GaussDB Application Development Guide
In GaussDB, you can connect to and perform operations on a database through APIs such as JDBC, ODBC, libpq, Psycopg, ECPG, and Go.
JDBC
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is a Java API for running SQL statements. It provides unified access APIs for different relational databases. It allows Java applications to use SQL statements to perform database operations, such as querying, inserting, updating, and deleting data.
Some key features and usage of JDBC are as follows:
- Database connection management: JDBC allows applications to establish connections to databases and manages the lifecycle of these connections.
- SQL execution: JDBC can be used to query, update, and delete SQL statements. This is achieved by constructing SQL statements in Java code and sending them to the database.
- Transaction management: JDBC APIs can be used to start, commit, or roll back transactions to ensure the consistency and integrity of database operations.
- Exception handling: JDBC defines a group of exception classes to handle various exceptions that may occur during database operations. Developers can use the try-catch block to capture and handle these exceptions.
- Batch processing: JDBC provides the batch processing function, which allows multiple SQL statements to be executed concurrently, improving the efficiency of database operations.
- Metadata access: JDBC can be used to obtain the metadata information of the database, such as the table structure, column name, and data type. Developers then can dynamically construct SQL query statements or perform operations based on the database structure.
In conclusion, JDBC provides a flexible and powerful bridge that enables Java applications to interact with various databases and to implement data persistence and management. GaussDB supports JDBC 4.2 and requires JDK 1.8 for code compiling. It does not support JDBC-ODBC bridging.
For details about JDBC-based development, see Development Based on JDBC.
ODBC
Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a Microsoft API for accessing databases in C/C++ based on the X/OPEN CLI. It provides a unified method for applications to access various database management systems (DBMSs) without considering specific database types or OS platforms. ODBC allows applications to use SQL to query, insert, update, and delete data in a database. Applications interact with the database through the APIs provided by ODBC, which enhances their portability, scalability, and maintainability.
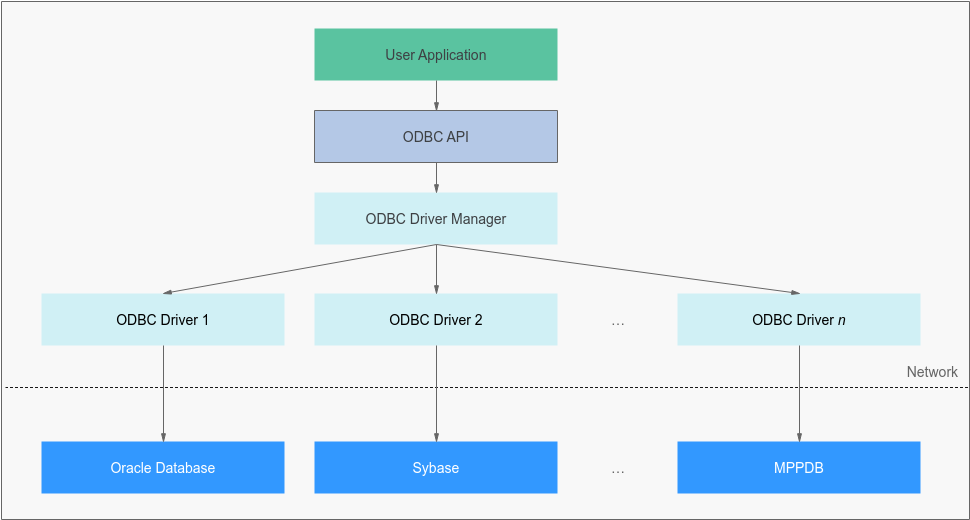
The ODBC architecture consists of three main components: application, ODBC driver manager, and ODBC driver. Applications use ODBC APIs to communicate with the ODBC driver manager which loads and manages ODBC drivers. The ODBC drivers are responsible for communicating with a specific database, executing SQL queries, and returning results. For details about the ODBC system architecture, see Figure 1.
In conclusion, ODBC provides a flexible and cross-platform method that allows users to easily connect applications to various databases without worrying about the details of a specific database system.
For details about ODBC-based development, see Development Based on ODBC.
GaussDB supports ODBC 3.5 in the following environments.
|
OS |
Platform |
|---|---|
|
EulerOS 2.5 |
x86_64 |
|
EulerOS 2.9 |
Arm64 |
|
EulerOS 2.10 |
x86_64 |
|
EulerOS 2.10 |
Arm64 |
|
Windows 7 |
x86_32 |
|
Windows 7 |
x86_64 |
|
Windows Server 2008 |
x86_32 |
|
Windows Server 2008 |
x86_64 |
|
Kylin V10 |
x86_64 |
|
Kylin V10 |
Arm64 |
|
UnionTech V20 |
x86_64 |
|
UnionTech V20 |
Arm64 |
The ODBC Driver Manager running on Unix or Linux can be unixODBC or iODBC. unixODBC-2.3.7 is used as the component for connecting to the database.
Windows has a native ODBC Driver Manager. You can locate Data Sources (ODBC) by choosing .

The current database ODBC driver is based on an open-source version and may be incompatible with Huawei-developed data types such as tinyint, smalldatetime, and nvarchar2.
ODBC limitations:
- ODBC does not support user-defined types and does not support user-defined parameters in stored procedures.
- When the proc_outparam_override parameter is enabled for the database, ODBC cannot properly call the stored procedure that contains the out parameter.
- ODBC does not support read on the standby node in a cluster for DR.
libpq
libpq is a C application programming API to GaussDB. libpq contains a set of library functions that allow client programs to send query requests to GaussDB servers and obtain query results. It is also the underlying engine of other GaussDB APIs, such as ODBC.
For details about libpq-based development, see Development Based on libpq.
Psycopg
Psycopg is a Python API used to execute SQL statements and provides a unified access API for GaussDB. Applications can perform data operations based on psycopg. Psycopg2 is the encapsulation of libpq and is implemented using the C language, which is efficient and secure. It provides cursors on both client and server, asynchronous communication and notification, and the COPY TO and COPY FROM functions. It supports multiple types of Python out-of-the-box and adapts to GaussDB data types. Through the flexible object adaptation system, you can extend and customize the adaptation. Psycopg2 is compatible with Unicode.
GaussDB supports the psycopg2 feature and allows psycopg2 to be connected in SSL mode.
For details about Psycopg-based development, see Psycopg-based Development.
|
OS |
Platform |
Python Version |
|---|---|---|
|
EulerOS 2.5 |
|
3.8.5 |
|
EulerOS 2.9 |
|
3.7.4 |
|
EulerOS 2.10, Kylin V10, and UnionTech20 |
|
3.7.9 |
|
EulerOS 2.11 and SUSE 12.5 |
|
3.9.11 |

During psycopg2 compilation, OpenSSL of GaussDB is linked. OpenSSL of GaussDB may be incompatible with OpenSSL of the OS. If incompatibility occurs, for example, "version 'OPENSSL_1_1_1f' not found" is displayed, use the environment variable LD_LIBRARY_PATH to isolate the OpenSSL provided by the OS and the OpenSSL on which GaussDB depends.
For example, when the application software client.py that calls psycopg2 is executed, the environment variable is explicitly assigned to the application software.
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/path/to/gaussdb/libs:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH python client.py
In the preceding command, /path/to/pyscopg2/lib indicates the directory where the OpenSSL library on which GaussDB depends is located. Change it as required.
ecpg
Embedded SQL C Preprocessor for GaussDB Kernel (ECPG) is an embedded SQL preprocessor for C programs. An embedded SQL program consists of code written in an ordinary programming language, in this case C, mixed with SQL commands in specially marked sections. To build the program, the source code (*.pgc) is first passed through the embedded SQL preprocessor, which converts it to an ordinary C program (*.c), and afterwards it can be processed by a C compiler. The converted ECPG program calls functions in the libpq library through the embedded SQL library (ecpglib), and communicates with a GaussDB Kernel server using the normal frontend-backend protocol.
EXEC SQL ...;
These statements syntactically take the place of a C statement. Depending on the particular statement, they can appear at the global level or within a function. Embedded SQL statements follow the case-sensitivity rules of normal SQL code, and allow nested C code-style comments (part of the SQL standard). However, the C part of the program follows the standards of the C program and does not support nested comments.
For details about ECPG-based development, see ECPG-based Development.
Go
Go is a language driver used to connect to and operate GaussDB. It provides some APIs for connecting to and operating GaussDB. You can use these APIs to perform operations such as query, insert, update, and delete.
Some functions and usage of a Go driver are as follows:
- Database connection: A Go driver can connect to a database through db.Open. The connection string can be in URL or DSN format.
- SQL execution and query: A Go driver provides APIs such as db.Exec and db.Query for SQL execution and query.
- Transaction management: A Go driver provides the Tx API for transaction management. It implements methods such as starting, committing, and rolling back transactions to ensure the consistency and atomicity of database operations.
- Metadata access: A Go driver provides the ColumnType API to query column attribute information in the database, including whether the column can be empty, database type name, length, and number of decimal places.
- Reusability: A Go driver provides the Prepare method for preparing SQL statements. The SQL statements can be executed for multiple times. You only need to change the input parameters to improve database reusability.
For details about Go-based development, see Development Based on the Go Driver.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot