Secure Boot
Secure Boot
Secure Boot ensures the integrity of each component during system boot-up and prevents components that have no valid signatures from being loaded. It protects the system and user data from security threats as well as bootkit and rootkit attacks. HCE supports Secure Boot.
- Verifying that Secure Boot has been enabled
After the OS is booted, run the following command to check whether Secure Boot is enabled:
mokutil --sb-state SecureBoot enabled #Secure Boot has been enabled.
- Enabling kernel .ko signature verification
Secure Boot is implemented by signature verification. By default, the HCE kernel is not compiled with forcibly enabled signature verification. You need to enable signature verification using the kernel parameter module.sig_enforce.
To enable .ko signature verification:
- EFI: Add module.sig_enforce=1 to the /boot/efi/EFI/hce/grub.cfg file.
- BIOS: Add module.sig_enforce=1 to the /boot/grub2/grub.cfg file.
Figure 1 Enabling .ko signature verification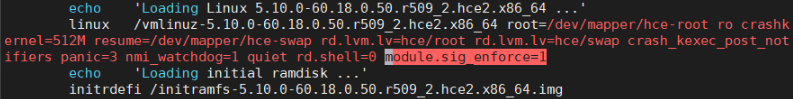
Kernel parameter
Value
Description
module.sig_enforce
0
Disables the kernel's signature verification on the .ko module. The setting takes effect after the system is rebooted.
1
Enables the kernel's signature verification on the .ko module. The setting takes effect after the system is rebooted.
- Viewing the public key certificate for signatures in HCE 2.0:
hce-sign-certificate-1.0-2.hce2.x86_64.rpm in https://repo.huaweicloud.com/hce/2.0/updates/x86_64/Packages/
- Reference for importing a certificate to BIOS:
Kunpeng: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100088647/97a0d5a0
2288H V5: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1000163372/afc5c7f8?idPath=23710424|251364409|21782478|21872244
2288H V6: https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/en/doc/EDOC1100195299/fdb56216?idPath=23710424|251364409|21782478|23692812

If you upgrade the OS of a server with Secure Boot enabled from HCE 2.0 released before March 2025 to HCE 2.0 released after May 2025 or upgrade shim, grub, or kernel packages separately, the OS may fail to boot after the upgrade and restart. Before the upgrade, prevent this issue by referring to "Detecting the Issue" in How Do I Handle Secure Boot Failures Caused by Certificate Changes? If the upgrade has been completed and the OS cannot be booted, handle this issue by referring to "Solution" in How Do I Handle Secure Boot Failures Caused by Certificate Changes?
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





