Setting Up an FTP Site (Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0)
Introduction
File Transfer Protocol (FTP) is a standard protocol for transferring files between computers over a network. It uses the client-server architecture and allows users to upload, download, rename, delete, and view files and directories from a remote server. FTP can work in active or passive mode:
- Active mode: The server initiatively connects to a port of the client to transmit data.
- Passive mode: The client initiatively connects to an open port of the server. This mode is for network environments with firewalls.
The following types of users can log in to FTP servers:
- Anonymous users
- Users can log in as anonymous or ftp without a password.
- This type of user is usually used to download public resources, for example, downloading open-source software from mirror sites.
- Such users are insecure and are only used to access certain directories such as /pub. Generally, they only have the read-only permission.
- Local users
- They are local users in Linux.
- Local users are usually used to share resources on an intranet or in a development and test environment.
- The username and password are from /etc/passwd and /etc/shadow. Local users have the same permissions as system users, which means there are certain operation risks.
- Virtual users
- A virtual user does not exist in the system. They are stored in an independent account database. Generally, virtual users are mapped to a host user (for example, vsftpd) for access control.
- GDBM or libdb is usually used for authentication of virtual users.
- Virtual users do not depend on system users, so they are more secure. Additionally, they have fine-grained permissions.
vsftpd (very secure FTP daemon) is an FTP server for Unix-like systems, including Linux. This section describes how to install and configure vsftpd in HCE 2.0. Local users and virtual users will be involved.
Preparations
- Prepare two ECSs and assign a public IP address or an EIP to each of them. Use one ECS as the FTP server and the other as the client.
- Configure security group inbound rules to allow traffic to the FTP server over port 21.
Prerequisites
A yum repository has been configured. For details about how to configure a yum repository accessed over the Internet, see Configuring Repositories and Installing Software for HCE.
Installing vsftpd
- Install vsftpd.
dnf install vsftpd
- Start vsftpd.
systemctl start vsftpd
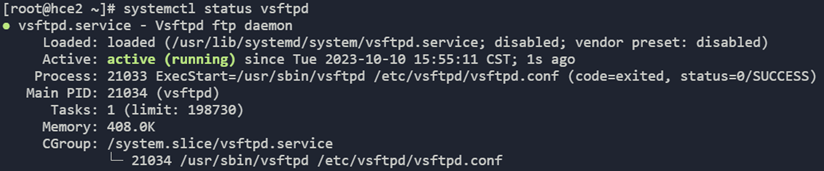
- Check the vsftpd status.
systemctl status vsftpd
If active (running) is displayed, vsftpd is started, as shown in Figure 1.

Enable vsftpd to automatically start up upon system boot if needed.
systemctl enable vsftpd
Setting the FTP Server to Local User Authentication
- Add a local user for the FTP service.
- Create a local user for the FTP service.
adduser ftpuser
- Set a password for the new user.
passwd ftpuser
- Create a local user for the FTP service.
- Configure the vsftpd service.
- Create a directory and file for the FTP service (the following are examples only).
mkdir -p /data/ftp/ touch /data/ftp/test.txt
- Set the owner of the directory to the new user.
chown -R ftpuser:ftpuser /data/ftp/
- Open the /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf file and set the following parameters:
# Listen to IPv4 sockets. listen=YES # Determine whether to configure IPv6 listening. listen_ipv6=NO
Append other parameters to the configuration file. Set pasv_address to an available public IP address or EIP.
# Set the root directory of the local user. local_root=/data/ftp # Restrict all users to their home directories. chroot_local_user=YES # Enable the passive mode. pasv_enable=YES pasv_address=<public-IP-address-of-the-FTP-server> # Determine whether to allow users to access other directories. chroot_list_enable=NO allow_writeable_chroot=YES # If chroot_list_enable is set to YES, you need to set chroot_list_file to a file that contains the users who can access other directories. # chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list # Set the port range that can be used in passive mode. Use a high port range to improve the security of accessing the FTP server. # Specify the lower limit of the port range. In this example, the value is 5000. You can change it based on the site requirements. pasv_min_port=5000 # Specify the higher limit of the port range. In this example, the value is 5010. You can change it based on the site requirements. pasv_max_port=5010

Retain the default values for other parameters.

The /etc/vsftpd/chroot_list file must be created regardless of whether chroot_list_enable is configured.
- Restart vsftpd.
systemctl restart vsftpd
- Create a directory and file for the FTP service (the following are examples only).
- Verify the configuration.
- Check the port used by vsftpd.
netstat -natp | grep vsftpd
By default, port 21 is used.
- Configure security group inbound rules to enable port 21 and ports 5000 to 5010.
- Run the following command on the client ECS to install the FTP client:
yum install ftp
- Run the following command on the client to access the FTP service:
ftp <FTP-server-public-IP-address >
- Enter the username and password as prompted.
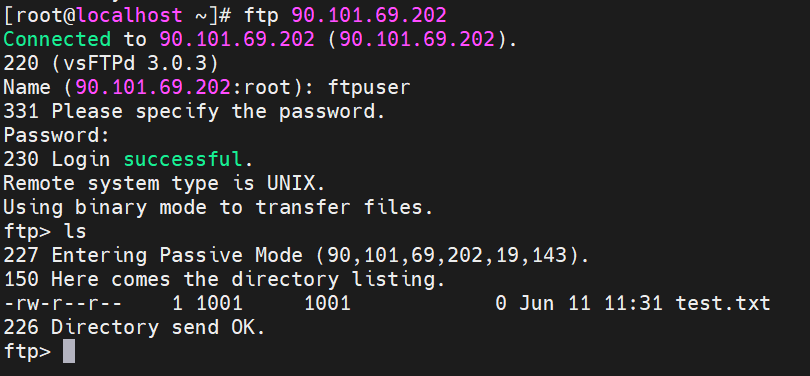
- After the login is successful, run ls. If the test.txt file is displayed, the configuration is successful.
Figure 2 Verification example
- Check the port used by vsftpd.
Setting the FTP Server to Virtual User Authentication
- Create a host account for virtual users and disable shell login.
useradd vsftpd -s /bin/false
Virtual users will be mapped to the host account vsftpd. This account is used to access system resources but cannot be used to log in to the system.
- Create a GDBM database.
gdbmtool /etc/vsftpd/login.pag store ftpuser 123456
- ftpuser: virtual username (example)
- 123456: password (example)
- login.pag: file for storing user passwords
- Configure Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM). Open the /etc/pam.d/vsftpd file, delete the existing content, and add the following content:
auth required pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/login account required pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/login

db=/etc/vsftpd/login indicates login.pag without the file name extension.
- Edit the vsftpd configuration file /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf to add the following content:
guest_enable=YES guest_username=vsftpd user_config_dir=/etc/vsftpd/user_conf # Enable the passive mode. pasv_enable=YES pasv_address=<public-IP-address-of-the-FTP-server> # Determine whether to allow users to access other directories. chroot_list_enable=NO allow_writeable_chroot=YES # Set the port range that can be used in passive mode. Use a high port range to improve the security of accessing the FTP server. # Specify the lower limit of the port range. In this example, the value is 5000. You can change it based on the site requirements. pasv_min_port=5000 # Specify the higher limit of the port range. In this example, the value is 5010. You can change it based on the site requirements. pasv_max_port=5010
- Configure permissions of the virtual user.
- Create a directory for configuring user permissions.
mkdir -p /etc/vsftpd/user_conf
- Write the following content to the /etc/vsftpd/user_conf/ftpuser file:
# Allow write operations (upload, rename, and delete). write_enable=YES # Allow local system users (including virtual users) to log in to the FTP server. local_enable=YES # Set the permission mask used by a local user to create a file or directory. local_umask=077 # Set the permission mask used by an anonymous user to create a file or directory. anon_umask=022 # Set the root directory for virtual users or local users. These users can only access this directory and its subdirectories. local_root=/home/vsftpd/ftp # Allow anonymous users to upload files. anon_upload_enable=YES # Allow anonymous users to create directories. anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES # Allow anonymous users to perform other write operations, such as renaming and deleting files. anon_other_write_enable=yes

For vsftp, virtual users are mapped to a local user (host user), but their permissions are controlled in the same way as anonymous users. So, some anonymous user settings are also needed to enable the write permission of virtual users.
- Create a directory for configuring user permissions.
- Prepare the FTP root directory and assign permissions.
mkdir -p /home/vsftpd/ftp/pub chmod 777 /home/vsftpd/ftp/pub
- Restart the vsftpd service.
systemctl restart vsftpd
- Verify the configuration.
- Check the port used by vsftpd.
netstat -natp | grep vsftpd
By default, port 21 is used.
- Configure security group inbound rules to enable port 21 and ports 5000 to 5010.
- Run the following command on the client ECS to install the FTP client:
yum install ftp
- Run the following command on the client to access the FTP service:
ftp <FTP-server-public-IP-address >
- Enter the username and password as prompted.
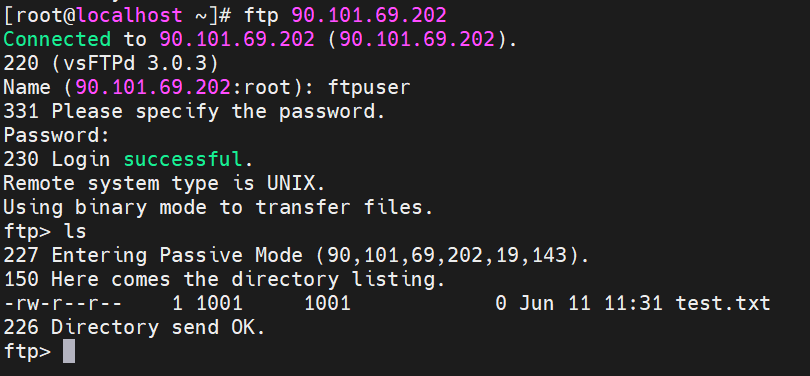
- After the login is successful, run ls. If the test.txt file is displayed, the configuration is successful.
Figure 3 Verification example
- Check the port used by vsftpd.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot