) and is simpler.
Return type: integer
Example:
1 2 3 4 5 |
SELECT length('database'); length -------- 8 (1 row) |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





