Using SGLang and Docker to Manually Deploy a DeepSeek-R1 or DeepSeek-V3 Model on Multi-GPU Linux ECSs
Scenarios
DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1 are two high-performance large language models launched by DeepSeek. DeepSeek-R1 is an inference model that is designed for math, code generation, and complex logical inference. Reinforcement learning (RL) is applied to this model to improve the inference performance. DeepSeek-V3 is a model that focuses on general tasks such as natural language processing, knowledge Q&A, and content creation. It aims to balance high performance and low cost and is suitable for applications such as intelligent customer service and personalized recommendation. In this section, we will learn how to use SGLang to quickly deploy a DeepSeek-R1 or DeepSeek-V3 model.
Solution Architecture
This solution requires at least one primary node and one secondary node.
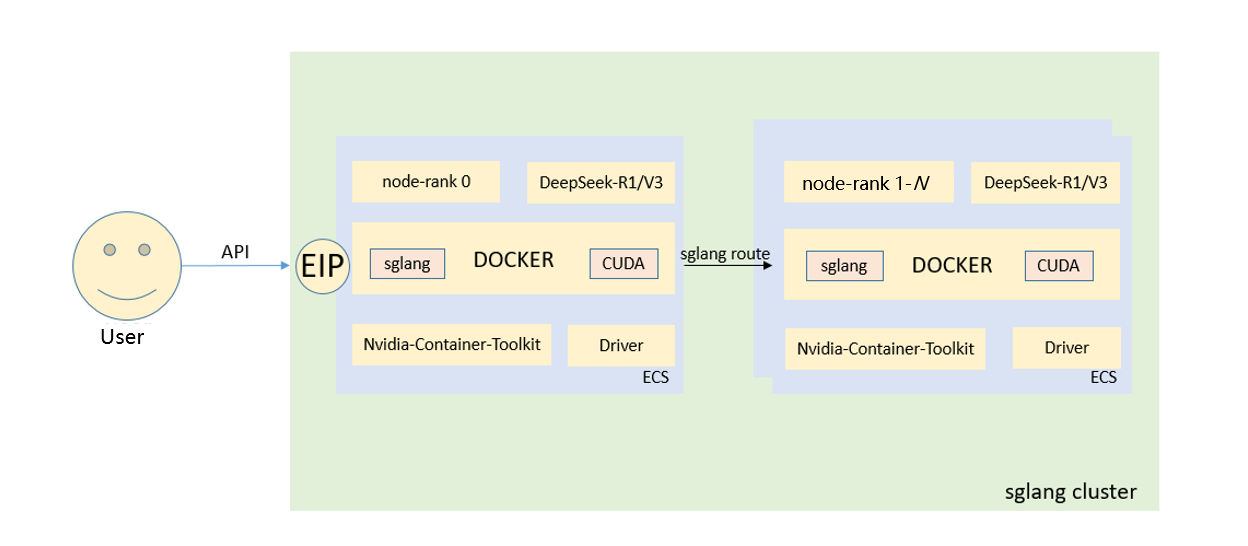
Advantages
You will be able to manually deploy DeepSeek-R1 and DeepSeek-V3 models using SGLang and Docker, and better understand model dependencies. This will give you a chance to experience the superb inference performance of DeepSeek-R1 and DeepSeek-V3 models. The SGLang framework has a built-in data parallel router that automatically connects the router to all workers after they are started. You can use SGLang easily without requiring the external Ray cluster framework.
Resource Planning
|
Resource |
Description |
Cost |
|---|---|---|
|
VPC |
VPC CIDR block: 192.168.0.0/16 |
Free |
|
VPC subnet |
|
Free |
|
Security group |
Inbound rule:
|
Free |
|
ECS |
|
The following resources generate costs:
For billing details, see Billing Mode Overview. |
Manually Deploying a DeepSeek-R1 or DeepSeek-V3 model Using SGLang and Docker on Multi-GPU Linux ECSs
To use SGLang and Docker to manually deploy a DeepSeek-R1 or DeepSeek-V3 model on multi-GPU Linux ECSs, do as follows:
- Create a GPU ECS.
- Check the GPU driver and CUDA versions.
- Install Docker.
- Install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit.
- Install dependencies, such as modelscope.
- Download a Docker image.
- Download the DeepSeek-R1 or DeepSeek-V3 model file.
- Start the primary and all secondary nodes of SGLang.
- Call a model API to test the model performance.
Procedure
- Create a GPU ECS.
- Select the public image Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0 or Ubuntu 22.04 without a driver installed. The following uses Ubuntu 22.04 is used as an example.
Figure 2 Selecting an image
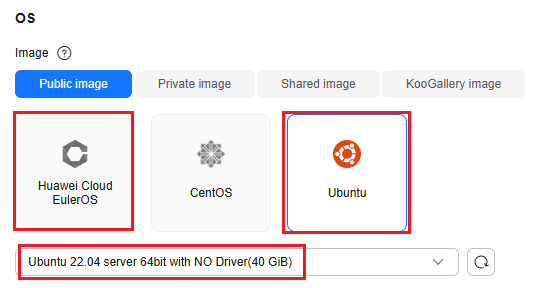
- Select Auto assign for EIP. An EIP will be assigned for downloading dependencies and calling model APIs.
