gh-ost
Context
Percona offers an open-source DDL tool, pt-osc. It executes operations by using triggers to copy rows from the original table to the new table. Using triggers can speed up synchronization but causes a large overhead, affecting the performance of the primary database. In addition, data copies and data changes may be processed concurrently. If a table is frequently updated during migration, a large number of lock contention problems may occur.
gh-ost is an open-source online DDL tool provided by GitHub. Unlike pt-osc, gh-ost does not depend on triggers. Instead, it simulates the standby database to obtain incremental changes from binlogs in the row format and asynchronously applies the changes to the ghost table. It decouples the migration's write load from the workload of the primary server, avoiding the impact on the performance of the primary database. Asynchronously applying incremental changes also avoids lock contention caused by triggers. In addition, gh-ost maintains a heartbeat table to record each phase in the DDL process. When an exception occurs, data can be restored to the specified position based on the heartbeat log. This solves the problem that pt-osc needs to start from the beginning when an exception occurs.
Process
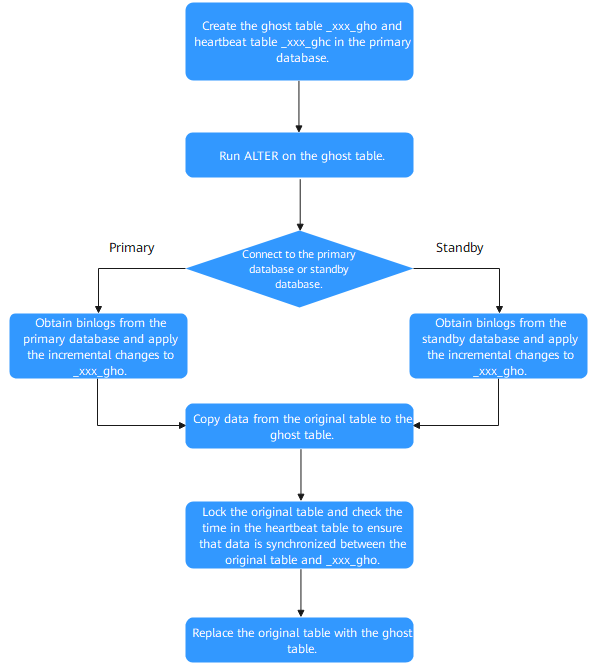
Three gh-ost Modes
- (Default mode) gh-ost connects to the standby database and performs a cutover in the primary database.
- In the primary database, gh-ost creates the _xxx_gho table with the same structure as the original table and the _xxx_ghc table that records the change status. The _xxx_ghc table is used to write the progress and time of online DDL operations.
- The structure of the _xxx_gho table is modified.
- The existing data of the original table is copied to _xxx_gho in the primary database.
- The incremental binlogs are obtained from the standby database and the incremental changes are applied to _xxx_gho.
- The original table is locked and the time in the _xxx_ghc table is checked to ensure that data is synchronized between the original table and _xxx_gho.
- The original table is replaced with _xxx_gho.
- gh-ost connects to the primary database and performs a cutover in the primary database.
- The _xxx_gho and _xxx_ghc tables are created in the primary database.
- The structure of the _xxx_gho table is modified.
- The existing data of the original table is copied to _xxx_gho in the primary database.
- The incremental binlogs are obtained from the primary database and the incremental changes are applied to _xxx_gho.
- The original table is locked and the time in the _xxx_ghc table is checked to ensure that data is synchronized between the original table and _xxx_gho.
- The original table is replaced with _xxx_gho.
- gh-ost performs a test and cutover on the standby database.
In this mode, gh-ost connects to the primary database. However, all operations are performed on the standby database and no modification is made to the primary database.
-migrate-on-replica means that gh-ost directly migrates the table on the standby database. It performs the cutover when replication of the standby database is running.
-test-on-replica indicates that the migration is only for test purposes. Replication is stopped before a cutover is performed. The original table and temporary table are swapped and then swapped back. The original table returns to its original place. Both of the tables are left with replication stopped. You may examine the two and compare data.
Common Parameters
For details about gh-ost parameters, see the official documentation.
Constraints
- Row-based binlogs must be used, and the value of binlog_row_image must be FULL.
- The required user permissions include SUPER, REPLICATION CLIENT, and REPLICATION SLAVE.
- If the binlogs are in the row format, you can add -assume-rbr. In this case, the SUPER permission is not required.
- Tables with foreign key constraints are not supported.
- Tables with triggers are not supported.
- The tables before and after DDL execution must have the same primary key or non-null unique indexes.
- If the primary key or non-null unique index of a table to be migrated contains enumeration types, the migration efficiency will be greatly reduced.
Example
gh-ost -max-load=Threads_running=20 \
-critical-load=Threads_running=100 \
-chunk-size=2000 -user="temp"
-password="test" -host=**.*.*.* \
-allow-on-master -database="sbtest" -table="sbtest1" \
-alter="engine=innodb" -cut-over=default \
-exact-rowcount -concurrent-rowcount -default-retries=120 \
-timestamp-old-table -assume-rbr -panic-flag-file=/tmp/ghost.panic.flag \
-execute
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





