CPU Performance Configuration
C-states control the sleep levels that a CPU can enter when it is idle. The sleep levels are numbered from C0 (the CPU is executing instructions) to C6 (the deepest sleep level where the CPU is in a very low-power state). When the CPU enters a deeper C-state, the wake-up time increases. In some load scenarios that require high real-time performance, the performance is affected. Therefore, if you have high requirements on performance stability, set the C-state to C1 to reduce the CPU response, ping, and TCP/UDP latency.
Procedure
This section uses c9.large.2 and Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0 as an example to describe how to disable deep hibernation for CPUs. The command output varies depending on ECS flavors and images.
- Log in to the target ECS.
For details, see Login Overview (Linux).
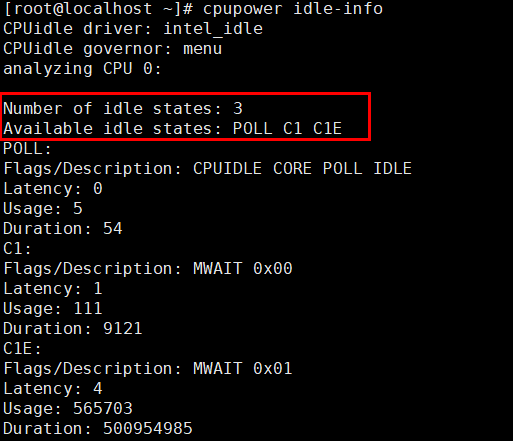
- Run the following command to check CPUidle driver and supported C-states:
cpupower idle-info
The figure below shows the command output. Number of idle states indicates the number of supported C-states, and Available idle states indicates the supported C-states.

If no CPUidle driver is displayed in the command output, you may need to update the image.
- Modify the C-states parameters in the /etc/default/grub file.
- Open the /etc/default/grub file.
sudo vim /etc/default/grub
- Press i to enter the editing mode.
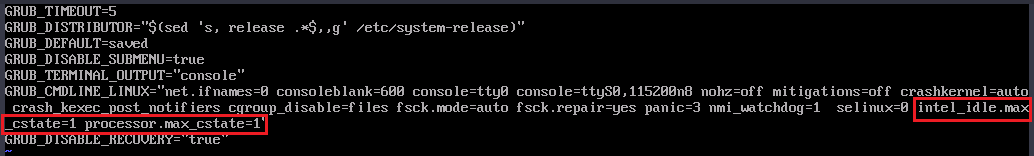
- Locate the GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX= line and add intel_idle.max_cstate=1 and processor.max_cstate=1 to the end of it to set the deepest C-state of idle CPUs to C1.
- Press Esc, type :wq, and press Enter to save the file and exit.
- Regenerate the grub configuration file.
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg

The GRUB file address varies depending on the image or boot mode. For example, in Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0 booted from UEFI, the command is sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/efi/EFI/hce/grub.cfg.
Run the following command to query the boot mode:
[ -d /sys/firmware/efi ] && echo "UEFI Boot Detected" || echo "Legacy BIOS Boot Detected"
- Open the /etc/default/grub file.
- Restart the ECS for the configuration to take effect.
sudo reboot
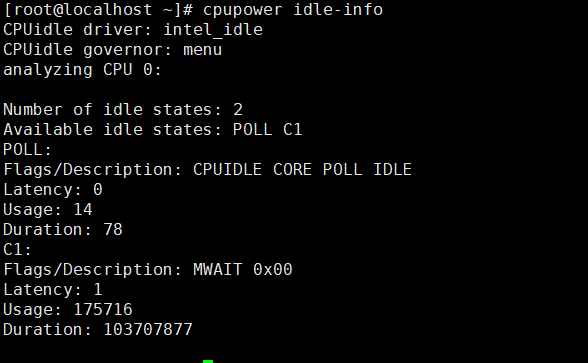
- Run the following command to check the CPUidle driver and supported C-states:
cpupower idle-info
If the command output shown in the following figure is displayed, the system supports only two C-states (POLL and C1).
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





