IPv4/IPv6 Dual-Stack Network
What Is an IPv4/IPv6 Dual-Stack Network?
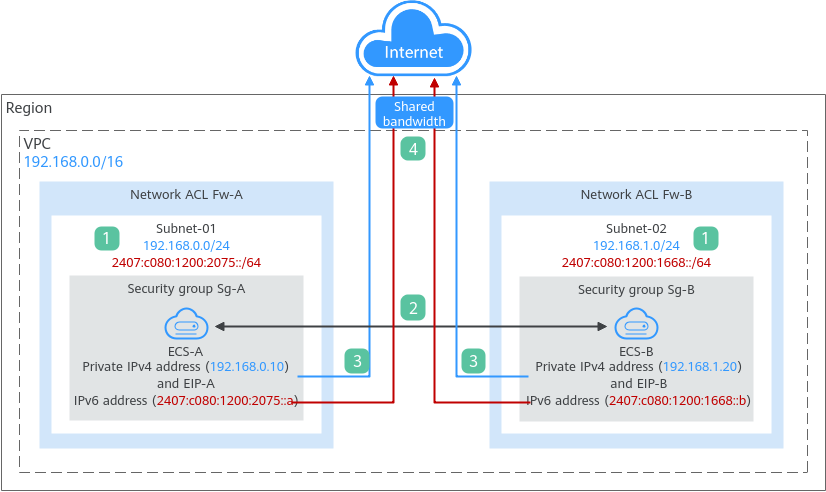
An IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack network allows your resources, such as ECSs, to use both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses for private and public network communications. Figure 1 shows how an IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack network works.
|
Step |
Description |
|---|---|
|
1 |
If you enable IPv6 when adding a VPC subnet, an IPv6 CIDR block is automatically assigned to the subnet. You cannot customize the IPv6 CIDR block. |
|
2 |
Subnets in the same VPC can communicate with each other by default. Network ACLs protect subnets, and security groups protect the instances in it.
As shown in Figure 1, if allow rules are configured for network ACLs Fw-A and Fw-B and security groups Sg-A and Sg-B, ECS-A and ECS-B can communicate with each other:
|
|
3 |
To enable instances to communicate with the Internet using IPv4 addresses, you need to buy an EIP and bind it to the instance. An EIP can be bound to only one instance. As shown in Figure 1, you can bind EIP-A to ECS-A and EIP-B to ECS-B so that ECS-A and ECS-B can communicate with the Internet. |
|
4 |
To enable instances to communicate with the Internet using an IPv6 address, you need to add the IPv6 address to a shared bandwidth. You can add multiple IPv6 addresses to a shared bandwidth. As shown in Figure 1, you can add the IPv6 addresses of ECS-A and ECS-B to a shared bandwidth so that ECS-A and ECS-B can communicate with the Internet. |
Notes and Constraints
- The IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack function is free for now, but will be billed at a later date (price yet to be determined).
- The IPv6 function is now available for open beta test in certain regions. You can check which regions support this function on the console. You can use the IPv6 function only after obtaining the OBT permission.
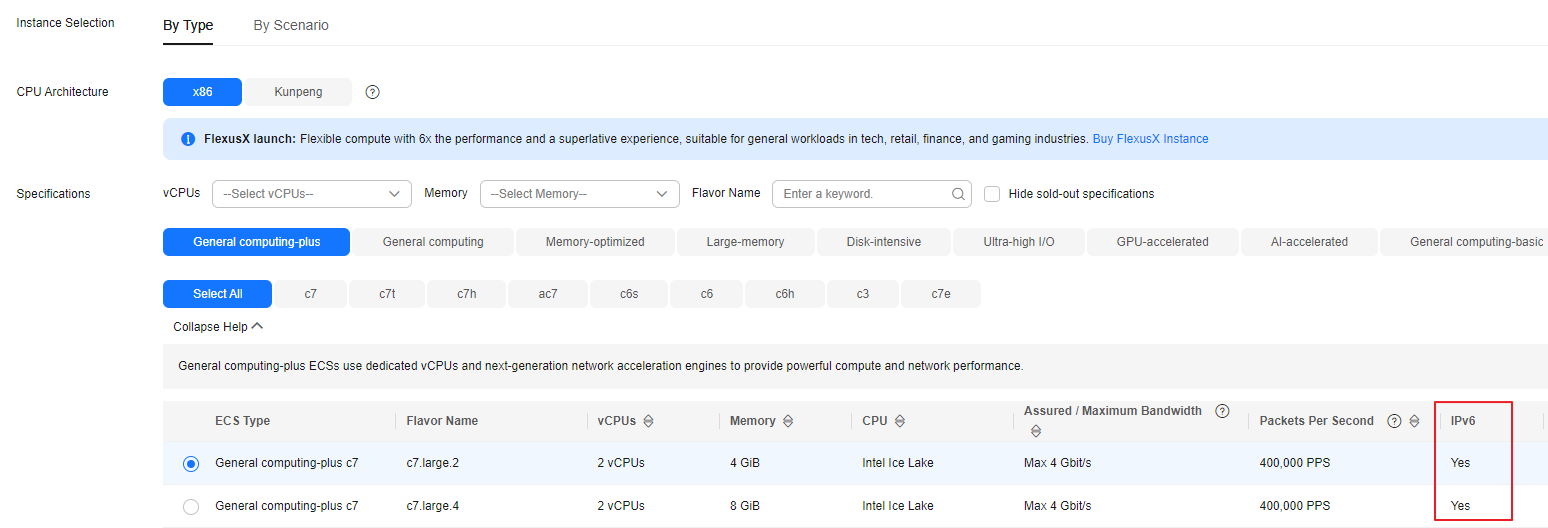
- Only ECSs with certain flavors support IPv6. You need to select such an ECS to use an IPv4/IPv6 dual-stack network.
IPv4/IPv6 Dual-Stack Application Scenarios
|
Application Scenario |
Scenario |
Subnet |
ECS |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Private communication using IPv6 addresses |
Your applications deployed on ECSs need to communicate with other systems (such as databases) through private networks using IPv6 addresses. |
|
|
|
Public communication using IPv6 addresses |
Your applications deployed on ECSs need to provide services accessible from the Internet using IPv6 addresses. |
|
|
|
Your applications deployed on ECSs need to both provide services accessible from the Internet and analyze the access request data using IPv6 addresses. |
|
Application Scenario |
Description |
Subnet |
ECS |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Public communication using IPv6 addresses |
Your applications deployed on ECSs need to provide services accessible from the Internet using IPv6 addresses. |
IPv4 CIDR block |
|

Operation Guide on IPv6 Networks
Operations on an IPv6 network are similar to those on an IPv4 network. Only some functions are configured in a different way. Table 4 describes how you can build and use an IPv6 network.
|
Scenario |
Description |
Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Creating an IPv6 subnet |
Select Enable for IPv6 CIDR Block when creating a subnet. An IPv6 CIDR block will be automatically assigned to the subnet.
|
|
|
Viewing in-use IPv6 addresses |
In the subnet list, click the subnet name. On the displayed page, view in-use IPv4 and IPv6 addresses on the IP Addresses tab. |
|
|
Adding a security group rule (IPv6) |
Add a security group rule with Type set to IPv6 and Source or Destination set to an IPv6 address or IPv6 CIDR block. |
|
|
Adding a network ACL rule (IPv6) |
Add a network ACL rule with Type set to IPv6 and Source or Destination set to an IPv6 address or IPv6 CIDR block. |
|
|
Purchasing an EIP (IPv6) |
When purchasing an EIP, select Enable IPv6 Internet access, or choose More > Enable IPv6 EIP in the Operation column of an existing IPv4 EIP. After IPv6 EIP is enabled, both IPv4 and IPv6 EIPs are assigned. |
|
|
Adding an IPv6 EIP or IPv6 address to a shared bandwidth |
After purchasing a shared bandwidth, you can add IPv6 EIPs or IPv6 addresses to it. |
|
|
Adding an IPv6 route to the VPC route table |
Add a route with Destination and Next Hop set to an IPv4 or IPv6 CIDR block.
|
|
|
Assigning a virtual IPv6 address |
If IPv6 is enabled for a VPC subnet, you can set IP Address Type to IPv6 when assigning for a virtual IP address. |
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot