Working Principles
There are generally two modes of defending against UDP floods: dynamic fingerprint learning and UDP traffic limiting. The former may mistakenly learn normal service payloads as attack fingerprints, leading to false positives. The latter may block both normal and attack traffic, affecting your service.
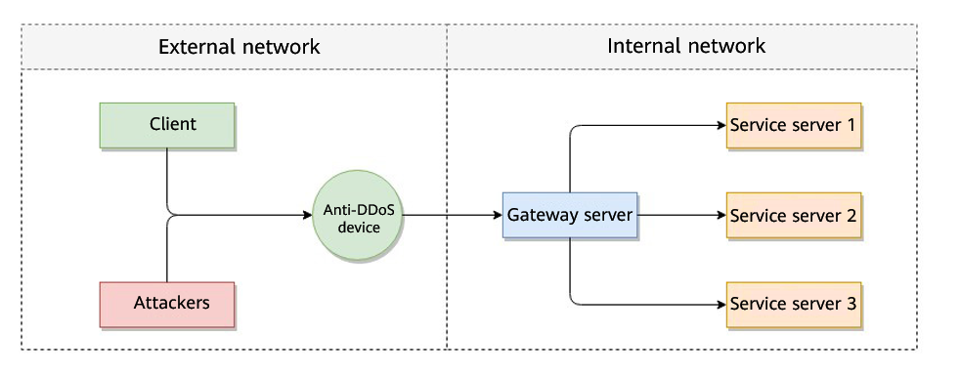
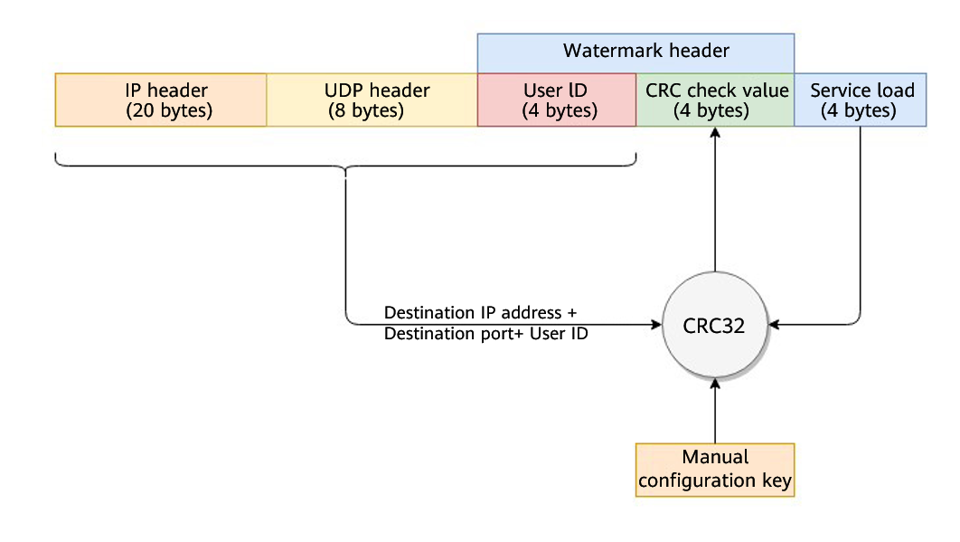
As shown in Figure 2, the Huawei cloud solution adds watermark header information to UDP packets to distinguish normal service packets from attack packets. The offline Anti-DDoS device verifies the UDP watermark and allows only the normal service packets to pass through, while blocking the attack packets.
The client and Anti-DDoS device need to use the same information structure and calculation rule. The calculation rule refers to the hash factor and hash algorithm for calculating the watermark value. In this solution, the hash factor uses: the destination IP address, destination port, user identifier, and the watermark keyword; and the hash algorithm uses the CRC32.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot