How do I Enable LDAPS on the AD Server?
If an enterprise needs to enable LDAPS so that cloud desktops can communicate with AD server applications using LDAPS, perform the following operations:
- If an independent AD server is used, enable LDAPS on the Active AD server > verify the connection between LDAPS and the active AD server.
- If the AD servers work in active/standby mode, enable LDAPS on the active AD server > verify the connection between LDAPS and the active AD server > enable LDAPS on the standby AD server > verify the connection between LDAPS and the standby AD server.
Enabling LDAPS on the Active AD Server
- Log in to the active AD server. On the taskbar in the lower left corner, click
 and click Server Manager. The server configuration page is displayed, as shown in Figure 1.
and click Server Manager. The server configuration page is displayed, as shown in Figure 1.
- In the Dashboard tab page, click Add roles and features. The Add Roles and Features Wizard dialog box is displayed.
- Click Next until the Select destination server page is displayed.
- Select a destination server.
To obtain the name and IP address of the destination server, choose Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers > Domain Controllers on the Dashboard tab page of Server Manager.
- Click Next. The Select server roles page is displayed.
- Click Active Directory Certificate Services.
- Retain the default settings and click Add Features.
- Click Next until the Select role services page is displayed.
- Select Certification Authority Web Enrollment and click Add Features.
- Select Certification Enrollment Policy Web Service and click Add Features.
- Click Next until the confirmation page is displayed.
- Click Install.
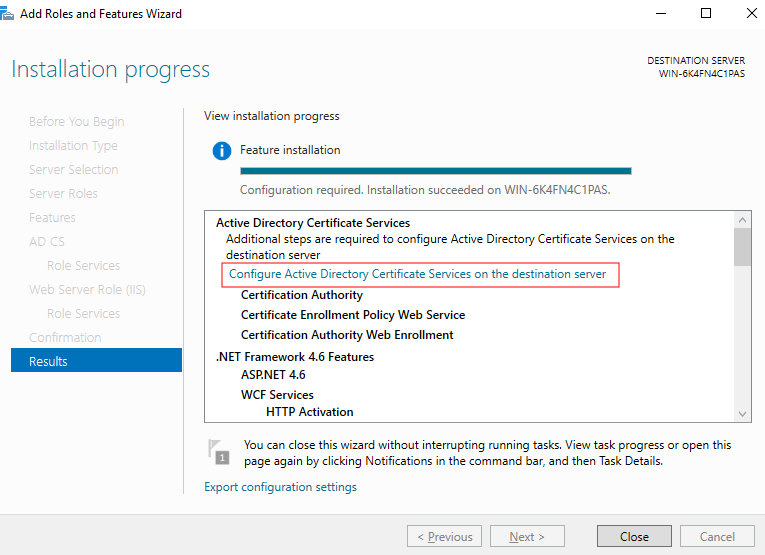
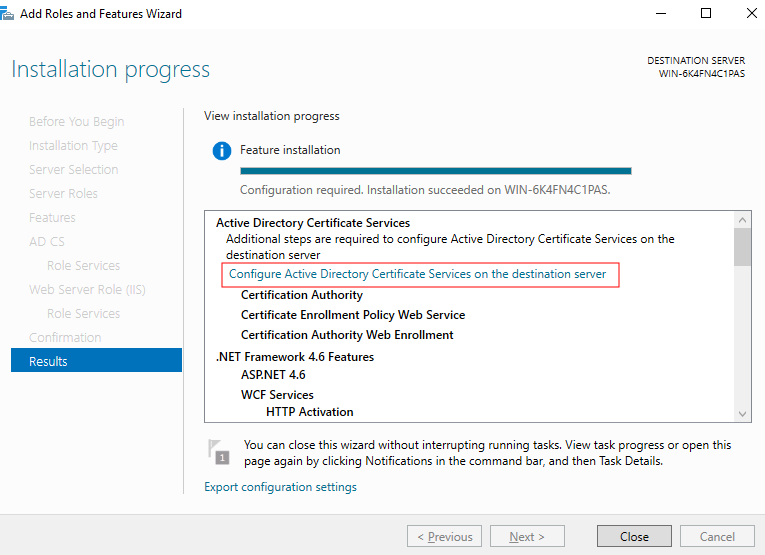
- After the installation is complete, click Configure Active Directory Certificate Services on the destination server under Active Directory Certificate Services, as shown in Figure 2. The AD CS Configuration page is displayed.
- Retain the default settings and click Next. The Role Services page is displayed.
- Select Certificate Authority, Certificate Authority Web Enrollment, and Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service, and click Next. The Setup Type page is displayed.
- Select Enterprise CA and click Next. The Specify the type of the CA page is displayed.
- Select Root CA and click Next. The Specify the type of the private key page is displayed.
- Select Create a new private key and click Next. The encryption configuration page is displayed.
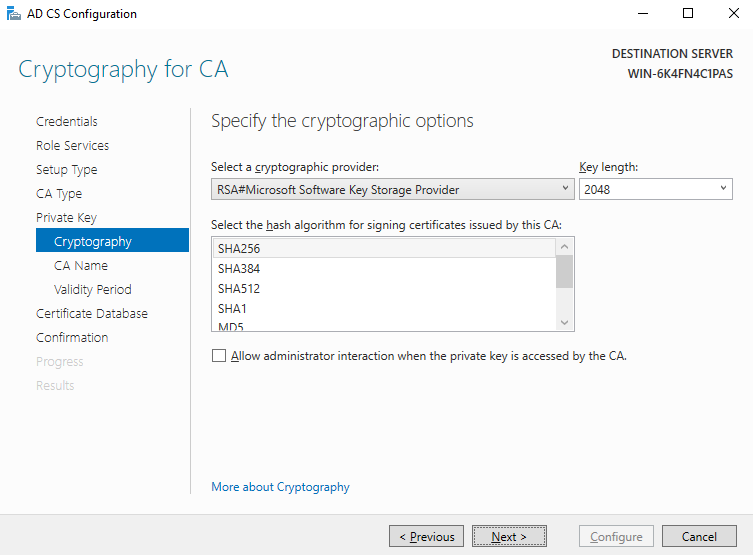
- Set Key length to 2048 and select SHA256 for the hash algorithm for signing certificates issued by the CA. Retain the default values for other parameters, as shown in Figure 3.
- Click Next.
- Select Select a certificate and assign it later for SSL and click Next. The confirmation page is displayed.
- Click Configure.
- After the configuration is complete, click Close.
- Restart the active AD server.
Verifying the LDAPS Connection of the Active AD Server
- On the desktop of the active AD server, click
 and enter Ldp to start Ldp.
and enter Ldp to start Ldp. - On Connection, click Connect.
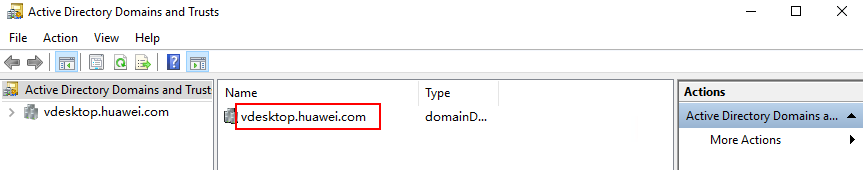
- In Server, enter the domain name to be connected, for example, vdesktop.domain.com.
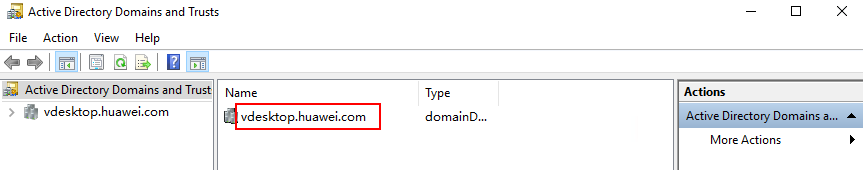
To obtain the target domain name, choose Tools > Active Directory Domains and Trusts on the Dashboard tab page of Server Manager. The domain list page is displayed. The required domain name is displayed in the Name column, as shown in Figure 4.
- Enter 636 in Port.
- Select SSL.
- Click OK.
If RootDSE information is displayed in the right pane, the connection is successful.
Enabling LDAPS on the Standby AD Server
- On the desktop of the active AD server, click
 and enter Run to start the application.
and enter Run to start the application. - Enter mmc in Open to go to Console Root.
- Choose File > Add/Remove Snap-ins.
- In the Available snap-ins list, double-click Certificates.
- Select Computer account and click Next to select a computer.
- Select Local computer: (the computer this console is running on), click Finish, and click OK.
- Under the Console Root, expand Certificates.
- Choose Personal > Certificates.
- Right-click the certificate whose Intended Purposes is All and choose All Tasks > Export. The certificate export wizard page is displayed.
- Click Next.
- Select Yes, export the private key and click Next.
- Select Personal Information Exchange-PKCS#12(.PFX), select Include all certificates in the certification path if possible, and click Next. The security configuration page is displayed.
- Select Group or user names, select Password, and set the password. Click Next.
Record the password, which will be used when you import a certificate.
- Click Browse, select a path for storing the certificate, set the certificate name, click Save, and click Next. The information confirmation page is displayed.
- Confirm the information and click Finish.
- Log in to the standby AD server.
- Copy the active AD server certificate exported from 15 to the standby AD server.
- Open Server Manager.
- In the Dashboard tab page, click Add roles and features. The Add Roles and Features Wizard dialog box is displayed.
- Click Next until the Select destination server page is displayed.
- Select a destination server.
To view the name and IP address of the destination server, choose Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers > Domain Controllers on the Dashboard tab page of Server Manager.
- Click Next. The Select server roles page is displayed.
- Click Active Directory Certificate Services.
- Retain the default settings and click Add Features.
- Click Next until the Select role services page is displayed.
- Select Certification Authority Web Enrollment and click Add Features.
- Select Certification Enrollment Policy Web Service and click Add Features.
- Click Next until the confirmation page is displayed.
- Click Install.
- After the installation is complete, click Configure Active Directory Certificate Services on the destination server under Active Directory Certificate Services, as shown in Figure 5. The AD CS Configuration page is displayed.
- Retain the default settings and click Next. The Role Services page is displayed.
- Select Certificate Authority, Certificate Authority Web Enrollment, and Certificate Enrollment Policy Web Service, and click Next. The Setup Type page is displayed.
- Select Enterprise CA and click Next. The Specify the type of the CA page is displayed.
- Select Root CA and click Next. The Specify the type of the private key page is displayed.
- Select Use existing private key, select Select a certificate and use its associated private key, and click Next.
- Click Import, select the certificate file copied to the standby AD server in 17, enter the password set in 13, and click OK.
- After the certificate is imported, select the certificate in the Certificates list and click Next.
- Select Select a certificate and assign it later for SSL and click Next. The confirmation page is displayed.
- Click Configure.
- After the configuration is complete, click Close.
- Restart the standby AD server.
Verifying the LDAPS Connection of the Standby AD Server
- On the desktop of the standby AD server, click
 and enter Ldp to start Ldp.
and enter Ldp to start Ldp. - On Connection, click Connect.
- In Server, enter the domain name to be connected, for example, vdesktop.domain.com.
To obtain the target domain name, choose Tools > Active Directory Domains and Trusts on the Dashboard tab page of Server Manager. The domain list page is displayed. The required domain name is displayed in the Name column, as shown in Figure 6.
- Enter 636 in Port.
- Select SSL.
- Click OK.
If RootDSE information is displayed in the right pane, the connection is successful.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot