Building a Comprehensive Metric System
This section describes how to build a metric system and a dashboard for all-round, multi-dimensional, and visualized monitoring of resources and applications.
Scenario
In the Internet era, user experience is the top priority. The page response speed, access latency, and access success rate often affect user experience. If such information cannot be obtained in a timely manner, a large number of users will be lost. O&M personnel of an online shopping mall used open-source software to collect metrics. However, these metrics are scattered and cannot be displayed centrally.
Solution
AOM implements one-stop, multi-dimensional O&M for cloud applications. In the access center, ingest metrics of businesses, applications, and Prometheus middleware. You can also customize dashboards for monitoring and set alarm rules through a unified entry to implement routine inspection and ensure normal service running.
|
Type |
Source |
Example |
How to Ingest |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Business metrics |
Device log SDKs and extracted ELB logs |
UV, PV, latency, access failure rate, and access traffic |
|
|
Transaction monitoring or reported custom metrics |
URL calls, maximum concurrency, and maximum response time |
||
|
Application metrics |
Component performance graphs or API performance data |
URL calls, average latency, error calls, and throughput |
|
|
Middleware metrics |
Native or cloud middleware data |
File system capacity and file system usage |
|
|
Other layer metrics |
Generally container or cloud service data, such as compute, storage, network, and database data |
CPU usage, memory usage, and health status |
Ingest Metrics at Other Layers (Example: container metrics and cloud service metrics) |
Prerequisites
- ELB logs have been ingested to LTS.
- An ECS has been bound to the environment.
Step 1: Build a Metric System
- Ingest business metrics.
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Access Center > Access Center.
If you want to switch from the new Access Center to the old one, click Back to Old Version in the upper right corner.
- In the Business panel on the right, click a target card.
- Ingesting ELB log metrics
- Log metrics can be automatically ingested.
- Choose Dashboard > Dashboard in the navigation pane, select the created dashboard, and click
 in the upper right corner of the page. On the Log Sources tab, enter the corresponding SQL statement to check the log metrics. For example, to check traffic metrics, enter an SQL statement and click Search.
in the upper right corner of the page. On the Log Sources tab, enter the corresponding SQL statement to check the log metrics. For example, to check traffic metrics, enter an SQL statement and click Search.
- Ingesting APM transaction metrics
- Install an APM probe for the workload. For details, see Installing an APM Probe.
- After the installation is complete, log in to the console of the service where the probe is installed and trigger the collection of APM transaction metrics. In the example of an online shopping mall, you can add a product to the shopping cart to trigger the collection.
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Metric Browsing. In the right pane, select the ingested APM metrics to view.
- Ingesting ELB log metrics
- Ingest application metrics.
- To install an APM probe for a workload, perform the following steps:
- Log in to the CCE console and click a target cluster.
- Choose Workloads in the navigation pane, and select the type of workload whose metrics are to be reported to AOM.
- Click a target workload. On the APM Settings tab page, click Edit in the lower right corner.
- Select the APM 2.0 probe, set Probe Version to latest-x86, set APM Environment to phoenixenv1, and select the created application phoenixapp1 from the APM App drop-down list.
- Click Save.
- After the installation is complete, log in to the console of the service where the probe is installed and trigger the collection of application metrics. In the example of an online shopping mall, you can add a product to the shopping cart to trigger the collection.
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Metric Browsing. In the right pane, select the ingested application metrics to view.
- To install an APM probe for a workload, perform the following steps:
- Ingest middleware metrics.
- Upload the data to the ECS.
- Download the mysqld_exporter-0.14.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz package from https://prometheus.io/download/.
- Log in to the ECS as the root user, upload the Exporter software package to the ECS, and decompress it.
- Log in to the RDS console. On the Instances page, click an RDS DB instance name in the instance list. On the basic information page, view the RDS security group.
- Check whether port 3306 is enabled in the RDS security group.
Figure 1 Checking whether the RDS port is enabled

- Go to the decompressed folder and configure the mysql.cnf file on the ECS:
cd mysqld_exporter-0.14.0.linux-amd64 vi mysql.cnf
For example, add the following content to the mysql.cnf file:
[client]
user=root (RDS username)
password=**** (RDS password)
host=192.168.0.198 (RDS public IP address)
port=3306 (port)
- Run the following command to start the mysqld_exporter tool:
nohup ./mysqld_exporter --config.my-cnf="mysql.cnf" --collect.global_status --collect.global_variables &
- Run the following command to check whether the tool is started properly:
curl http://127.0.0.1:9104/metrics
If the command output shown in Figure 2 is displayed, the tool is started properly.
- Ingest middleware metrics using VM access mode.
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Global Settings. On the displayed page, choose UniAgents.
- On the UniAgents page, install the UniAgent for the ECS. For details, see Manual Installation.
To switch from the new UniAgent management page to the old one, click Back to Old Version.
- In the navigation pane, choose Access Center > Access Center. In the Prometheus Middleware panel on the right, click a target card.
- In the dialog box that is displayed, configure a collection task and install Exporter. For details, see Exporter Access in the VM Scenario.
- Click Create.
- After the ingestion is complete, choose Metric Browsing in the navigation pane on the left. In the right pane, view the ingested middleware metrics.
- Upload the data to the ECS.
- Ingest metrics at other layers. The following shows how to ingest container metrics and cloud service metrics. For how to ingest other types of metrics, see Connecting to AOM.
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Access Center > Access Center.
- In the Prometheus Running Environments or Prometheus Cloud Services panel, click a target card.
- Select a container metric card:
For example, if you select the CCE card, the ICAgent is installed by default after you purchase a CCE cluster.
- Select a cloud service metric card:
- Click a cloud service card. In the dialog box that is displayed, select the cloud service to monitor. For example, RDS or DCS.
- Select an enterprise project and a Prometheus instance for cloud services. By default, the Prometheus instance for cloud services under your specified enterprise project is selected. It is grayed and cannot be selected here.
- Click Connect Now.
- Select a container metric card:
- After the connection is complete, choose Metric Browsing in the navigation pane on the left. In the right pane, select the ingested metrics to view.
Step 2: Add a Dashboard for Unified Monitoring
- Create a metric alarm rule.
You can set threshold conditions in metric alarm rules for resource metrics. If a metric value meets the threshold condition, a threshold alarm will be generated. If no metric data is reported, an insufficient data event will be generated.
Metric alarm rules can be created in the following modes: Select from all metrics and PromQL. The following uses Select from all metrics as an example.
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Alarm Center > Alarm Rules.
- On the Prometheus Monitoring tab page, click Create Alarm Rule.
- Set the basic information about the alarm rule, such as the rule name.
- Set parameters about the alarm rule. Set Rule Type to Metric alarm rule and Configuration Mode to Select from all metrics, and select a Prometheus instance from the drop-down list.
- Set alarm rule details.
You need to set information such as the statistical period, condition, detection rule, trigger condition, and alarm severity. The detection rule consists of the statistical mode (Avg, Min, Max, Sum, and Samples), determination criterion (≥, ≤, >, and <), and threshold value. For example, if Statistical Period is 1 minute, Rule is Avg >1, Consecutive Periods is 3, and Alarm Severity is Critical, a critical alarm will be generated when the average metric value is greater than 1 for three consecutive periods.
- Under Advanced Settings, set information such as Check Interval and Alarm Clearance. In this example, retain the default settings.
- Set an alarm notification policy. For details, see Table 2.
Figure 3 Alarm notification
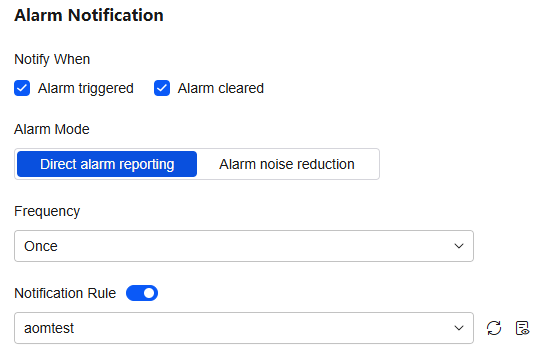
Table 2 Alarm notification policy parameters Parameter
Description
Example Value
Notify When
Set the scenario for sending alarm notifications. By default, Alarm triggered and Alarm cleared are selected.
- Alarm triggered: If the alarm trigger condition is met, the system sends an alarm notification to the specified personnel by email or SMS.
- Alarm cleared: If the alarm clearance condition is met, the system sends an alarm notification to the specified personnel by email or SMS.
Retain the default value.
Alarm Mode
- Direct alarm reporting: An alarm is directly sent when the alarm condition is met. If you select this mode, set an interval for notification and specify whether to enable a notification rule.
- Frequency: interval for sending alarm notifications. Select a desired value from the drop-down list.
- Notification Rule: After the rule is enabled, the system sends notifications based on the associated SMN topic and message template. If there is no notification rule you want to select, click Add Rule in the drop-down list to create one. For details, see Creating an Alarm Notification Rule.
Alarm Mode: Select Direct alarm reporting.
Frequency: Select Once.
Notification Rule: aomtest
- Click Confirm. Then click View Rule to view the created rule.
Click a rule name to view details. If a monitored object meets the configured alarm condition, a metric alarm is generated on the alarm list page. To view the alarm, choose Alarm Center > Alarm List in the navigation pane. If a host meets the preset notification policy, the system sends an alarm notification to the specified personnel by email, SMS, or WeCom.
- Create a dashboard.
- Create a dashboard.
- Log in to the AOM 2.0 console.
- In the navigation pane, choose Dashboard > Dashboard.
- Click Add Dashboard in the upper left corner of the list.
- In the displayed dialog box, set parameters.
- Click OK.
- Add a graph to the dashboard.
- In the dashboard list, click the created dashboard.
- Go to the target dashboard page and click
 in the upper right corner to add a graph to the dashboard. Select a proper graph as required.
in the upper right corner to add a graph to the dashboard. Select a proper graph as required.
Table 3 Adding a graph Graph Type
Data Source
Scenario
Metric graph
Metric data
Monitors the metrics about the business layer, application layer, and Prometheus middleware.
Log graph
Log data
Monitors business metrics or other log metrics, such as key metrics (latency, throughput, and errors) cleaned based on ELB logs.
The following describes how to add a metric graph for CPU usage and a log graph for latency.
- Add a metric graph for CPU usage.
Select the CPU Usage metric. After the setting is complete, the metric graph shown in Figure 5 is displayed.
- Add a log graph for latency. Click the Log Sources tab and set parameters to add a log graph.
You can directly obtain the SQL query statement from the graph.
- In the upper right corner of the graph display area, click Show Chart.
- In the Charts list, select required log metrics to monitor.
- The query statement corresponding to the metric is automatically filled in the SQL statement setting area.
After setting the parameters, click Add to Dashboard.
- Add a metric graph for CPU usage.
- You can repeat the preceding operations to add more graphs to the dashboard. Then click
 to save the dashboard.
to save the dashboard.
- Create a dashboard.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot








