REINDEX
Description
Rebuilds an index using the data stored in the index's table, replacing the old copy of the index.
There are several scenarios in which REINDEX can be used:
- An index has become corrupted, and no longer contains valid data.
- An index has become "bloated", that is, it contains many empty or nearly-empty pages.
- You have altered a storage parameter (such as a fill factor) for an index, and wish that the change takes full effect.
Precautions
- REINDEX DATABASE and REINDEX SYSTEM type cannot be performed in transaction blocks.
- Currently, only REINDEX INDEX and REINDEX TABLE are supported for global secondary indexes.
- If the index contains the lpi_parallel_method option and the value is PARTITION, and the parallel_workers value of the index's table is greater than 0, the index cannot be rebuilt in parallel. If the index does not contain the lpi_parallel_method option or the value of the option is set to AUTO, page-level parallel index is rebuilt by default. For details, see LPI_PARALLEL_METHOD.
- When REINDEX CONCURRENTLY is used to rebuild indexes online, the index sequence in the table changes, and the query plan may change.
Syntax
- Rebuild an ordinary index.
1REINDEX { INDEX | [INTERNAL] TABLE | DATABASE | SYSTEM } [ CONCURRENTLY ] name [ FORCE ];
- Rebuild the index and convert the type.
1REINDEX [ ( option [, ...] ) ] { INDEX } [ CONCURRENTLY ] name [ FORCE ];
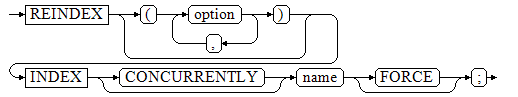
- Rebuild an index partition.
1 2
REINDEX { INDEX | [INTERNAL] TABLE } name PARTITION partition_name [ FORCE ];
Parameters
- INDEX
Rebuilds the specified index.
- TABLE
Rebuilds all indexes of a specified table. If a table has a TOAST table, the table will also be reindexed. If an index on the table has been invalidated by running alter unusable, the index cannot be rebuilt. Indexes in the TOAST table cannot be rebuilt when specifying the CONCURRENTLY option.
- DATABASE
Rebuilds all indexes within the current database. Indexes in the TOAST table within the current database cannot be rebuilt when specifying the CONCURRENTLY option.
- SYSTEM
Rebuilds all indexes on system catalogs within the current database. Indexes on user tables are not processed.
- option
Currently, only CROSSBUCKET is supported, and the value can only be ON or OFF. This parameter is used to determine whether the index of a hash bucket table is converted to a cross-bucket index (CBI) or local-bucket index (LBI). This conversion supports only the index of the distributed hash bucket table and does not support the GSI index. In the current version, only the session of the scale-out process can use the online index type conversion.
- CONCURRENTLY
Rebuilds an index (with ShareUpdateExclusiveLock) in non-blocking DML mode. When an index is rebuilt, other statements cannot access the table on which the index depends. If this keyword is specified, DML is not blocked during the rebuilding. Indexes in system catalogs cannot be rebuilt online. REINDEX INTERNAL TABLE CONCURRENTLY, REINDEX SYSTEM CONCURRENTLY, and REINDEX INVALID INDEX CONCURRENTLY are not supported. When REINDEX DATABASE CONCURRENTLY is executed, all indexes on user tables in the current database are rebuilt online (indexes on system catalogs are not processed). REINDEX CONCURRENTLY cannot be executed within a transaction. Online index rebuilding supports only B-tree and UB-tree indexes, ordinary indexes, global indexes, and local indexes. PCR UB-tree indexes and level-2 partitions are not supported. GSIs can be rebuilt online using REINDEX INDEX CONCURRENTLY, but expression GSIs and partial GSIs cannot be rebuilt online. During online GSI rebuild, do not execute DDL statements concurrently with other DDL statements. Otherwise, deadlocks and errors may occur. You can reconnect to the client and try again. Online parallel index rebuilding supports only ordinary indexes, global indexes, and local indexes of Astore and Ustore, and GSIs of Ustore. Other online index rebuilding specifications are inherited from the current version. If online index rebuilding fails, the system automatically clears new indexes to prevent resource occupation in scenarios such as manual cancellation, duplicate unique index key values, insufficient resources, thread startup failure, and lock timeout. If the system cannot automatically clear invalid new indexes (for example, the database breaks down, FATAL, or PANIC), you need to manually clear invalid new indexes (using the DROP INDEX statement) and temporary tables (using the DROP TABLE statement) as soon as possible to prevent more resources from being occupied. Generally, the suffix of an invalid index is _ccnew. For GSIs, the prefix of an invalid new index is ccgsi_tmp_index_. In the distributed system, failed indexes in DNs are automatically cleared and those in CNs need to be manually cleared. If a critical error occurs, the metadata of the failed indexes cannot be found on some nodes in the distributed system. The DROP INDEX statement cannot be used to delete these indexes. You need to use the DROP INDEX IF EXISTS statement to delete them. The execution of REINDEX INDEX CONCURRENTLY adds a four-level session lock to the table and its first several phases are similar to those of CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY. Therefore, the execution may be suspended or deadlocked, which is similar to that of CREATE INDEX CONCURRENTLY. For example, if two sessions perform the REINDEX CONCURRENTLY operation on the same index or table at the same time, a deadlock occurs. For details, see CONCURRENTLY.

This keyword is specified when an index is rebuilt. For Astore, you need to complete two full table scans for building. During the first scan, a new index is created without blocking read and write operations. During the second scan, the changes in the first scan are merged and updated. For Ustore, you need to complete a full table scan. During the scan, data generated by concurrent DML operations is inserted into the temporary table named index_oid_cctmp. After the scan is complete, you merge the temporary table to the new index suffixed with _ccnew{n} (for GSIs, the prefix is ccgsi_tmp_index_), delete the temporary table, exchange the old and new indexes, mark the old index as dead, enable the new index, and rebuild the index.
- name
Specifies the name of the index, table, or database whose index needs to be rebuilt. Tables and indexes can be schema-qualified.

REINDEX DATABASE and REINDEX SYSTEM can create indexes for only the current database. Therefore, name must be the same as the current database name.
- FORCE
Deprecated parameter. It is currently reserved for compatibility with earlier versions.
- partition_name
Specifies the name of the index or table to be reindexed.
Value range:
- The name of an index is specified if REINDEX INDEX is used.
- The name of a table is specified if REINDEX TABLE is used.

- REINDEX DATABASE and REINDEX SYSTEM cannot be performed in transaction blocks.
- REINDEX and REINDEX CONCURRENTLY do not support separate operations on TOAST tables or TOAST indexes.
Examples
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 |
-- Create the table tbl_test and insert data into the tables. gaussdb=#CREATE TABLE tbl_test(c1 int,c2 varchar); gaussdb=#INSERT INTO tbl_test VALUES (1, 'AAAAAAA'),(5, 'AAAAAAB'),(10, 'AAAAAAC'); -- Create an index and check the index size. gaussdb=#CREATE INDEX idx_test_c1 ON tbl_test(c1); gaussdb=#SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size('idx_test_c1')) AS size; size -------- 176 kB (1 row) -- Insert 10,000 data records and then delete the data. It is found that the index becomes larger. gaussdb=#INSERT INTO tbl_test VALUES (generate_series(1,10000),'test'); gaussdb=#DELETE FROM tbl_test WHERE c2 = 'test'; gaussdb=#SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size('idx_test_c1')) AS size; size -------- 504 kB (1 row) -- After an independent index is rebuilt, the index size is restored to the initial size. gaussdb=#REINDEX INDEX idx_test_c1; gaussdb=#SELECT pg_size_pretty(pg_total_relation_size('idx_test_c1')) AS size; size -------- 176 kB (1 row) -- Rebuild a single index online. gaussdb=#REINDEX INDEX CONCURRENTLY idx_test_c1; -- Rebuild all indexes in the table tbl_test. gaussdb=#REINDEX TABLE tbl_test; -- Rebuild all indexes in the table tbl_test online. gaussdb=#REINDEX TABLE CONCURRENTLY tbl_test; -- Drop the tbl_test table. gaussdb=#DROP TABLE tbl_test; |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