- Select the public image Huawei Cloud EulerOS 2.0 or Ubuntu 22.04 without a driver installed. The following uses Ubuntu 22.04 is used as an example.
- Check the GPU driver and CUDA versions.
Install the driver of version 535 and CUDA of 12.2. For details, see Manually Installing a Tesla Driver on a GPU-accelerated ECS.
- Install Docker.
- Update the package index and install dependencies.
apt-get update apt-get install -y ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release
- Add Docker's official GPG key.
mkdir -p /etc/apt/keyrings curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
- Set the APT source for Docker.
echo \ "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \ $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
- Install Docker Engine.
apt update apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
- Configure Docker Hub.
cat <<EOF > /etc/docker/daemon.json { "registry-mirrors": [ "https://docker.m.daocloud.io", "https://registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com" ] } EOF systemctl restart docker - Check whether Docker is installed successfully.
docker --version
- Update the package index and install dependencies.
- Install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit.
- Add NVIDIA's official GPG key.
curl -fsSL https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/gpgkey | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg \ && curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/stable/deb/nvidia-container-toolkit.list | \ sed 's#deb https://#deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg] https://#g' | \ sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-container-toolkit.list - Set the APT source for the NVIDIA Container Toolkit.
sed -i -e '/experimental/ s/^#//g' /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-container-toolkit.list
- Update the index package and install the NVIDIA Container Toolkit.
apt update apt install -y nvidia-container-toolkit
- Configure Docker to use the NVIDIA Container Toolkit.
nvidia-ctk runtime configure --runtime=docker systemctl restart docker
- Add NVIDIA's official GPG key.
- Install dependencies, such as modelscope.
- Update the pip.
python -m pip install --upgrade pip -i https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/pypi/web/simple
- Install modelscope.
pip install modelscope -i https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/pypi/web/simple

ModelScope is an open-source model community in China. It is fast to download models from ModelScope if you are in China. However, if you are outside China, download models from Hugging Face.
- Update the pip.
- Download a Docker image.
You can download the latest container image provided by SGLang or the image created by the Huawei Cloud heterogeneous computing team.
- Download the latest image from the SGLang official website.
docker pull lmsysorg/sglang:latest
- Download an image created by the Huawei Cloud heterogeneous computing team.
docker pull swr.cn-north-9.myhuaweicloud.com/hgcs/lmsysorg/sglang:latest
- Download the latest image from the SGLang official website.
- Download the DeepSeek-R1 or DeepSeek-V3 model file.
- Create a script for downloading a model.
vim download_models.py
Add the following content to the script:
from modelscope import snapshot_download model_dir = snapshot_download('deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1', cache_dir='/root', revision='master')The model name DeepSeek-R1 is used as an example. You can change it to DeepSeek-V3. The local directory for storing the model is /root. You can change it as needed.
- Download the model.
python3 download_models.py
The total size of the model is 642 GB. The download may take 24 hours or longer, which is related to the EIP bandwidth.
- Create a script for downloading a model.
- Start the primary and all secondary nodes of SGLang.
Case 1: A RoCE network is available.
- Start the primary node of SGLang.
Node 0:
docker run --gpus all \ # Use all GPUs. --shm-size 512g \ # Size of the shared memory between the server and container. Set it based on the server configuration. -e NCCL_IB_GID_INDEX=3 \ # Use index 3, which corresponds to RoCE v2 routing. -e NCCL_IB_HCA='^=mlx5_bond_0' \ # Specify the NIC for RoCE communication. -e NCCL_SOCKET_IFNAME=bond0 \ # Specify the TCP/IP NIC (for example, bond0) for NCCL, which should be separated from the IB NIC to avoid interference. -e GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=bond0 \ # Specify the TCP/IP NIC (for example, bond0) for GLOO, which should be separated from the IB NIC to avoid interference. -v /mnt/paas/models:/root/.cache/huggingface \ # Mount point of the model path. --ipc=host --network=host --privileged \ # Use the host network. swr.cn-north-9.myhuaweicloud.com/hgcs/lmsysorg/sglang:latest \ # Container image name. python3 -m sglang.launch_server --model /root/.cache/huggingface/DeepSeek-V3 \ # Specify the model path. --served-model-name deepseek-v3 \ # Specify the model name. --tp 16 \ # Two nodes, each with 8 H20 GPUs. Set tensor parallelism (TP) to 16. --nnodes 2 \ # The total number of nodes. --node-rank 0 \ # Set the primary node to 0 and assign ranks to other nodes incrementally based on their orders. --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000 \ # Set the IP address and port of the current node. --dist-init-addr 192.168.1.143:30000 \ # Set the IP address and port of the primary node. --trust-remote-code - Start the secondary node of SGLang.
docker run --gpus all \ --shm-size 512g \ -e NCCL_IB_GID_INDEX=3 \ -e NCCL_IB_HCA='^=mlx5_bond_0' \ -e GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=bond0 \ -v /mnt/paas/models:/root/.cache/huggingface \ --ipc=host --network=host \ --privileged swr.cn-north-9.myhuaweicloud.com/hgcs/lmsysorg/sglang:latest python3 -m sglang.launch_server \ --model /root/.cache/huggingface/DeepSeek-V3 \ --served-model-name deepseek-v3 \ --tp 16 --nnodes 2 --node-rank 1 --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000 --dist-init-addr 192.168.1.143:30000 --trust-remote-code
- Add optimization parameters.
Case 2: No RoCE network is available.
- Start the primary node of SGLang.
docker run --gpus all \ # Use all GPUs. --shm-size 512g \ # Size of the shared memory between the server and container. Set this parameter based on the server configuration. -e GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=eth0 \ -v /mnt/paas/models:/root/.cache/huggingface \ # Mount point of the model path. --ipc=host --network=host \ # Use the host network. swr.cn-north-9.myhuaweicloud.com/hgcs/lmsysorg/sglang:latest \ # Container image name. python3 -m sglang.launch_server --model /root/.cache/huggingface/DeepSeek-V3 \ # Specify the model path. --served-model-name deepseek-v3 \ # Specify the model name. --tp 16 \ # Two nodes, each with 8 H20 GPUs. Set tensor parallelism (TP) to 16. --nnodes 2 \ # The total number of nodes. --node-rank 0 \ # Set the primary node to 0 and assign ranks to other nodes incrementally based on their orders. --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000 \ # Set the IP address and port of the current node. --dist-init-addr 192.168.1.143:30000 \ # Set the IP address and port of the primary node. --trust-remote-code - Start the secondary node of SGLang.
docker run --gpus all \ --shm-size 512g \ -e GLOO_SOCKET_IFNAME=eth0\ -v /mnt/paas/models:/root/.cache/huggingface \ --ipc=host --network=host \ swr.cn-north-9.myhuaweicloud.com/hgcs/lmsysorg/sglang:latest python3 -m sglang.launch_server \ --model /root/.cache/huggingface/DeepSeek-V3 \ --served-model-name deepseek-v3 \ --tp 16 \ --nnodes 2 \ --node-rank 1 \ --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000 \ --dist-init-addr 192.168.1.143:30000 \ --trust-remote-code
- Add optimization parameters.
- Start the primary node of SGLang.
- Call a model API to test the model performance.
- Call an API to chat.
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "DeepSeek-R1", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hello\n"}] }'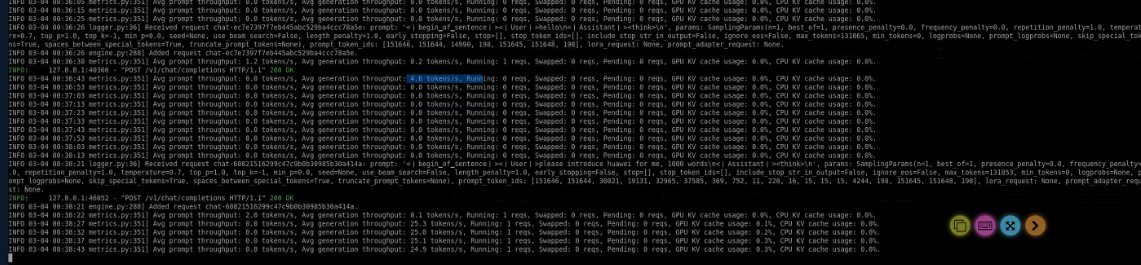
- If streaming conversation is required, add the stream parameter.
curl http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{ "model": "DeepSeek-R1", "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "hello\n"}], "stream": true }'
You can use an EIP to call a model API for chats from your local Postman or your own service.
- Call an API to chat.
FAQs
Symptom: When the primary SGLang node is started, the error message "SGLang only supports sm75 and above" is displayed.
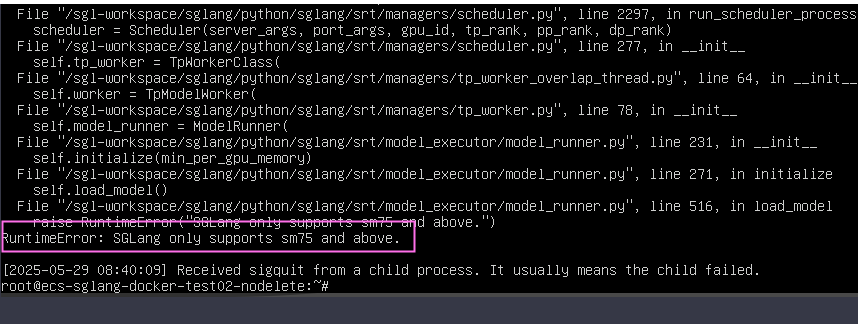
Cause: The GPU compute capability is insufficient. The compute capability must be at least SM7.5.
Solution: Replace the GPU with one whose compute capability is greater than or equal to SM7.5, for example, T4.
Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Provide feedbackThank you very much for your feedback. We will continue working to improve the documentation.See the reply and handling status in My Cloud VOC.
For any further questions, feel free to contact us through the chatbot.
Chatbot





