Variable Definition Statements
This section describes the declaration of variables in the PL/SQL and the scope of this variable in codes.
Variable Declaration
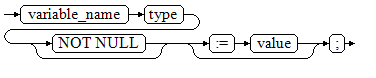
For details about the variable declaration syntax, see Figure 1.
The above syntax diagram is explained as follows:
- variable_name: specifies the name of a variable.
- type indicates the type of a variable.
- value indicates the initial value of the variable. (If the initial value is not given, NULL is taken as the initial value.) value can also be an expression.
Example
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
gaussdb=# DECLARE emp_id INTEGER := 7788; -- Define a variable and assign a value to it. BEGIN emp_id := 5*7784; -- Assign a value to the variable. END; / ANONYMOUS BLOCK EXECUTE |
In addition to the declaration of basic variable types, %TYPE and %ROWTYPE can be used to declare variables related to table columns or table structures.
%TYPE Attribute
%TYPE declares a variable to be of the same data type as a previously declared variable (for example, a column in a table). For example, if you want to define the my_name variable whose data type is the same as the data type of firstname in employee, you can define the variable as follows:
my_name employee.firstname%TYPE
-- Example
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employee;
NOTICE: table "employee" does not exist, skipping
DROP TABLE
CREATE TABLE employee(firstname varchar,secondname varchar);
CREATE TABLE
DECLARE
my_name employee.firstname%TYPE;
BEGIN
my_name = 'abc';
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_name);
END;
/
abc
ANONYMOUS BLOCK EXECUTE
In this way, you can declare my_name without the need of knowing the data type of firstname in employee, and the data type of my_name can be automatically updated when the data type of firstname changes.
TYPE employee_record is record (id INTEGER, firstname VARCHAR2(20));
my_employee employee_record;
my_id my_employee.id%TYPE;
my_id_copy my_id%TYPE;
-- Example
DECLARE
TYPE employee_record is record (id INTEGER, firstname VARCHAR2(20));
my_employee employee_record;
my_id my_employee.id%TYPE;
my_id_copy my_id%TYPE;
BEGIN
my_employee.id := 1;
my_employee.firstname := 'ab2';
my_id = 2;
my_id_copy = 3;
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_employee.id);
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_employee.firstname);
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_id);
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_id_copy);
END;
/
1
ab2
2
3
ANONYMOUS BLOCK EXECUTE
%ROWTYPE Attribute
%ROWTYPE declares data types of a set of data. It stores a row of table data or results fetched from a cursor. For example, if you want to define a set of data with the same column names and column data types as the employee table, you can define the data as follows:
my_employee employee%ROWTYPE
-- Example
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employee;
DROP TABLE
CREATE TABLE employee(firstname varchar,secondname varchar);
DECLARE
my_employee employee%ROWTYPE;
BEGIN
my_employee.firstname := 'ab1';
my_employee.secondname := 'ab2';
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_employee.firstname);
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_employee.secondname);
END;
/
ab1
ab2
ANONYMOUS BLOCK EXECUTE
The attribute can also be used on the cursor. The column names and column data types of this set of data are the same as those of the employee table. For the cursor in a package, %ROWTYPE can be omitted. %TYPE can also reference the type of a column in the cursor. You can define the data as follows:
CURSOR cur IS SELECT * FROM employee;
my_employee cur%ROWTYPE
my_name cur.firstname%TYPE
my_employee2 cur -- For the cursor defined in a package, %ROWTYPE can be omitted.
-- Example
SET behavior_compat_options = 'allow_procedure_compile_check';
SET
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS employee;
DROP TABLE
CREATE TABLE employee(firstname varchar,secondname varchar);
CREATE TABLE
CREATE OR REPLACE procedure proc1()
IS
CURSOR cur IS SELECT * FROM employee;
my_employee cur%ROWTYPE;
my_name cur.firstname%TYPE;
BEGIN
my_employee.firstname := 'ab1';
my_employee.secondname := 'ab2';
my_name := 'ab3';
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_employee.firstname);
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_employee.secondname);
DBE_OUTPUT.PRINT_LINE(my_name);
END;
/
CREATE PROCEDURE

- %TYPE cannot reference the type of a composite variable or a record variable, a column type of the record type, a column type of a variable of the cross-package composite type, or a column type of a cursor variable of the cross-package type.
- %ROWTYPE cannot reference the type of a composite variable or a record variable and the type of a cross-package cursor.
- If %TYPE is used to obtain the type from record.column and such type is defined by %TYPE, the constraint on the original type (such as NUMBER(3) and VARCHAR2(10)) is not retained.
Scope of a Variable
The scope of a variable indicates the accessibility and availability of the variable in code block. In other words, a variable takes effect only within its scope.
- To define a function scope, a variable must declare and create a BEGIN-END block in the declaration section. The necessity of such declaration is also determined by block structure, which requires that a variable has different scopes and lifetime during a process.
- A variable can be defined multiple times in different scopes, and inner definition can cover outer one.
- A variable defined in an outer block can also be used in a nested block. However, the outer block cannot access variables in the nested block.
gaussdb=# DECLARE
emp_id INTEGER :=7788; -- Define a variable and assign a value to it.
outer_var INTEGER :=6688; -- Define a variable and assign a value to it.
BEGIN
DECLARE
emp_id INTEGER :=7799; -- Define a variable and assign a value to it.
inner_var INTEGER :=6688; -- Define a variable and assign a value to it.
BEGIN
dbe_output.print_line('inner emp_id ='||emp_id); -- Display the value 7799.
dbe_output.print_line('outer_var ='||outer_var); -- Reference a variable of an outer block.
END;
dbe_output.print_line('outer emp_id ='||emp_id); -- Display the value 7788.
END;
/
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot