Enhancing Security for SSH Logins to Linux ECSs
Linux ECSs are generally logged in using SSH. How can I ensure login security for password-authenticated Linux ECSs? This section uses CentOS 7.6 as an example to describe how to enhance security for SSH logins.
|
Parameter |
Example Value |
|---|---|
|
Name |
ecs-f5a2 |
|
OS |
CentOS 7.6 64bit |
|
EIP |
119.3.xxx.x |
|
Login mode |
Password |
Changing the Default Login Port
- Remotely log in to the ECS using its password through SSH. For details, see Logging In to a Linux ECS Using an SSH Password.
- Run the following command to change the default port for SSH logins, for example, to 5000:
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Press i to enter insert mode. In line 17, delete the comment character (#) and change the port number to 5000.
Figure 1 Before the change Figure 2 After the change
Figure 2 After the change
- Press Esc and enter :wq to save and exit.
Adding a Firewall Rule to Open a Specified Port
The default firewall for CentOS 7 is firewalld, not iptables. Perform the operations described in this section only if Iptables has been installed on your ECS to open port 5000 for SSH logins.
- Run the following command to check whether Iptables has been installed:
service iptables status
- If information similar to the following is displayed, Iptables has not been installed. In such a case, skip this section and proceed with Adding a Security Group Rule.

- If information similar to the following is displayed, Iptables has been installed, and it is in active state. Then, go to 2.

- If information similar to the following is displayed, Iptables has not been installed. In such a case, skip this section and proceed with Adding a Security Group Rule.
- Run the following command to add an Iptables rule to open port 5000:
iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m state --state NEW -m tcp --dport 5000 -j ACCEPT
- Run the following command to check whether port 5000 is contained in the existing Iptables rules:
iptables -L -n

Adding a Security Group Rule
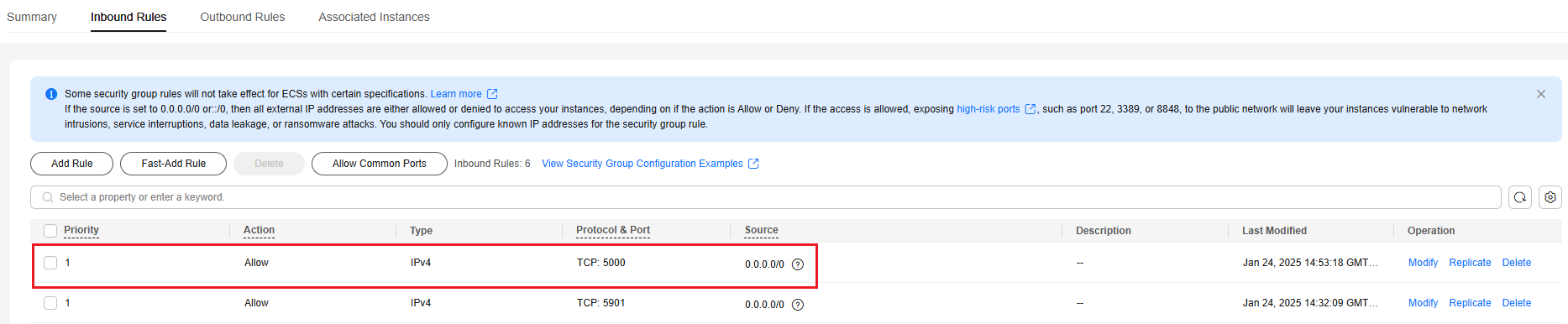
By default, port 22 is enabled in the inbound direction of a security group. After changing the SSH login port on your ECS to port 5000, add a rule for port 5000 to the security group.
- Log in to the ECS console and access the ECS list page.
- Click the ECS name ecs-f5a2 to go to the ECS details page.
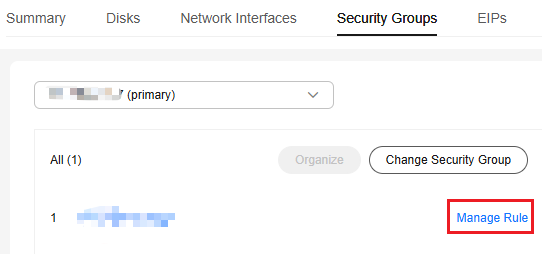
- On the Security Groups tab, click Manage Rule in the row of the security group for which you want to modify the rules.
Figure 3 Managing rules
- On the Inbound Rules tab, click Add Rule.
- Add an inbound rule, as shown in Figure 4.
Changing Password Authentication to Key-Pair Authentication
Create a key pair on the management console and bind it to your ECS to change the ECS login mode.
- Create a key pair by following the instructions provided in Creating a Key Pair, and keep the private key file secure.
- Log in to the DEW console and choose Key Pair Service in the navigation pane on the left.
- Click the ECS List tab, locate the row containing ecs-f5a2, and click Bind in the Operation column. Set parameters according to Figure 6, and click OK.
To disable password authentication, disable the password login mode on the Bind Key Pair page or edit the sshd_config configuration file.
Figure 5 Bind Key Pair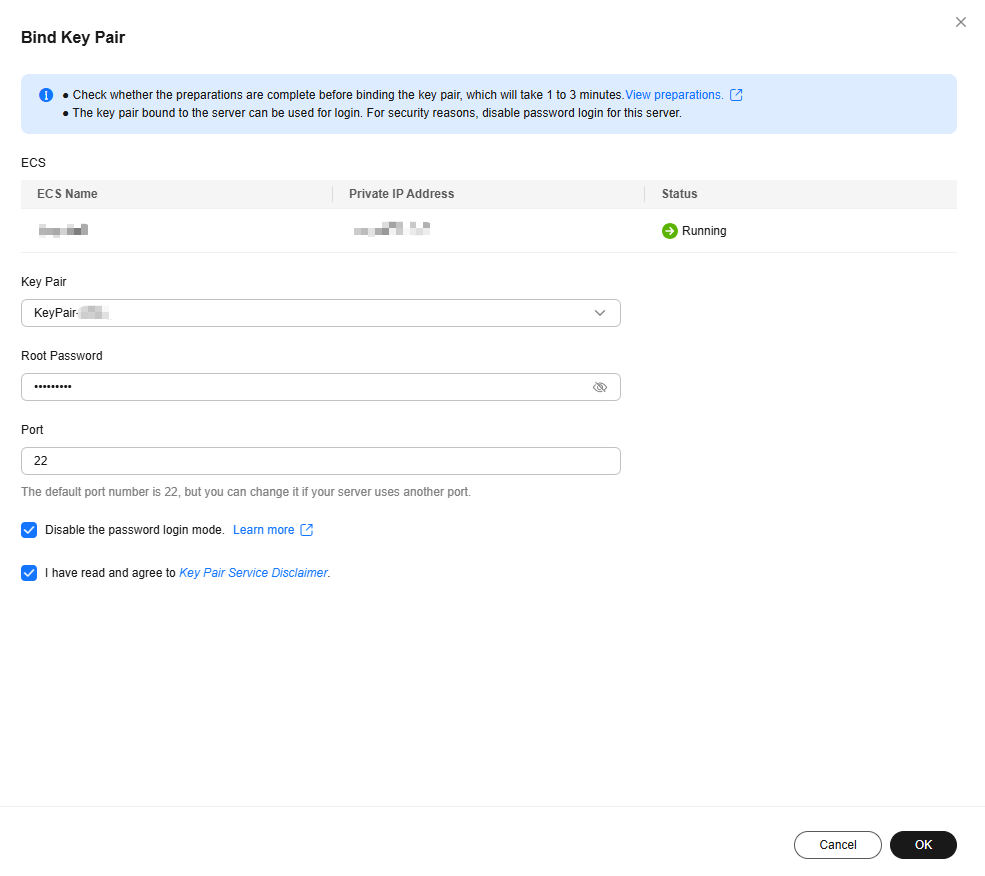
- Log in to the ECS, and edit the sshd_config file to disable password authentication.
vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
Press i to enter insert mode, and configure the data in last several lines according to the following figure.

Parameter description:
- PermitRootLogin: specifies whether to allow the root user to log in to the ECS. Set this parameter to yes.
- UseDNS: specifies whether DNS resolution is allowed. Set this parameter to no.
- PasswordAuthentication: specifies whether a login is authenticated using a password. Set this parameter to no.

During key pair binding in 3, you have selected "Disable the password login mode." The PasswordAuthentication value should be no. You only need to verify it.
Press Esc and enter :wq to save and exit.
- Run the following command to restart sshd:
systemctl restart sshd
- Log in to the ECS using Xshell or an SSH client. If password input is unavailable, as shown in Figure 6, the configuration is successful.
Editing hosts.allow and hosts.deny
The /etc/hosts.allow and /etc/hosts.deny files control remote access. You can configure these files to allow or deny the access from certain IP addresses or IP address ranges to a process running on the Linux ECS.
For example, if SSH is available only to the administrator, you can only allow access from the IP address ranges used by the administrator.
The ECS may be logged in anywhere. You are advised to edit /etc/hosts.allow to allow access from all IP addresses.
vim /etc/hosts.allow
Add sshd:ALL in the last line.

Identify ECS security risks using certain methods, for example, checking the SSH status, to detect risky IP addresses, and add them to /etc/hosts.deny to deny the access from these IP addresses.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot